6. Diagnosis
6.1. Overview
EC-Engineer is a diagnosis application specifically developed to analyze EtherCAT networks that are controlled by an EtherCAT MainDevice. Automated control systems usually require high availability of the whole system. Due to the rough industrial environment this is often hardly to achieve.
If high availability shall be guaranteed for an automated control system it is important to verify and maintain the field bus. Using EC-Engineer it is possible to take a look into the “health” of the EtherCAT system. Detection of signs of system degradation prior to running into a system failure will be of great benefit. In that case it is possible to exchange the problematic components (cables, SubDevice devices).
- Many aspects of diagnosis are covered by the EC-Engineer:
System analysis and maintenance
Error detection
Documentation
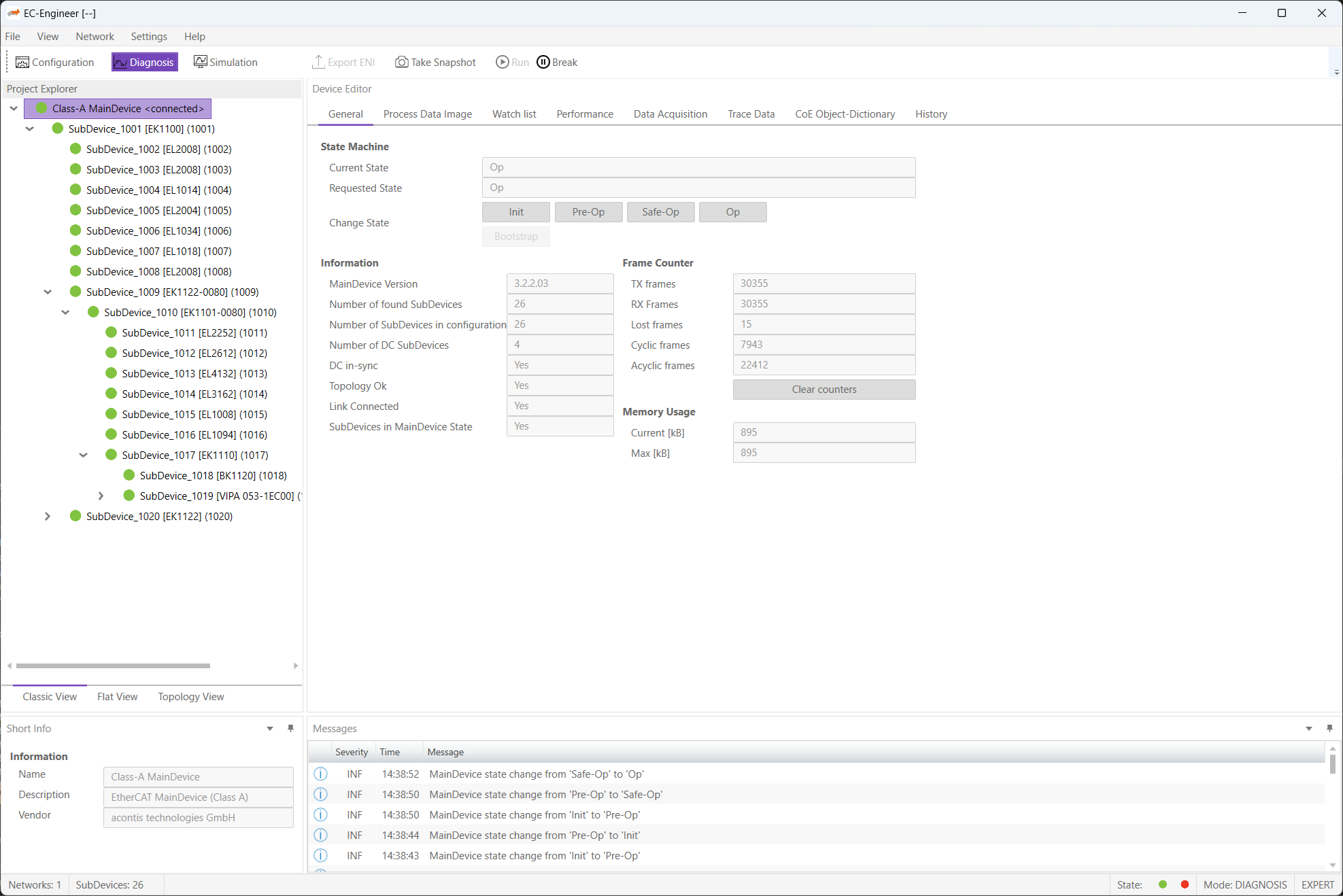
After switching into diagnosis mode of EC-Engineer, the user will see this page:
6.2. Device
This section shows the current “health” state of the MainDevice and helps the user to analyze MainDevice related problems.
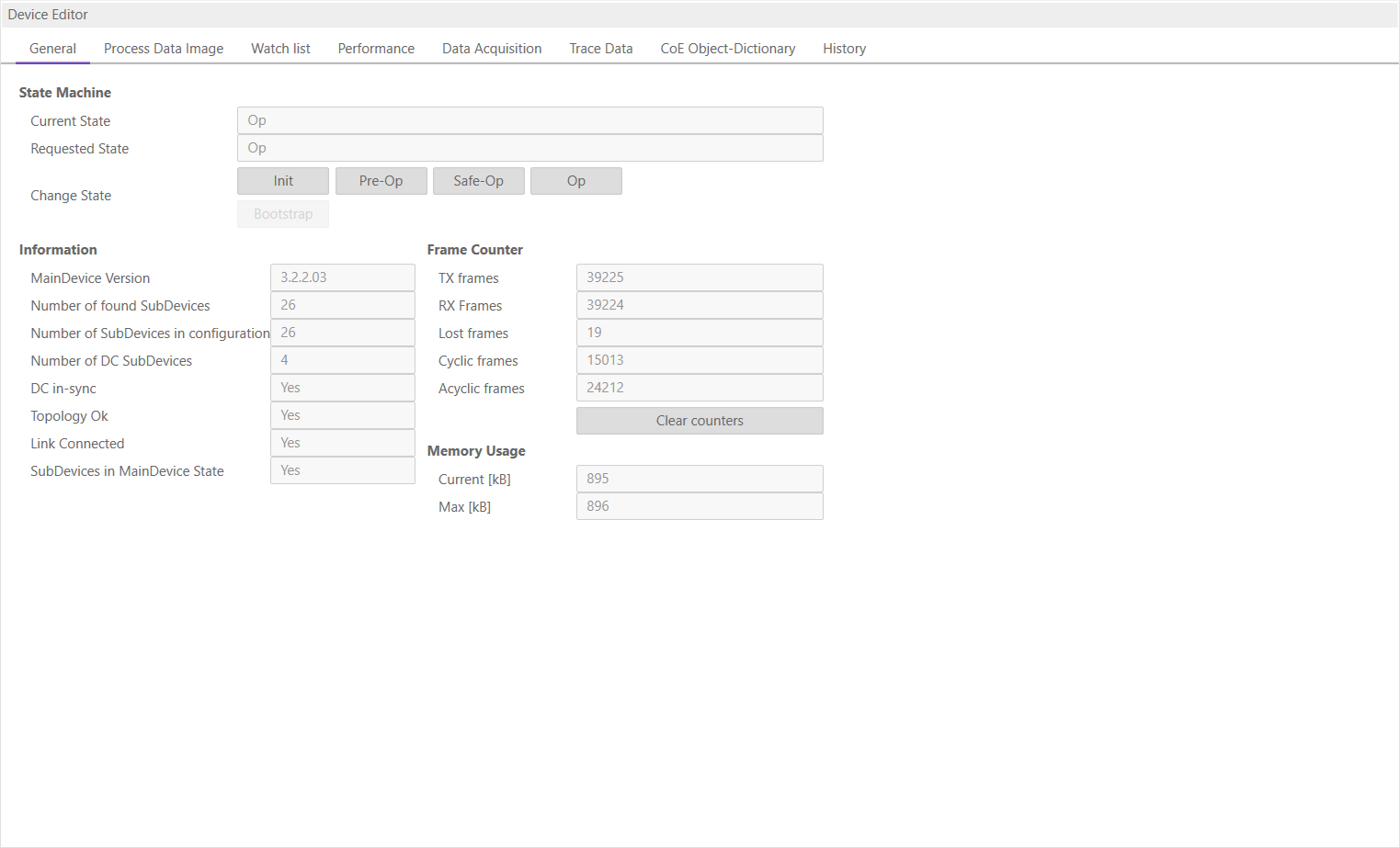
6.2.1. General
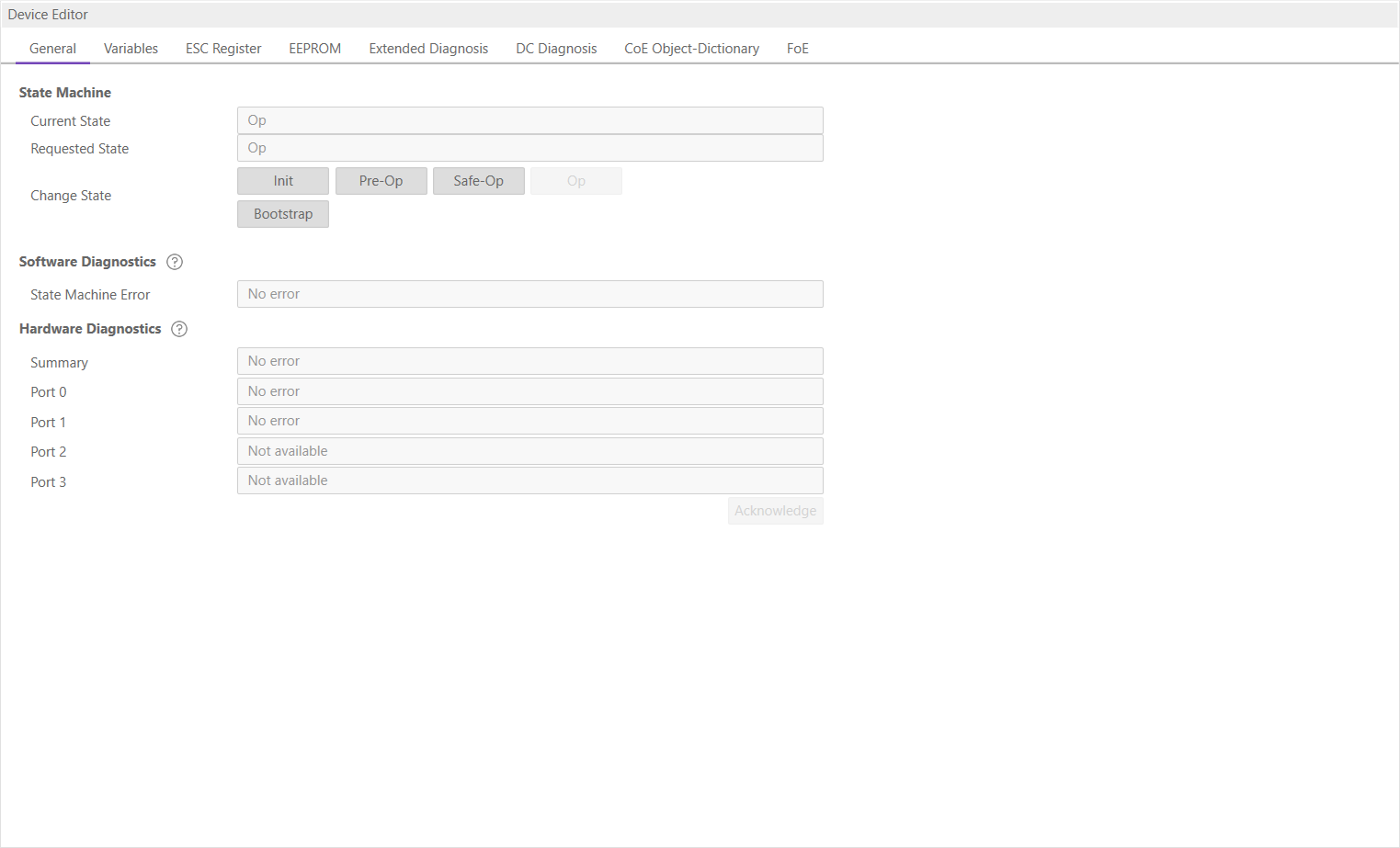
In this tab, the user can see the current state of the state machine of the MainDevice. He has also an overview over the current “health” state of his EtherCAT network:
- State Machine
- Current State:
Current state of the MainDevice
- Requested State:
Requested state of the MainDevice
- Change State:
MainDevice can reach the states INIT, PRE-OP, SAFE-OP and OP.
- Information
- Device version:
Version number of the running MainDevice
- Number of found SubDevices:
Number of SubDevices, which were found from device on the network
- Number of SubDevices in configuration:
Number of SubDevices, which are configured in the
ENIfile- Number of DC SubDevices:
Number of SubDevices with DC support, which were found from MainDevice on the network
- DC in-sync:
Signals that all SubDevices with DC support are correctly synchronized or not. If not all SubDevices are correctly synchronized, please refer the Message Window for more information.
