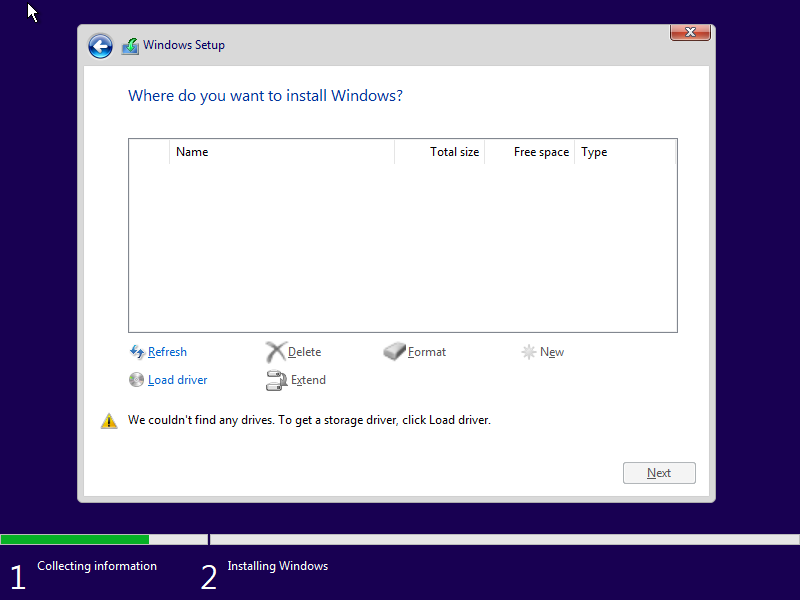
1. Introduction
This guide describes how to set up a Windows guest in the acontis Hypervisor. It is assumed that the steps listed in the Hypervisor Quick Start guide have been successfully executed.
2. Copy a Windows ISO installation media to the Hypervisor Host
In a first step, we need to copy the Windows installation media (ISO file) into the Hypervisor filesystem.
2.1. Using Filezilla (recommended)
Open a shell (right click on desktop and select ‘Open Terminal here’ or press CRTL + ALT + T) on the Hypervisor Host.
Determine the IP address of the system (with
ifconfigcommand and throughinetentry):rte@RTV-TP104:~$ ifconfig enp2s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 172.17.10.5 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255 inet6 fe80::ccbb:85f1:38d3:fa2a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 90:1b:0e:18:c9:83 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 4618420 bytes 4033770375 (4.0 GB) RX errors 0 dropped 8865 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 1460482 bytes 96608727 (96.6 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 6864 bytes 427092 (427.0 KB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 6864 bytes 427092 (427.0 KB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 vnet0: flags=99<UP,BROADCAST,NOTRAILERS,RUNNING> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.157.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.157.255 ether 00:60:c8:00:00:00 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 765775 bytes 74216258 (74.2 MB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 767935 bytes 74780268 (74.7 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
In this example the IP address is 172.17.10.5.
Hint
The device name enp2s0 differs on different PC/IPC’s!
Open Filezilla (get current version from https://filezilla-project.org/) and create new connection entry:
Push New site button
Give a qualified name
Select SFTP - SSH File Transfer Protocol
Give host IP/name. In screenshot above the last byte is
X-ed out. Replace it with the ‘detected’ IP address.Enter User name (same as at Hypervisor install)
Enter password (same as at Hypervisor install)
Push Connect button