- Topology OK:
Signals that topology is “okay” or not. If topology is not “okay”, you have a mismatch between the configured bus and the currently connected bus. Please open the ‘Network Mismatch Analyzer’ (Menu Network Network Mismatch Analyzer) to solve the problem.
- Link Connected:
Signals the link is connected.
- SubDevices in MainDevice State:
Signals that all SubDevices are in MainDevice state.
- Frame Counter
- TX frames:
Number of sent frames
- RX frames:
Number of received frames
- Lost frames:
Number of lost frames
- Cyclic frames:
Number of cyclic frames
- Acyclic frames:
Number of acyclic frames
- Memory Usage
- Current:
Current memory usage in bytes
- Max:
Maximum memory usage in bytes
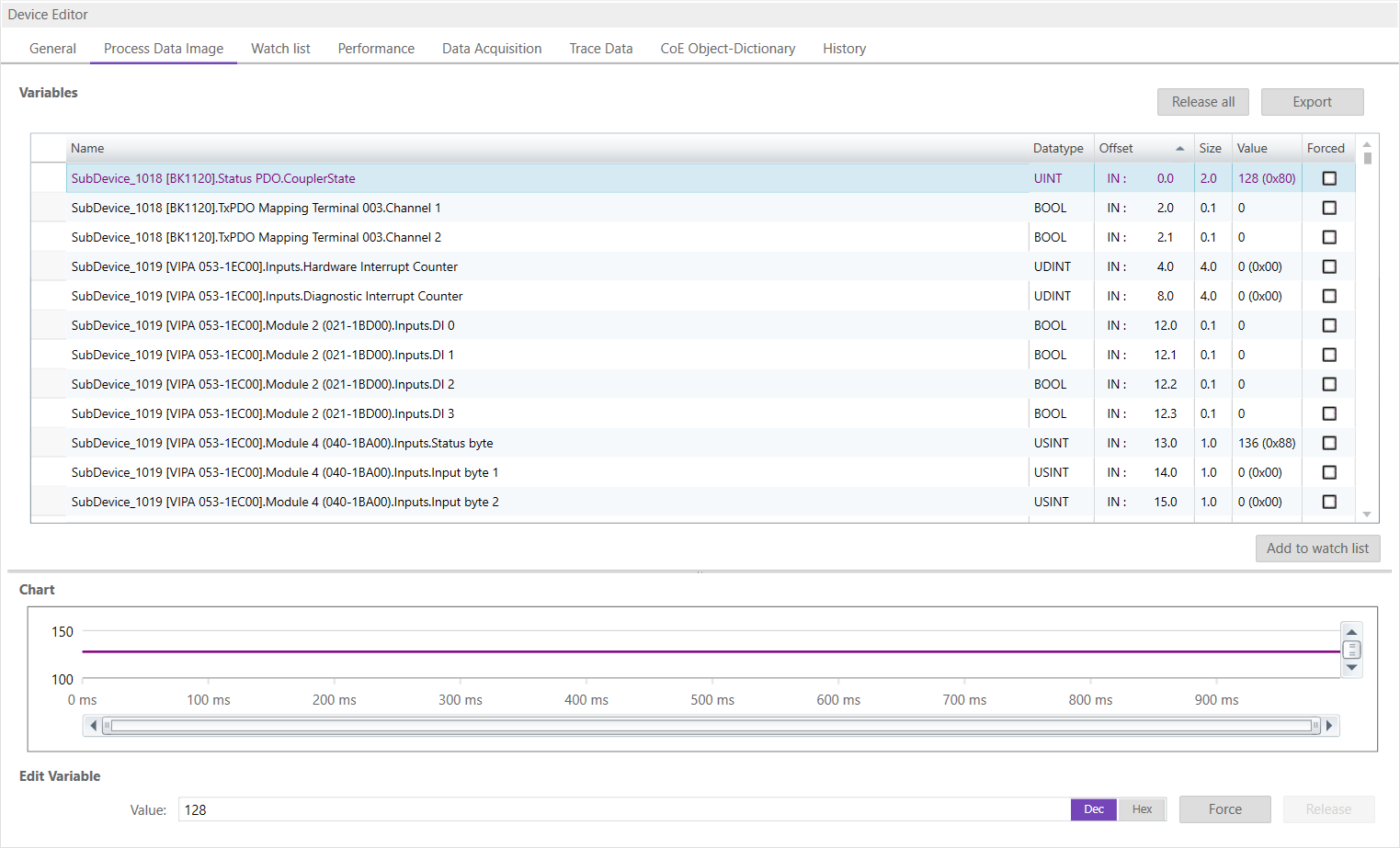
6.2.2. Process Data Image
In this tab, the user can see and change the values of the process variables. The variables will be forced to the value the user entered. The user can press release to release the variable. If one or two variables are selected, a chart of the values is shown. Also resize and zoom is possible to see more details. The chart will be updated every 250 milliseconds:
It is also possible to add the variables to a watch list (next chapter).
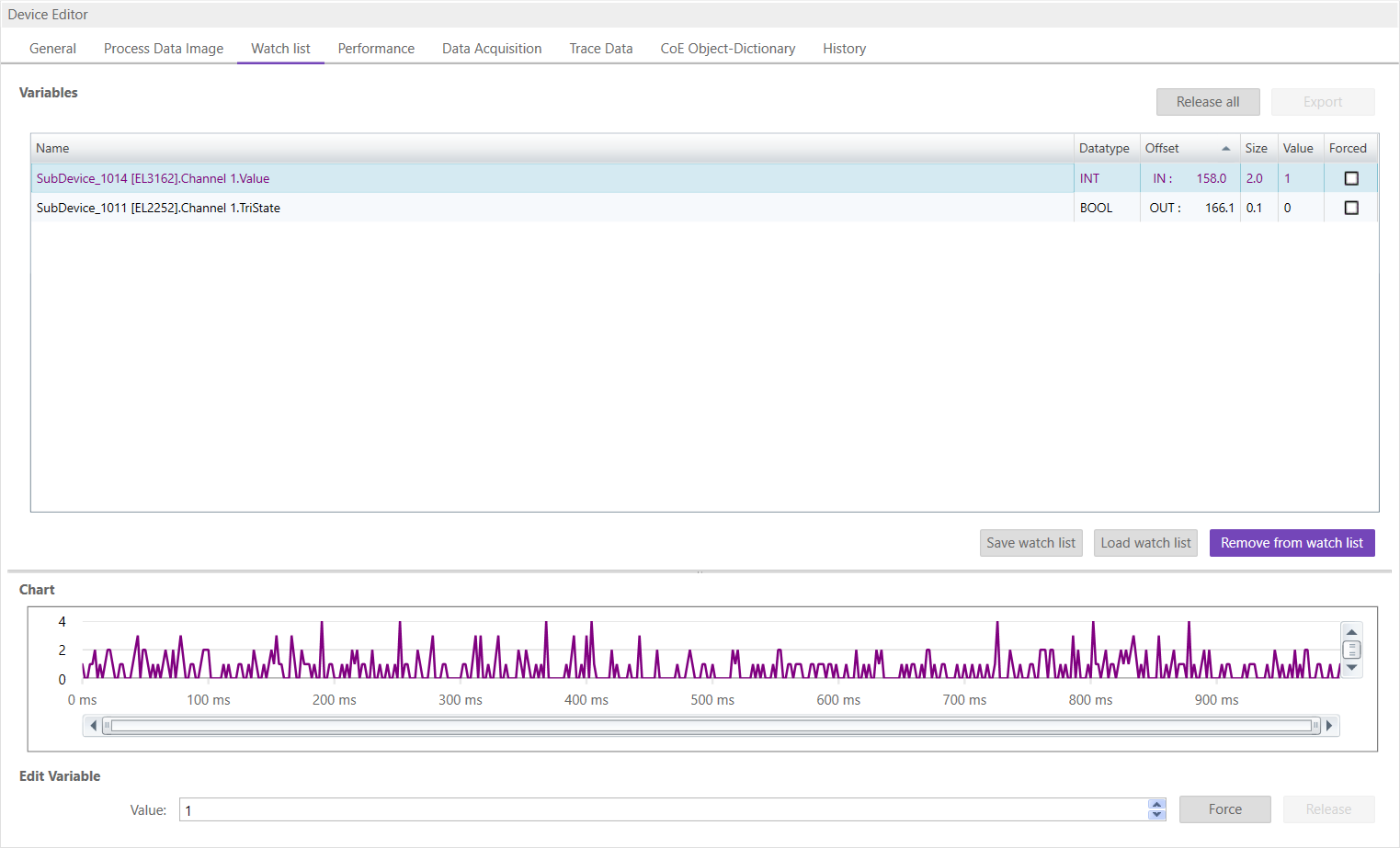
6.2.3. Watch list
In this tab, the user can monitor selected variables. He can go through the SubDevices and add variables to the watch list to monitor them. The user can also export or import the watch list, so changes can be saved:
6.2.4. Performance
- This tab is split into two sub tabs. On one the user can see the busload per cycle and per second:
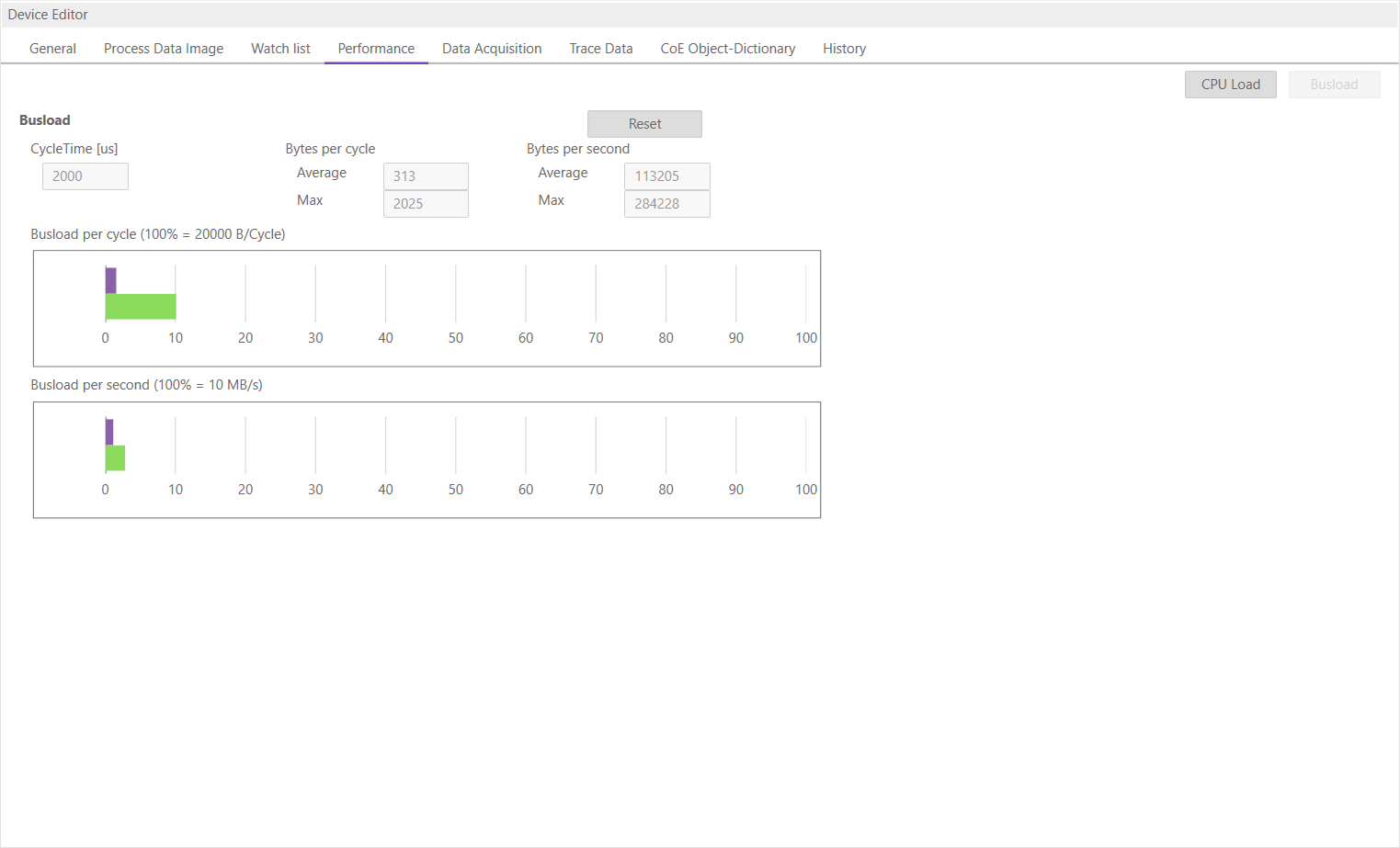
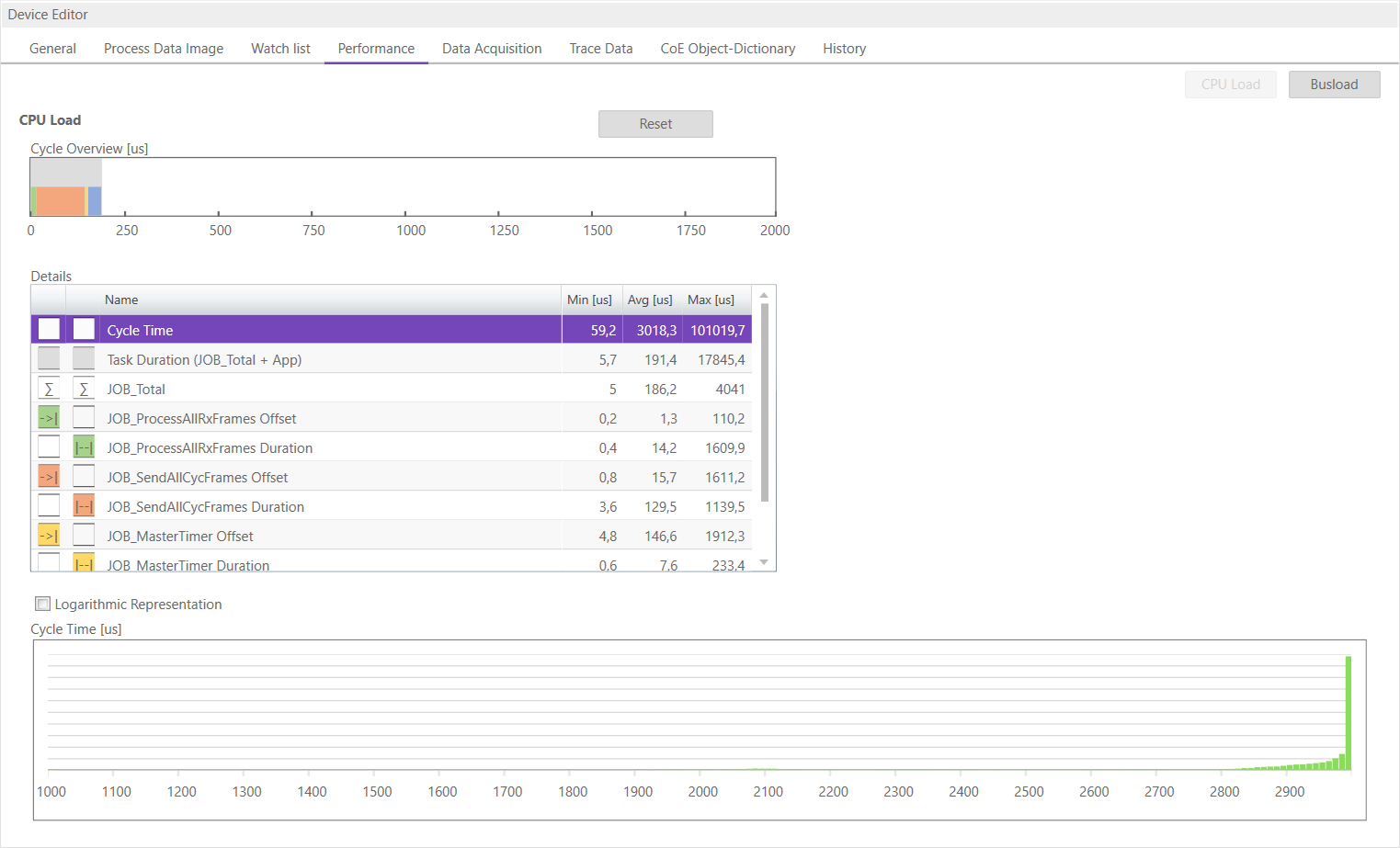
- On the other tab the user can the CPU load. In the grid is a list of all running jobs and how long they take. In the diagram above is a summary of all jobs. When a job is selected, the chart shows how many times a job has taken how long to complete.
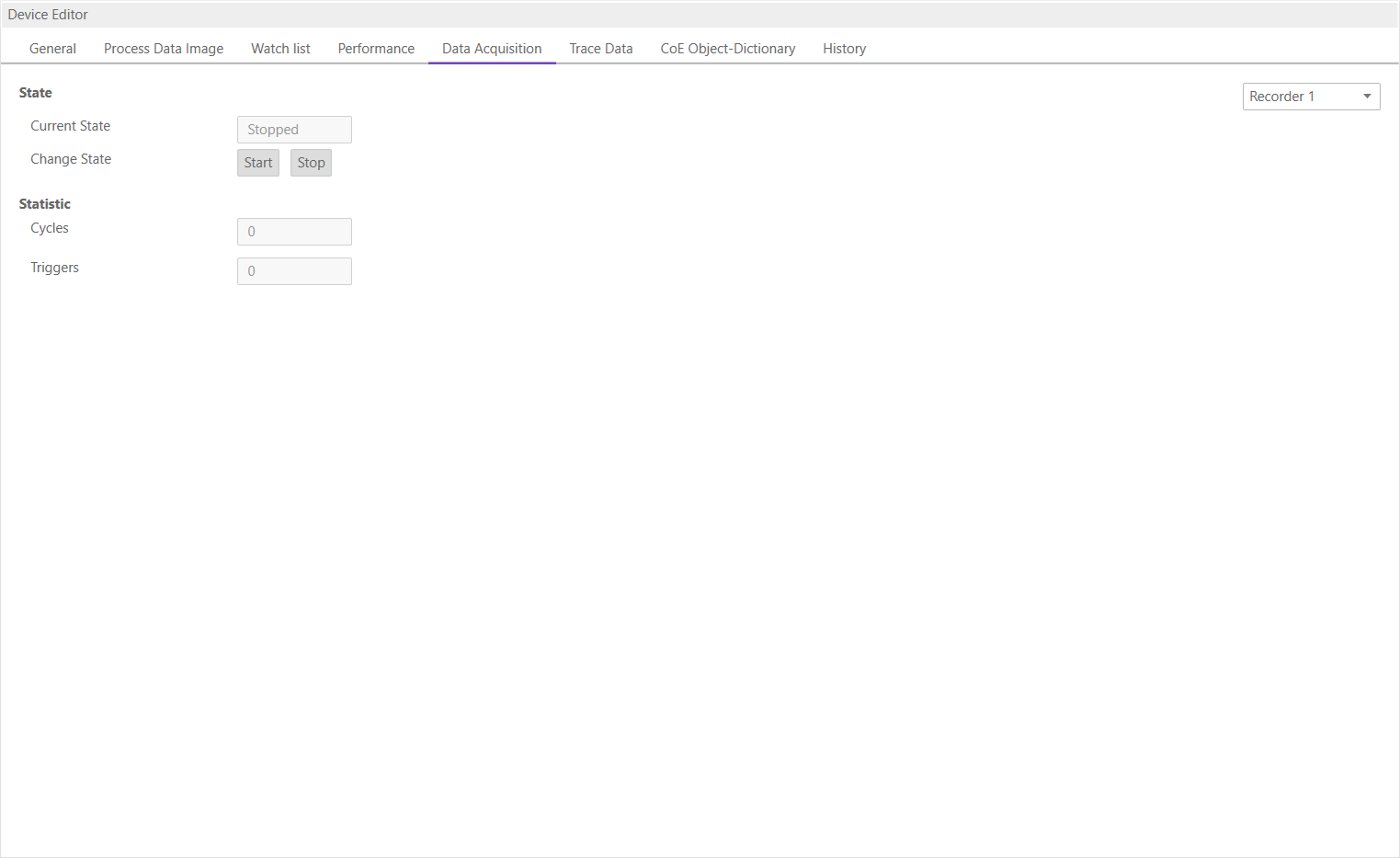
6.2.5. Data Acquisition Diagnosis
- In this tab, the user can start and stop the DAQ recorders. Also he can see some statistics of running recorders.
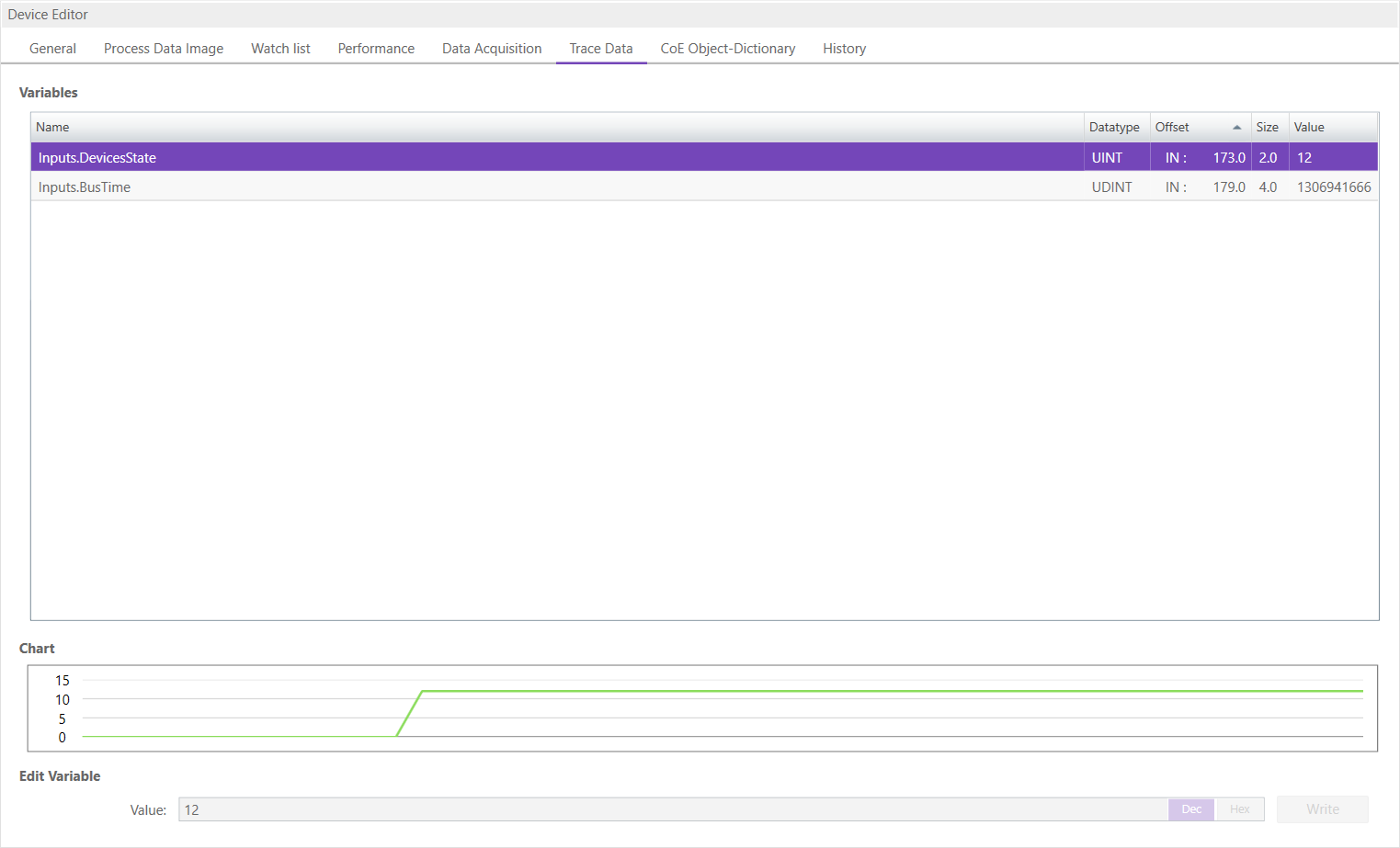
6.2.6. Trace Data (Expert)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the values of the trace variables. If he selects a variable he will see a chart of the values. The chart will be updated every 250 milliseconds:
6.2.7. CoE Object-Dictionary (Device)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the values of the object dictionary of the MainDevice:
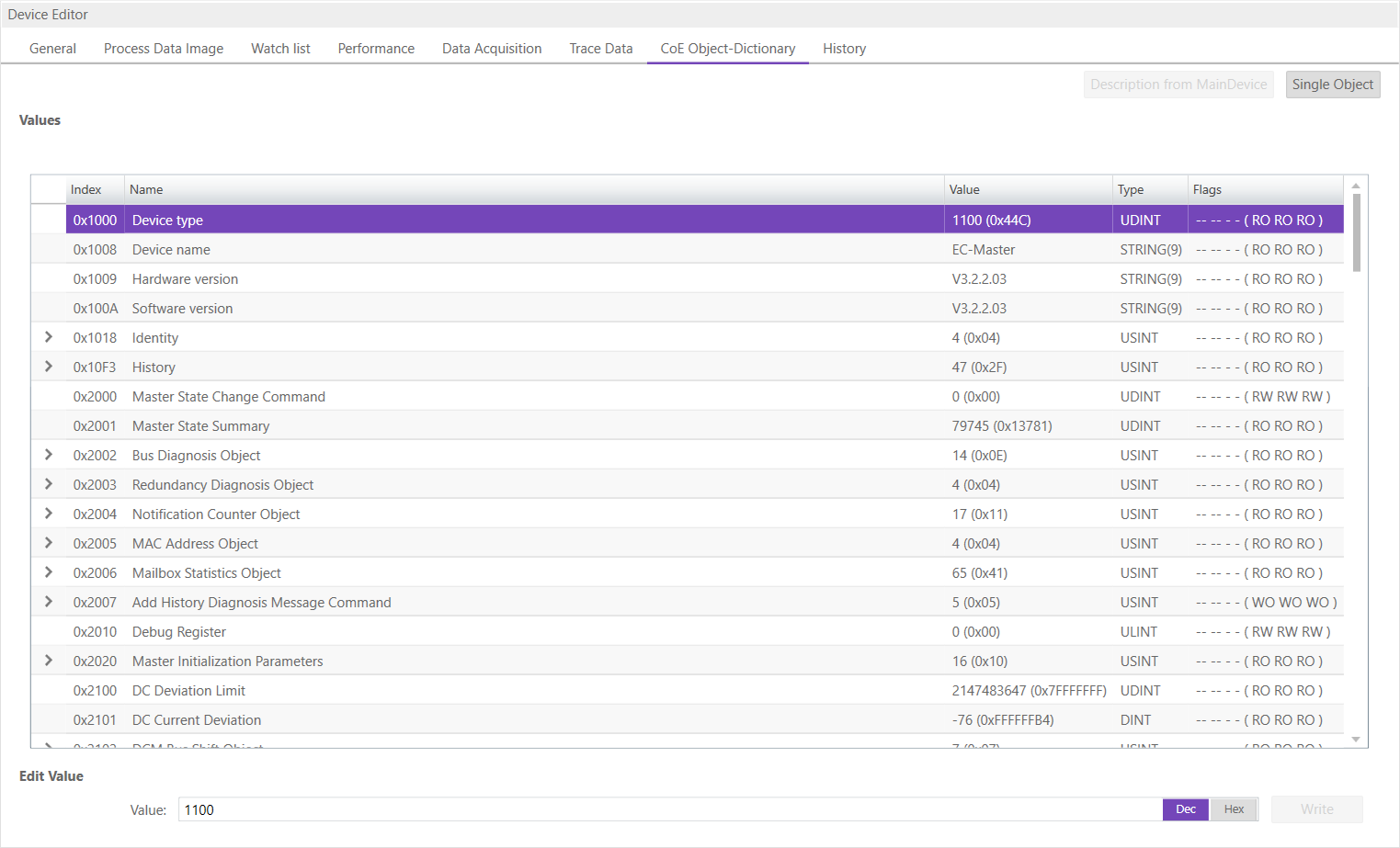
- Lists of CoE Object-Dictionary entries
Entries are uploaded by the MainDevice from the SubDevice
- The “Flags” column tells the user if this entry is an PDO entry and if it can be edited
“AA BB (CC DD EE)”
AA = Mapping as RX PDO or not
BB = Mapping as TX PDO or not
CC = Access rights for PreOp (RO, WO, RW)
DD = Access rights for SafeOp (RO, WO, RW)
EE = Access rights for Op (RO, WO, RW)
- Buttons
- Update:
Changes the selected entry
6.2.8. History (Device)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the diagnosis history of the MainDevice (Supported from EC-Master V2.7 and above). It is also possible to export the data:
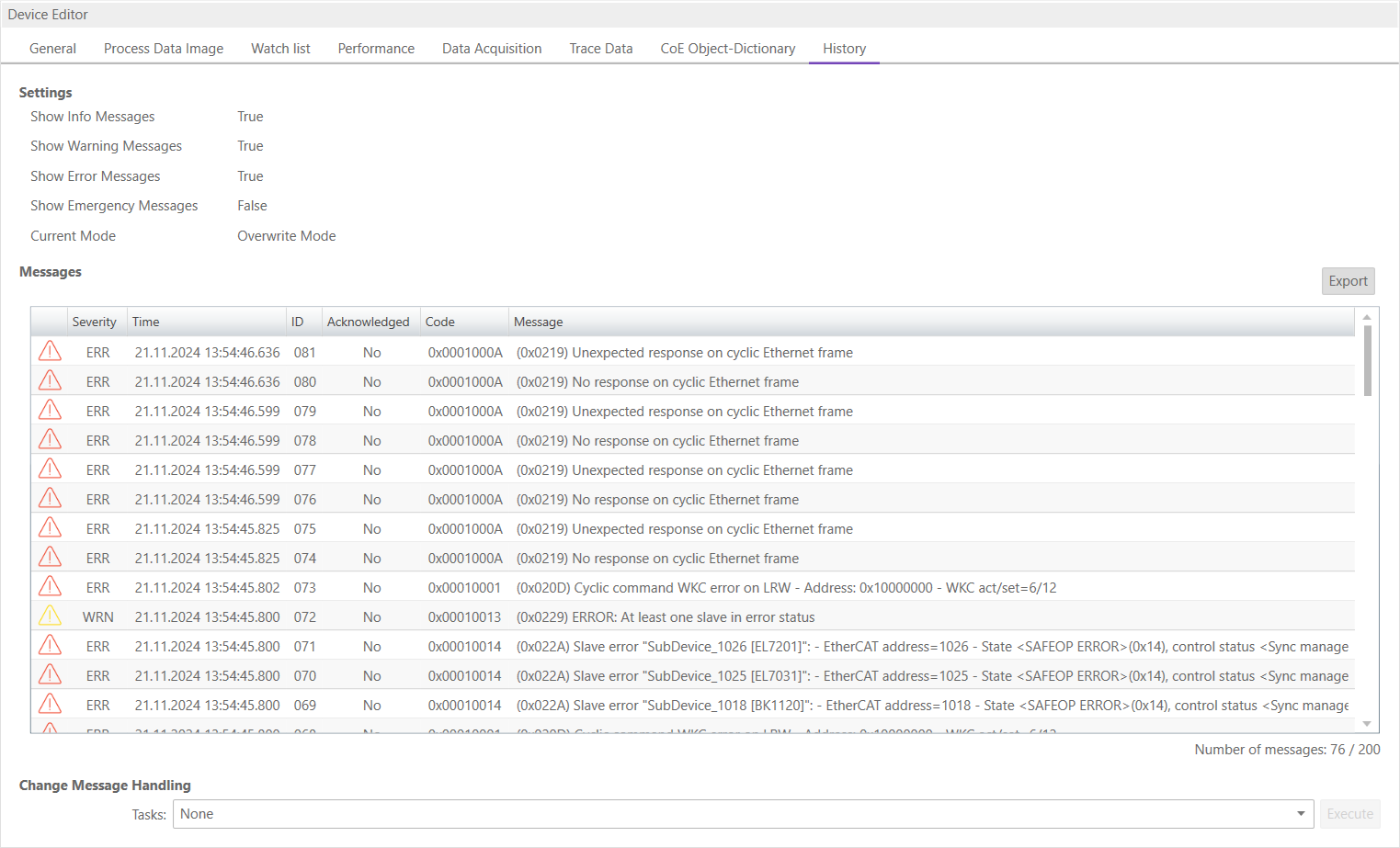
- Settings
- Show Info Messages:
Info messages will be collected from MainDevice
- Show Warning Messages:
Warning messages will be collected from MainDevice
- Show Error Messages:
Error messages will be collected from MainDevice
- Show Emergency Messages:
Not supported from MainDevice
- Current Mode:
Overwrite Mode: Messages will be overwritten if buffer is full Acknowledge Mode: Not supported from MainDevice
- Messages
List of history messages
- Change Message Handling
- Enable/Disable Info Messages:
Enable or disable info messages
- Enable/Disable Warning Messages:
Enable or disable warning messages
- Enable/Disable Info Messages:
Enable or disable info messages
- Enable/Disable Error Messages:
Enable or disable error messages
- Enable Acknowledge Mode:
Enable acknowledge mode
- Clear All Messages:
Clear all messages
6.3. SubDevice
This section shows the current “health” state of the selected SubDevice and helps the user to analyze SubDevice related problems.
6.3.1. General (SubDevice)
In this tab, the user can see the current state of the state machine of the SubDevice:
- State Machine
- Current State:
Current state of the selected SubDevice
- Requested State:
Requested state of the selected SubDevice
- Change State:
SubDevice can reach the states INIT, BOOTSTRAP, PRE-OP, SAFE-OP and OP.