Select the installation media file (the
.isoimage) in the Local tab on the left and upload it to/hv/guests/examples/windowsinto the Server tab on the right.
3. Guest Configuration
Prior to installing the guest, we need to configure the respective virtual machine (e.g. number of CPU cores, network settings etc.).
The configuration files guest_config.sh and usr_guest_config.sh are located in the guest folder.
The meaning of each configuration setting is explained in detail in those files.
You need to edit these files and adjust them according to your needs and environment.
Caution
If the guest is controlled by the System Manager tool, you must not change the guest_config.sh file (the content may be overwritten by the System Manager),
instead uncomment the respective settings in usr_guest_config.sh.
Example guests located in /hv/guests/examples are not controlled by the System Manager.
The number of CPU cores must not exceed the number of physical cores available in the system and not assigned to Real-time guests. For example, if on a quad core CPU, you need 2 cores for Real-time guests, the number of cores for the Windows guest must not exceed 2. The default parameters should fit for most cases.
gedit /hv/guests/examples/windows/guest_config.sh (and/or usr_guest_config.sh)
# Adapt following lines to your system and needs:
vmname=...
vmid=...
windows_guest=...
cdrom_iso=...
num_cpus=...
ramsize=...
You have to set the cdrom_iso parameter to the appropriate folder where the installation media ISO file had been copied before.
By default, the network connection is set up automatically (using DHCP). Please check the Hypervisor Manual for other settings.
Caution
Automatic network setting will only work, if the Ethernet cable is connected!
Caution
Please do not configure more CPUs than physically available (CPUs used for the Real-time OS are not available for the Windows guest).
Example: The maximum number of of CPUs on a quad-core CPU where 1 CPU is used for the Real-time OS is 3.
Caution
Please do not configure more RAM than available. The VM may unexpectedly crash if too much RAM is configured. You can determine the available RAM as follows:
cat /proc/meminfo | grep MemAvailable
4. Guest Installation
After VM configuration you need to start the guest for the first time. The guest console will be shown then (the guest output or desktop).
cd /hv/guests/examples/windows
hv_guest_start -view
Caution
if you see an error like (remote-viewer:5083): Gtk-WARNING : 11:15:50.298: cannot open display: :10.0, you may using a RDP connection when installing the guest. In this case the GUI Window (remote-viewer) will not be shown. To fix this execute the commands
sudo -u username xhost +SI:localuser:root
where the username is the username you are logged in with.
Then execute hv_guest_console to start the viewer.
The installation media iso file will be detected by the virtual bios, you need to press a key to boot from it:
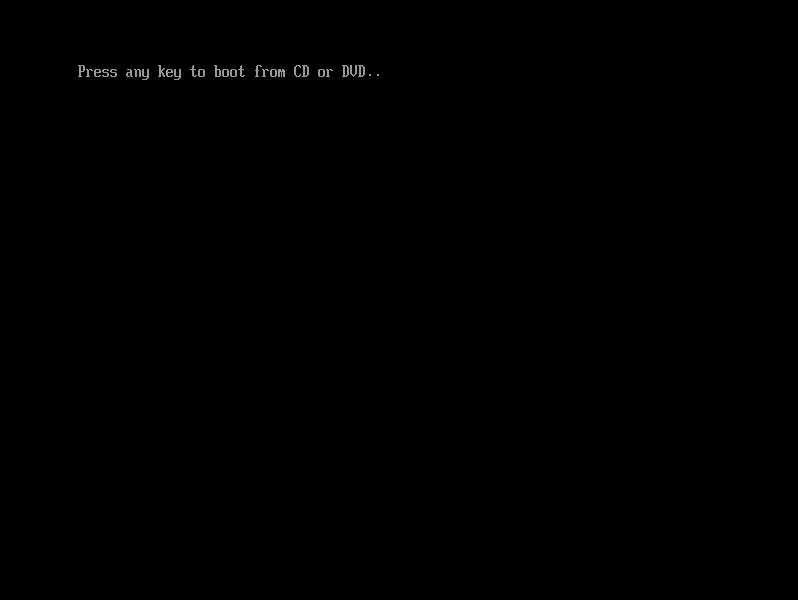
Hint
In case no key was pressed in time or the installation media was not found, the EFI shell will be started.
Option a) You can leave into BIOS by entering
exit. If you also leave BIOS the boot begins again and you can press a key to boot from CD.- Option b) You can manually start the CD’s bootloader by entering
$ FS0:$ \EFI\BOOT\BOOTX64.EFI
Hint
If the start EFI file is not set in the BIOS (BOOTX64.EFI does not exist), you need to type exit to leave the shell and switch into the BIOS.
There you need to select the CDROM in the boot menu.
5. Windows Installation
You need to browse to the CD Drive with the virtio drivers. Select the appropriate driver in the respective folder (e.g. \viostor\w10\amd64).
6. Hypervisor Guest Tools
After successfully installing Windows you need to install the SPICE Windows guest tools.
Open the Windows Explorer and install the spice guest tools.
The installation file is located in CD Drive (E:) virtio-win-0.1.215: virtio-win-guest-tools. Select and start to install these tools. In case a message box appears to confirm driver installation, please confirm install the driver(s).