- Software Diagnostics
- State Machine Error:
SubDevice error which occurred during state transition
- Hardware Diagnostics
- Summary:
Summary of hardware diagnostics
- Port A:
Port specific error
- Port D:
Port specific error
- Port B:
Port specific error
- Port C:
Port specific error
- Buttons
- Acknowledge:
Acknowledge the current error state and notify the user again if error state was changed again.
- Possible warning and errors:
- Disturbed Connection:
There may be problems in the connection between two SubDevices. The message will tell either that there is a problem between two SubDevices or two ports. The warning appears if error counters are increased (Invalid Frame: 0x300-0x306, RX Errors: 0x301-0x307, Lost Link: 0x308-0x30B). The value from which a warning is issued can be set in the User.xml files in C:/ProgramData/EC-Engineer. More information below.
- Bad Connection:
The same as “Disturbed Connection” but the error counters are higher. The value from which an error is issued can be set in the User.xml files in C:/ProgramData/EC-Engineer. More information below.
- Line break:
A line break is detected before a SubDevice. This error is detected by looking at the topology.
- Link missing:
A link is missing on input port of the SubDevice. This error is detected by looking at the topology.
- Multiple warnings:
There are multiple warning for this port.
- Multiple errors:
There are multiple errors for this port.
- Multiple warnings and errors:
There are multiple warning and errors for this port.
- State Machine:
See ETG1020 “Description of AL Status Codes” or ETG.1000.6. This error is detected by looking at the AL Status (0x130).
- How to solve errors?
Lost Link errors are often caused by the power supply system
Helpful might be the usage of an extra power supply
It is recommended to clear all error counters after startup
- How to change amount of errors leading to a warning or error:
Open C:/ProgramData/EC-Engineer
Search for DiagGeneral
- Change the values which should be adjusted
LostLink: The value entered is used
All others are calculated depending on the amount of cyclic frames: (Value / CyclicFrames) x 10^6
Note
Please refer also the “ETG.1600 EtherCAT Installation Guideline”: http://www.ethercat.org/ETG1600.
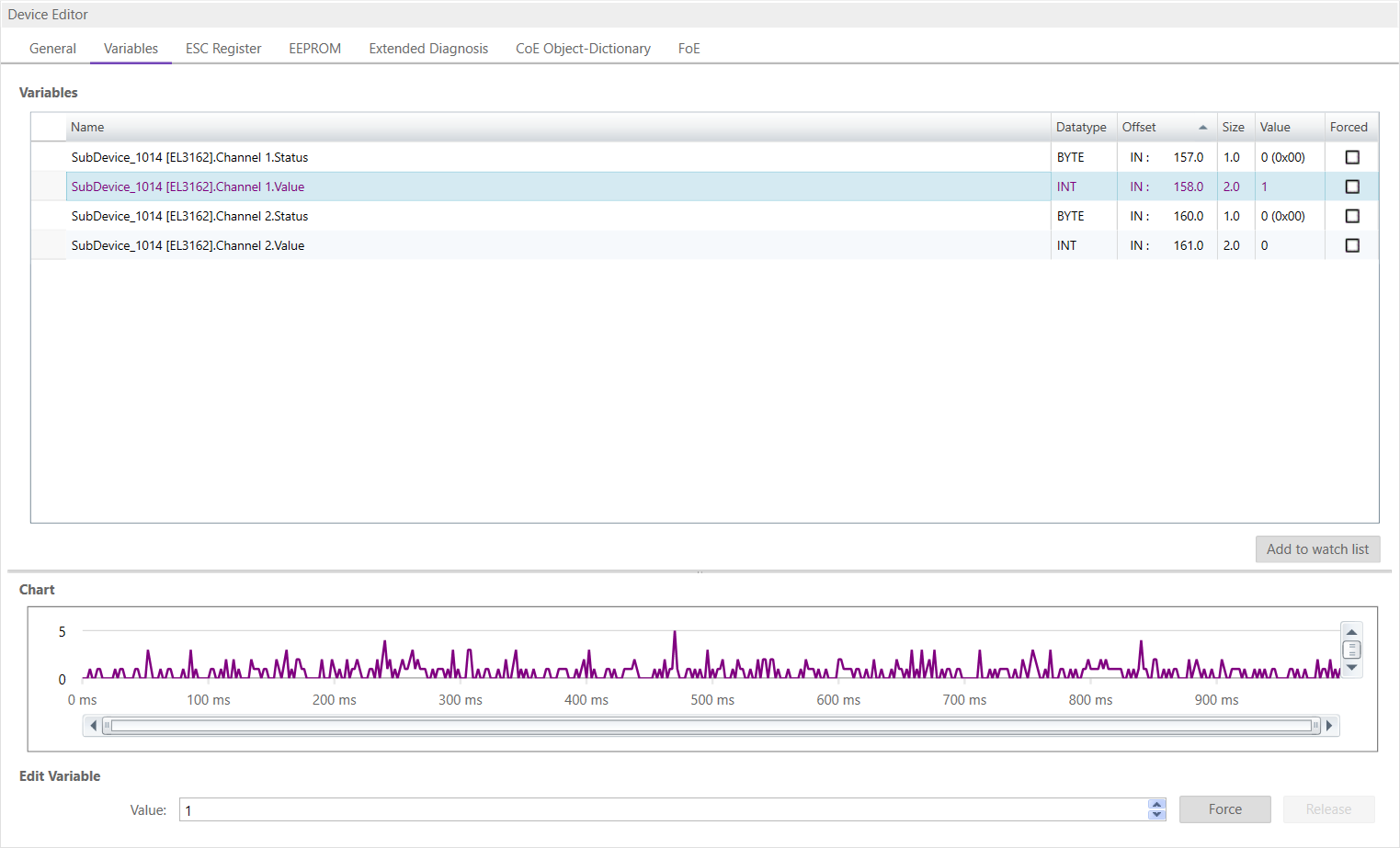
6.3.2. Variables
In this tab, the user can see and change the values of the process variables. The variables will be forced to the value the user entered. The user can press release to release the variable. If one or two variables are selected, a chart of the values is shown. Also resize and zoom is possible to see more details. The chart will be updated every 250 milliseconds:
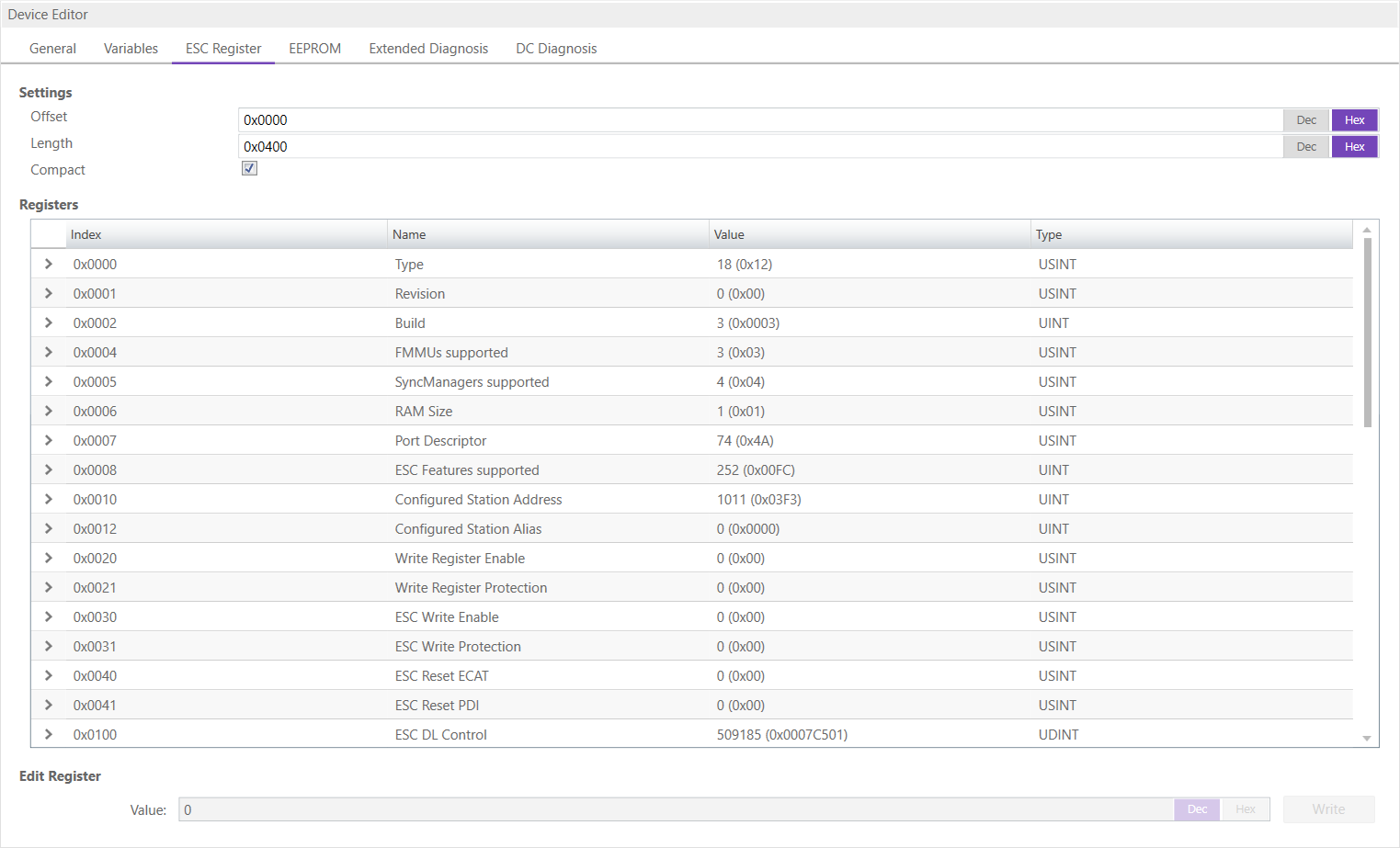
6.3.3. ESC Register
In this tab, the user can see the values of the registers. In the settings section he can set the offset and the length. If he activates the compact view, he will only see the registers which have a description:
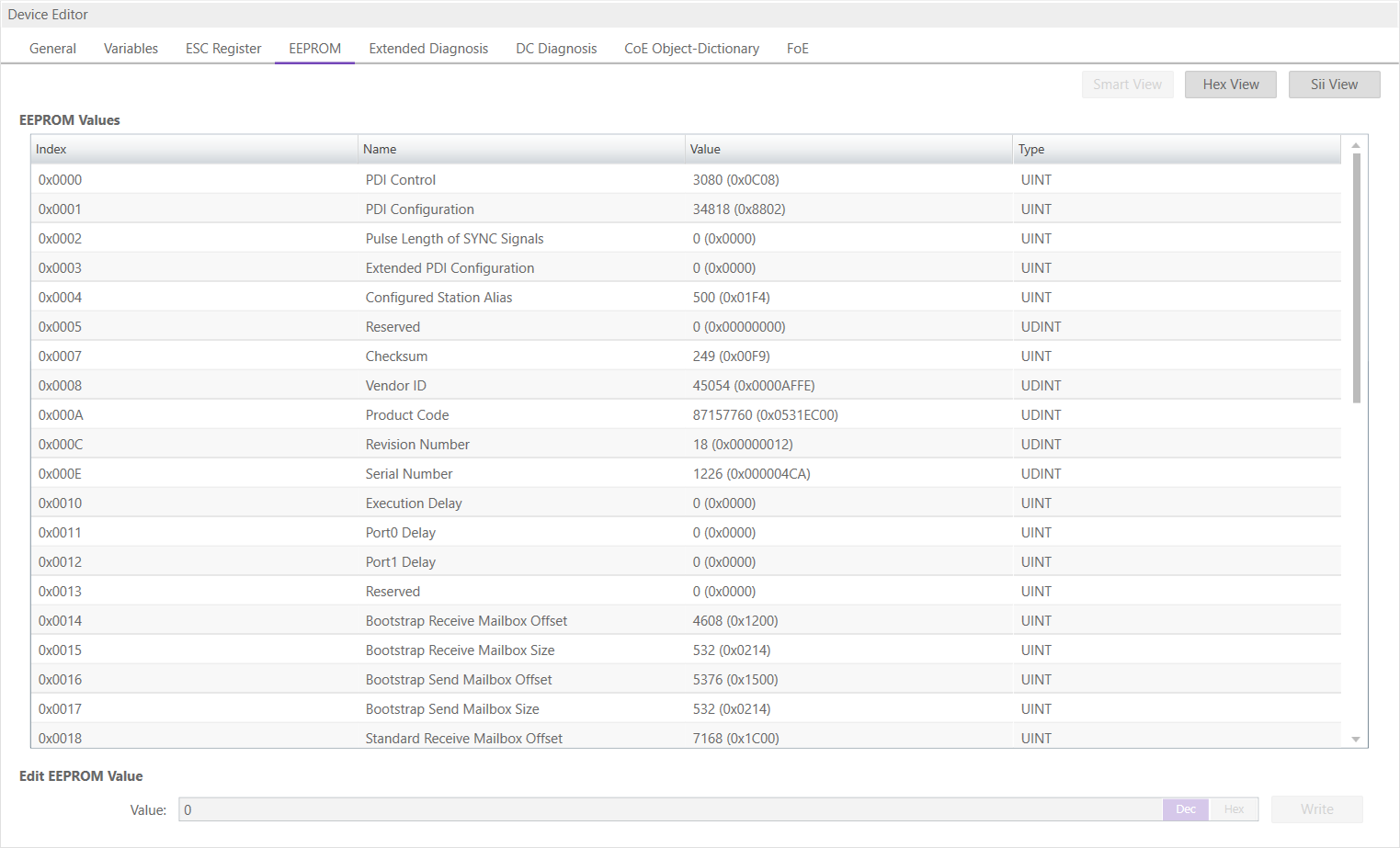
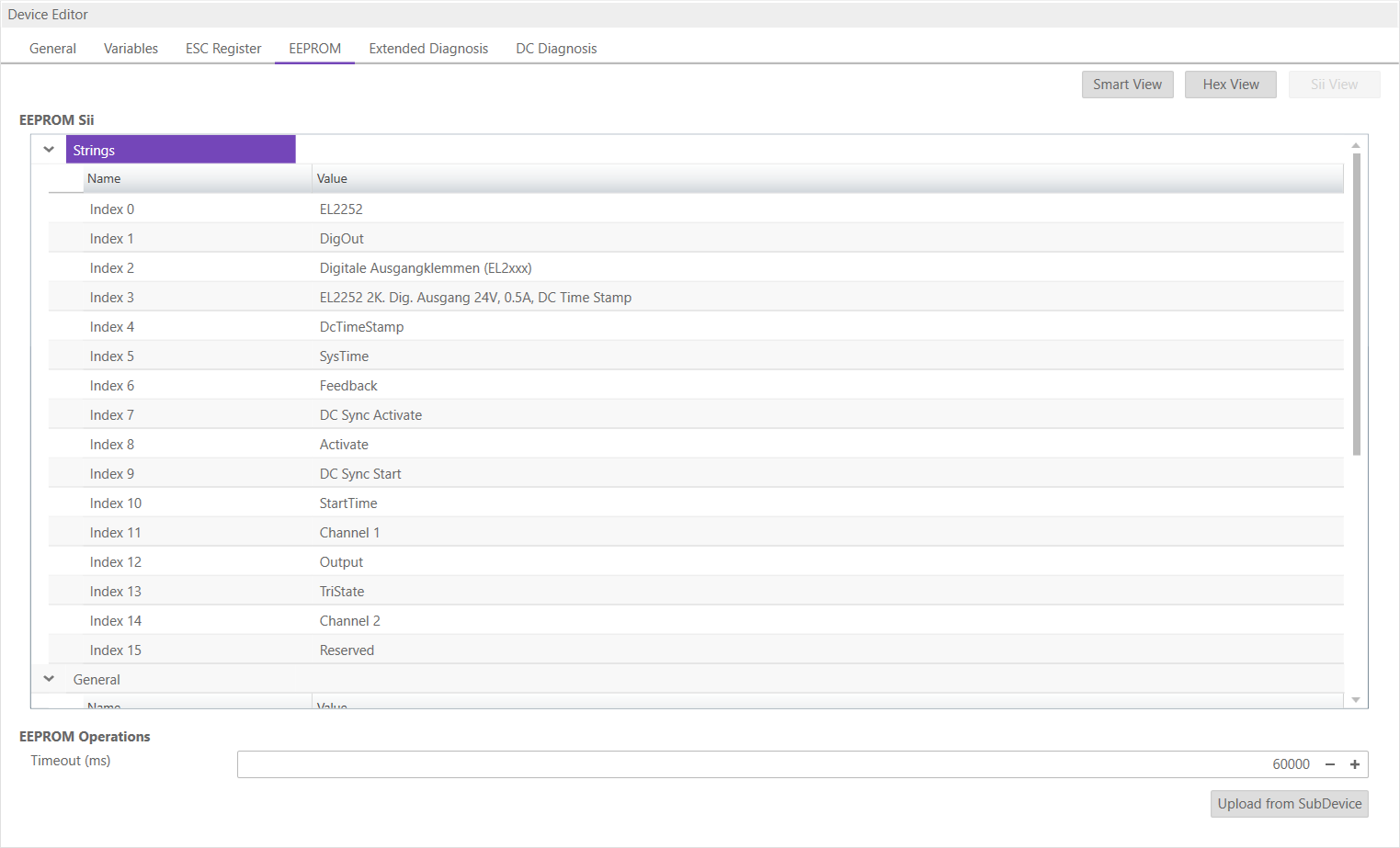
6.3.4. EEPROM
This tab consists of 3 views:
- Smart View
In this view, the user can see and change the values of the EEProm.