After the setup finished, you may not be able to use the mouse anymore. This is related to a new driver installed which is not supported by the viewer application. In any case, close the setup message box (type enter, while the focus is on the finish box).
Shutdown Windows
You need to shut down the guest (do NOT reboot Windows!).
If this not possible inside the guest, please run hv_guest_stop in the guest folder (/hv/guests/examples/windows).
If shutdown does not work, you need to close the setup windows before (e.g. using tab keys to select the finish button).
Adjust the file
usr_guest_config.sh(to avoid booting the installation media again)gedit /hv/guests/examples/windows/usr_guest_config.shcomment "cdrom_iso" with #
Start the Windows guest
hv_guest_start -view
Due to hardware changes, Windows may automatically reboot once. Mouse and desktop may still not work properly. In this case, please install all the latest Windows updates.
Caution
- In some cases the guest network does not work after guest tools installation. In case a guest reboot does not help you may try to execute the following steps:
Open the Windows Device Manager
Open “Network Adapters” and check if “Red Hat VirtIO Ethernet Adaper” has an exclamation mark near its icon.
Delete all adapters with the exclamation mark (drivers deletion checkbox should not be checked out!).
Then let Windows look for hardware changes, the drivers should be found and installed properly.
7. RTOS Communication Support
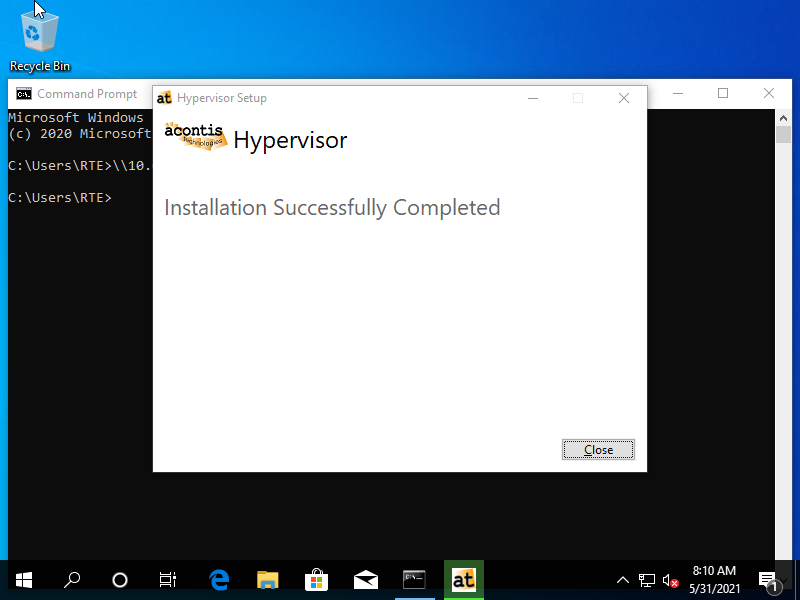
To communicate with an RTOS via the Hypervisor we need to install RTOSVisor.exe containing the required drivers and packages.
Hint
If you encounter a message like Applying execute package: RteRuntime_x64. Error 0x80070643: Failed to install MSI package when running this command, you may have got a test version of the RTOSVisor.
In test versions unsigned drivers are included. You need to enable testsigning before installing the guest support.
Step 1: Run Command Prompt as administrator.
Step 2: Input the command in the window:
bcdedit /set testsigning onand press Enter. Reboot the guest.
Open CMD prompt in Windows guest and enter the following:
Call \\10.0.2.4\qemu\files\RTOSVisor.exe



8. Power & sleep
Sleep and Hibernate are currently not supported (S3 or S4 mode). Disable Sleep (Windows Settings – System – Power and sleep):

9. Windows and Real-time guest in parallel
In this step, we will run Windows and Real-Time Linux in parallel.
Caution
The hv.config configuration file is a link to the RT-Linux example guest configuration file. See also chapter Example guest folders in the Hypervisor Manual for more information.
Shutdown Windows, do NOT reboot!
Reboot the Hypervisor Host
sudo rebootAfter system reboot, open a shell terminal again (right click on desktop and select ‘Open Terminal here’ or press CRTL + ALT + T). Then, run the Real-time Linux guest
cd /hv/guests/examples/rt-linux hv_guest_start -view
Open a second shell terminal
Start the Windows guest
cd /hv/guests/examples/windows hv_guest_start -view
After logging in into Windows, execute “Hypervisor Attach” (Desktop icon)

Download and install the appropriate putty package from https://www.putty.org/
Open the RT-Linux shell: execute “Hypervisor Putty” (Desktop icon)

Log in into Real-Time Linux and run the Real-time demo:
vmf64 login: root password: root RealtimeDemo