- Hex View
In this view, the user can create an EEPROM from an
ESIfile, upload the EEPROM from the SubDevice, load an EEPROM from the disk, download the EEPROM to the SubDevice or save the EEPROM to disk.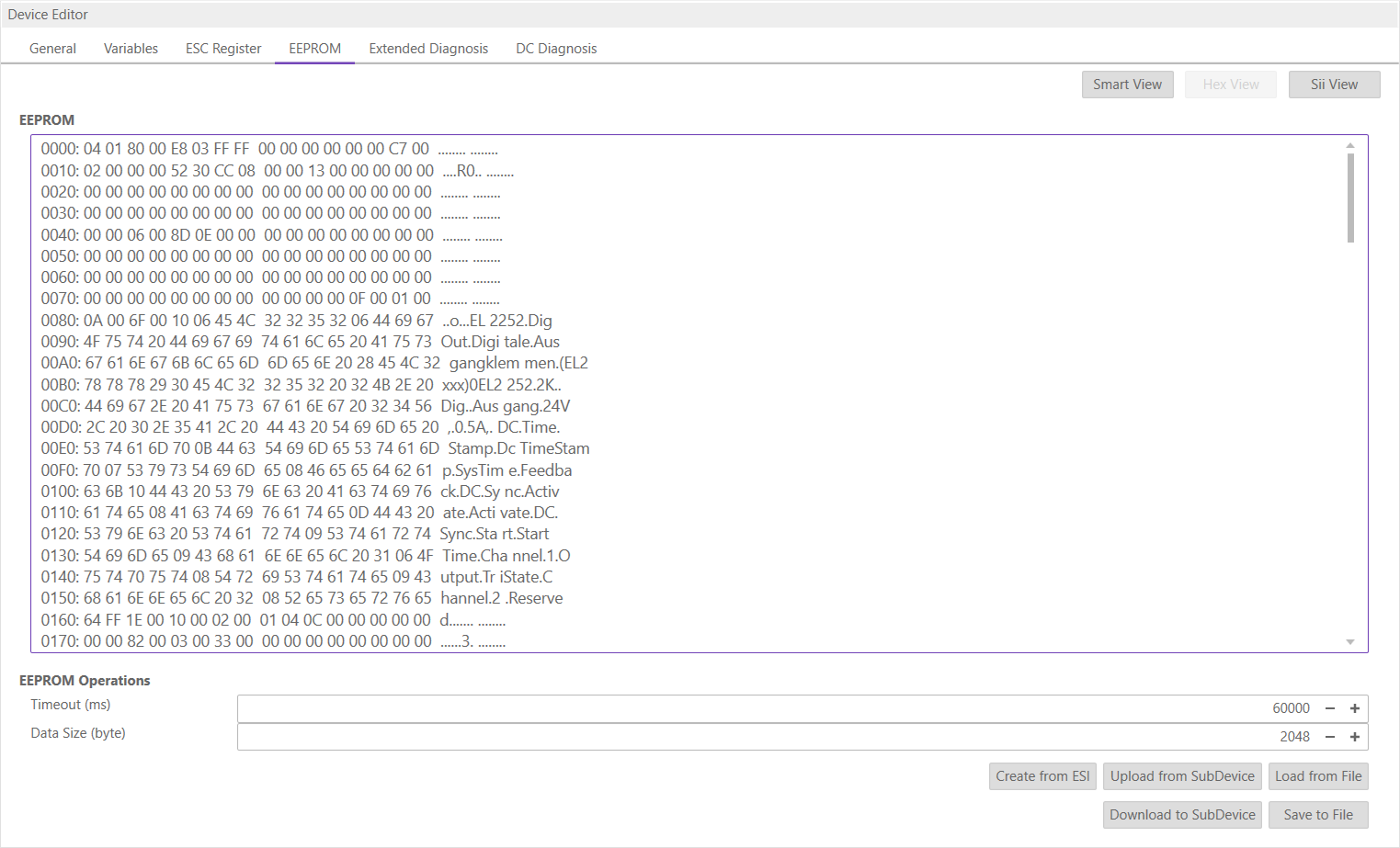
- SII View
In this view, the user can create a SubDevice Information Interface (SII), by uploading the EEPROM data from the SubDevice.
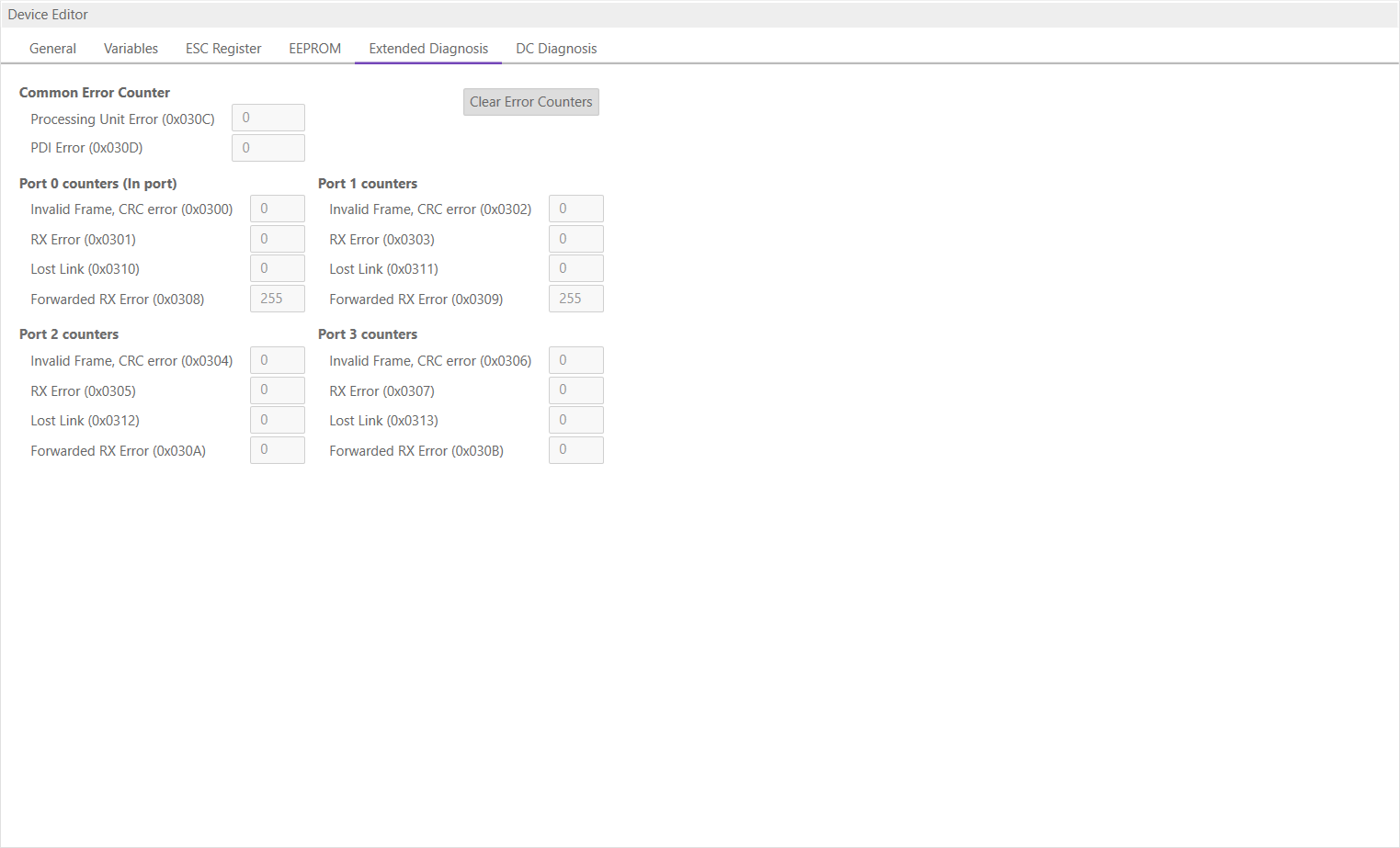
6.3.5. Extended Diagnosis
In this tab, the user can see the extended diagnosis information:
There will be a red ! to signalize that a counter is higher than 0. Except for the forwarded errors.
If an error counter is ‘-’ it was not read. If it is ‘0’ it is really zero. So there is a difference between ‘0’ and ‘-‘.
- Common Error Counter
- Processing Error Counter:
Indicates that SubDevice received “not EtherCAT frames”, which are not allowed in the EtherCAT segment (of course acceptable in a test environment)
- PDI Error Counter:
Counts if a PDI access has an interface error (read from register: 0x30D)
- Port 0..3
Invalid Frame Counter of Port y (read from register: 0x0300+y*2)
RX Error Counter of Port y (read from register: 0x0300+y*2+8Bit)
Lost Link Counter of Port y (read from register: 0x0310+y)
Forwarded RX Error Counter of Port y (read from register: 0x0308+y)
- Acknowledge warning
If one of the error counters increase there will be a warning in the tree, sigalized with an icon. With this button it is possible to acknowledge this warning. So the SubDevice can be monitored again and the icon will come back with the next error.
To see this information the error counters must be read by the EtherCAT MainDevice. Only if this is activated the EC-Engineer is able to read this. Here is a quick overview on how to activate this function on different MainDevices:
- acontis EC-Master:
To activate the error collection of the acontis EC-Master, the follwing API has to be called:
/* SubDevice statistics polling for error diagnostic */ EC_T_DWORD dwPeriodMs = 1000; dwRes = ecatIoCtl(EC_IOCTL_SET_SLVSTAT_PERIOD, (EC_T_BYTE*)&dwPeriodMs, sizeof(EC_T_DWORD), EC_NULL, 0, EC_NULL); if (dwRes != EC_E_NOERROR) { EcLogMsg(EC_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, (pEcLogContext, EC_LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, "ecatIoControl(EC_IOCTL_SET_SLVSTAT_PERIOD) returns with error=0x%x\n", dwRes)); goto Exit; }
6.3.6. DC Diagnosis
- In this tab, the user can see all DC related values of the SubDevice:
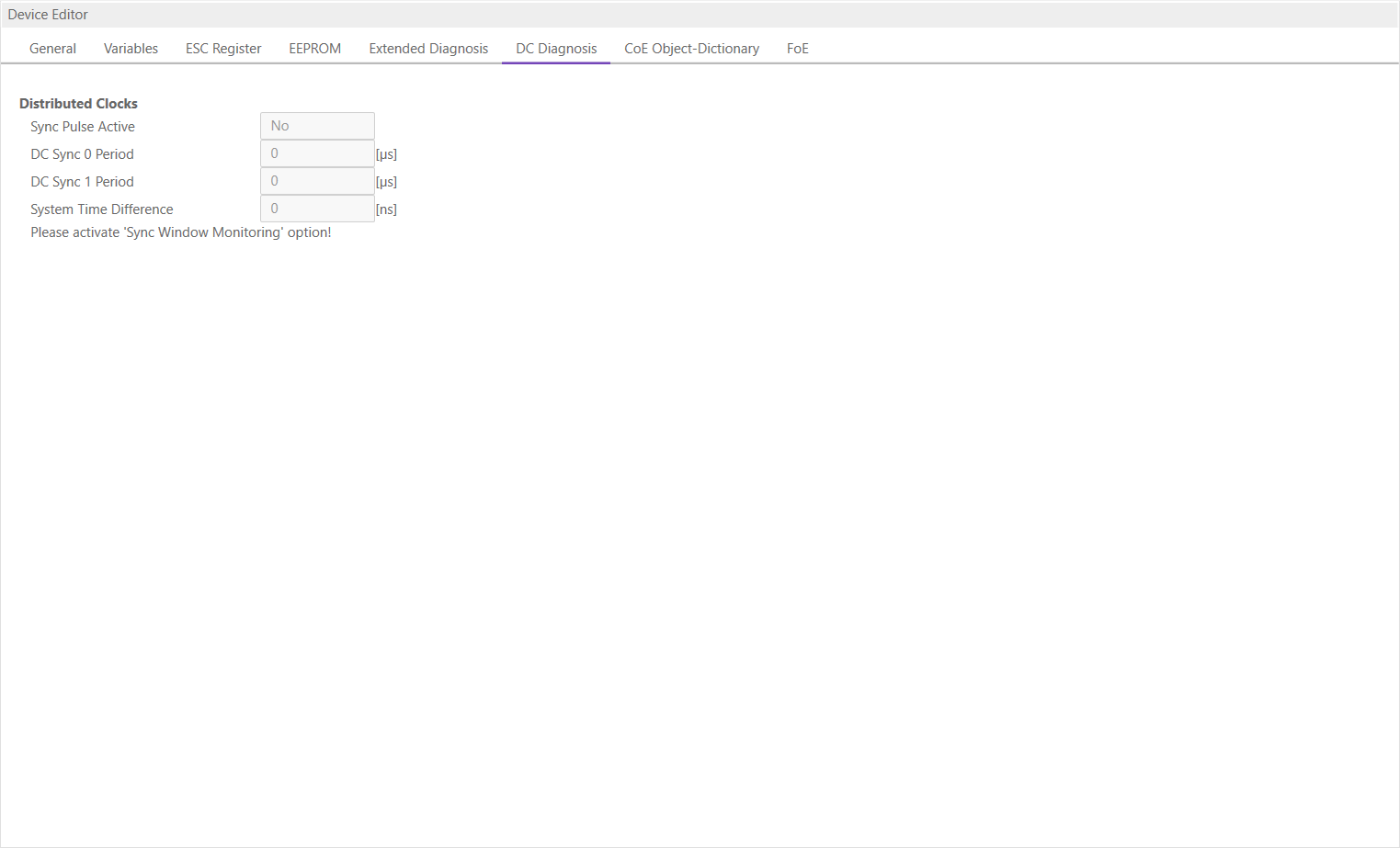
- Distributed Clock
- Sync Pulse Active:
Sync pulse was received or not
- DC Sync 0 Period:
Configured period for sync unit 0
- DC Sync 1 Period:
Configured period for sync unit 1
- System Time Difference:
Time difference of SubDevice clock to reference clock
Note
The option “Sync Window Monitoring” must be enabled.
6.3.7. CoE Object-Dictionary
This tab consists of different modes:
- Description from
ESI In this tab, the user can see the description of the object dictionary from
ESIand the values from the SubDevice.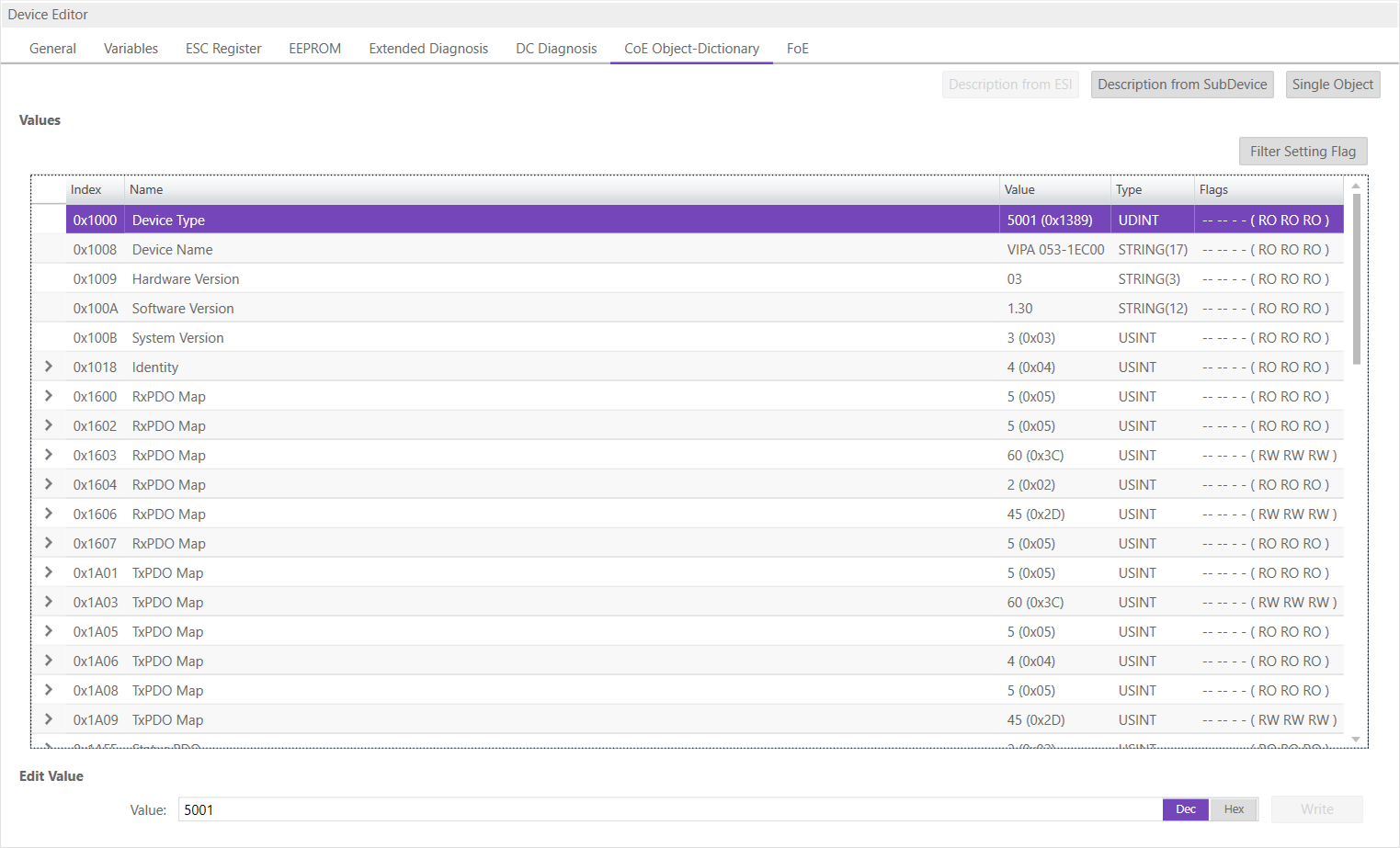
- Lists of CoE Object-Dictionary entries
Entries comes from
ESI- The “Flags” column tells the user if this entry is an PDO entry and if it can be edited
“AA BB C D (EE FF GG)”
AA = Mapping as RX PDO or not
BB = Mapping as TX PDO or not
C = Backup Flag
D = Settings Flag
EE = Access rights for PreOp (RO, WO, RW)
FF = Access rights for SafeOp (RO, WO, RW)
GG = Access rights for Op (RO, WO, RW)
- Buttons
- Write:
Writes the selected entry
- Description from SubDevice
In this tab, the user can see the description of the object dictionary and the values from SubDevice. He can also change the values and has the possiblillty to export the object dictionary.
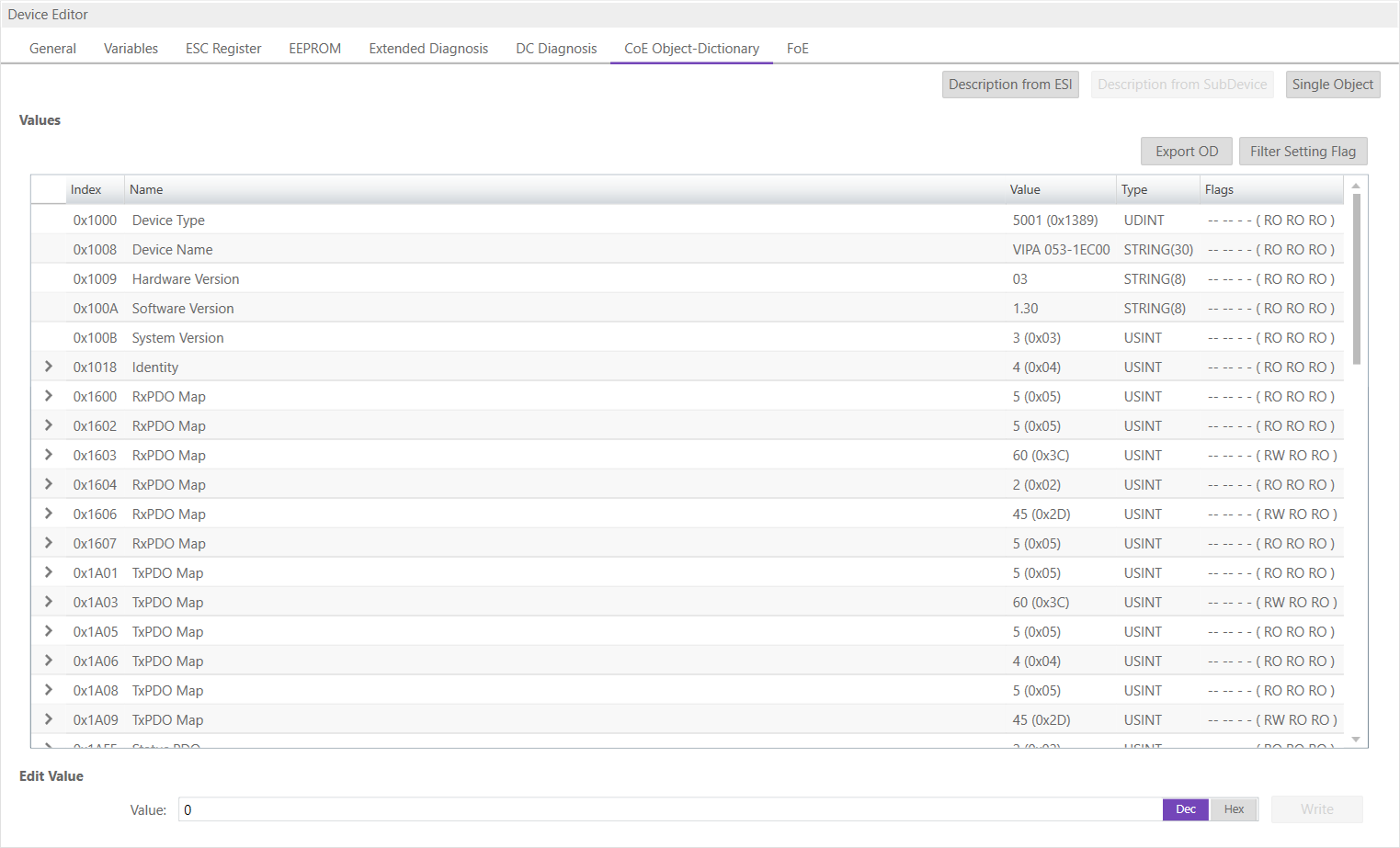
- Lists of CoE Object-Dictionary entries
Entries are uploaded from the SubDevice (if “SDO Information Service” is supported)
- The “Flags” column tells the user if this entry is an PDO entry and if it can be edited
“AA BB C D (EE FF GG)” - AA = Mapping as RX PDO or not - BB = Mapping as TX PDO or not - C = Backup Flag - D = Settings Flag - EE = Access rights for PreOp (RO, WO, RW) - FF = Access rights for SafeOp (RO, WO, RW) - GG = Access rights for Op (RO, WO, RW)
- Buttons
- Write:
Writes the selected entry
- Single Object
In this tab, the user can read and write (not EC-Inspector) the values of the object dictionary of the SubDevice.
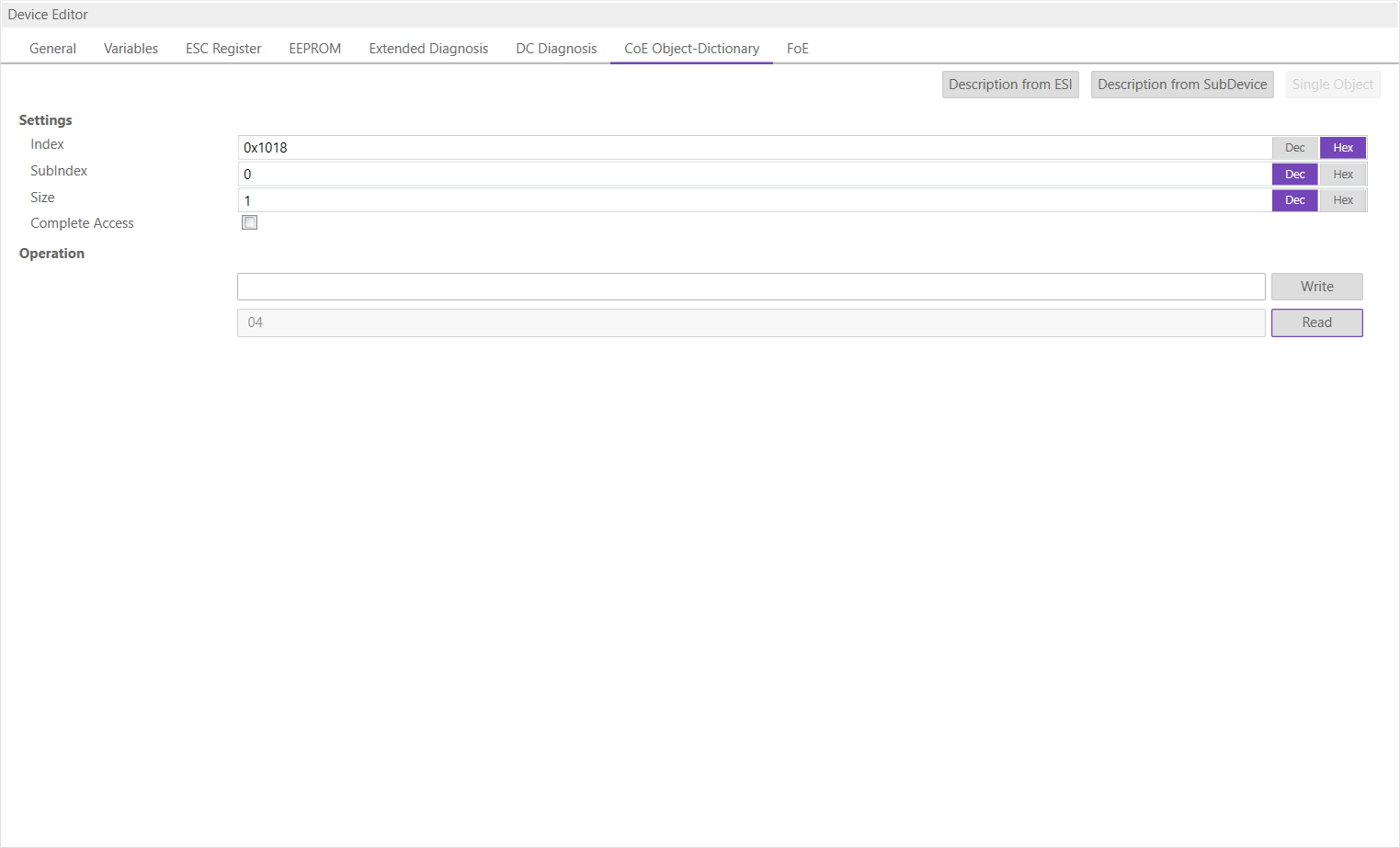
- Settings
- Index:
Index of the CoE value
- SubIndex:
SubIndex of the CoE value
- Size:
Size of the CoE value (only used for reading)
- Complete Access:
Activate, if complete access mode should be used for reading or writing the CoE value (can be used only if it is supported from SubDevice)
- Operation
- Write:
Writes the value to the SubDevice (Hex format, like: “00 11 22 33 …”)
- Read:
Reads the value from SubDevice (Hex format, like: “00 11 22 33 …”)
6.3.8. SoE Object-Dictionary
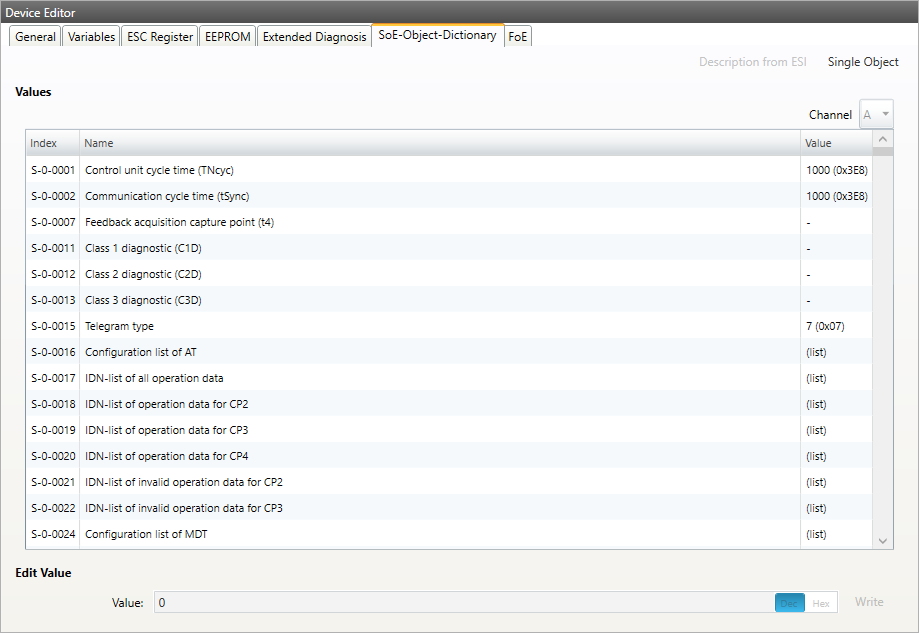
- Lists of SoE Object-Dictionary entries
Values are uploaded by the MainDevice from the SubDevice
Entries comes from the
ESI
- Buttons
- Write:
Writes the selected entry
- Expert View
In this tab, the user can read and write the values of the object dictionary of the SubDevice:
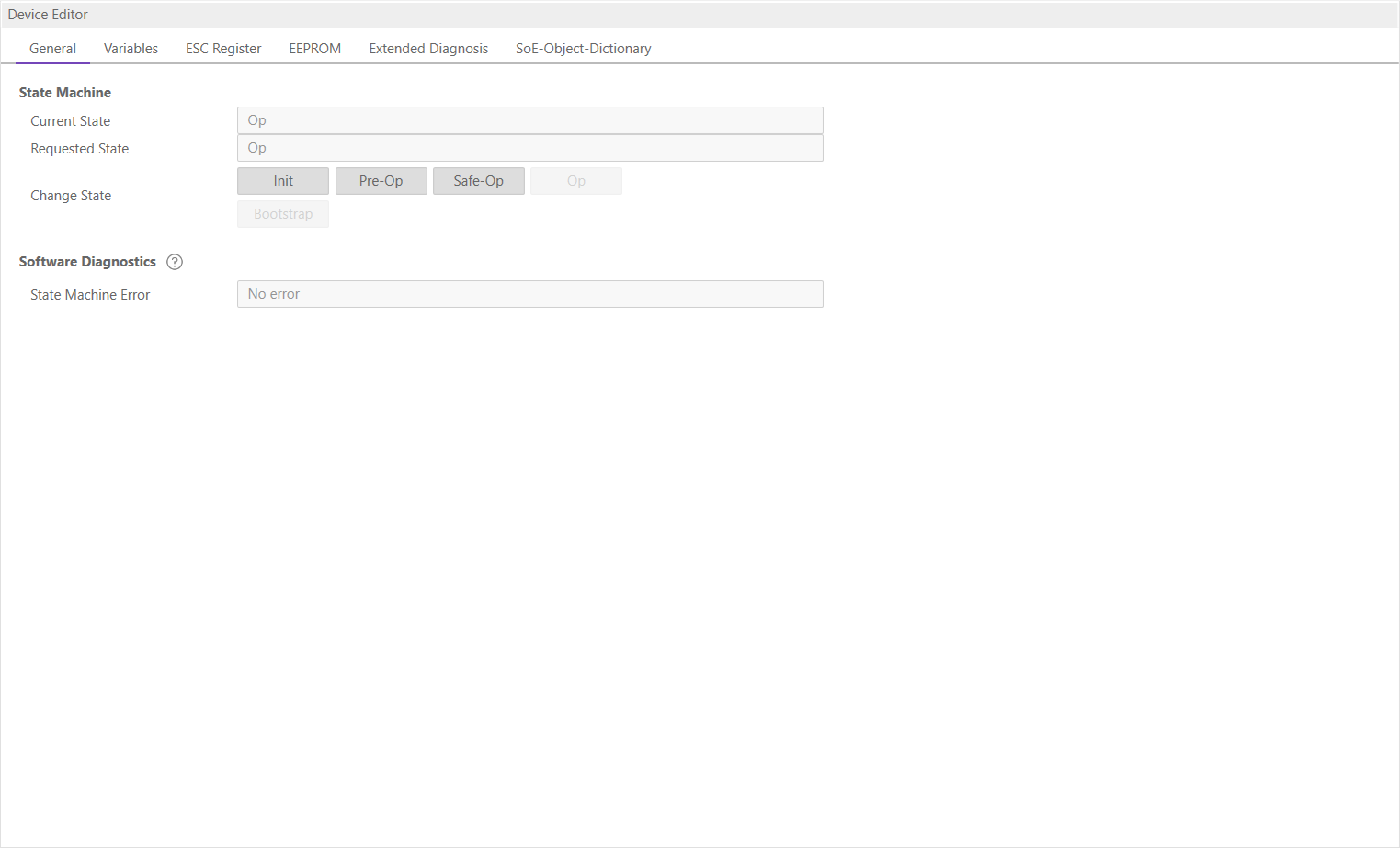
- Settings
- Channel:
Channel of the SoE value
- IDN:
Index of the CoE value
- Size:
Size of the CoE value (only used for reading)
- Operation
- Write:
Writes the value to the SubDevice (Hex format, like: “00 11 22 33 …”)
- Read:
Reads the value from SubDevice (Hex format, like: “00 11 22 33 …”)
6.3.9. File over Ethernet (FoE)
- In this tab, the user has the possibility to download or upload a file to the SubDevice:
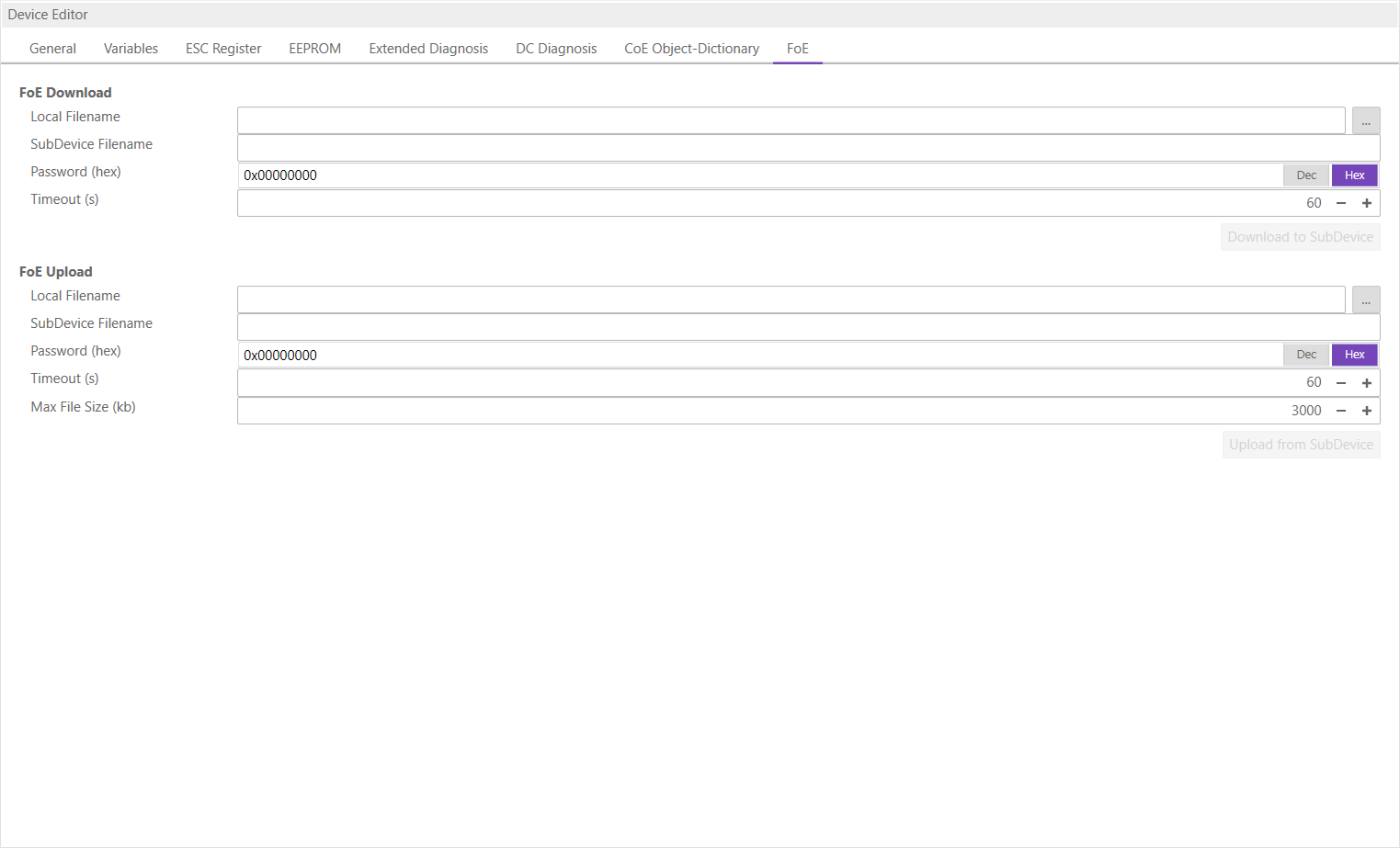
- FoE Operations
- Local Filename:
Name of the file on the harddrive
- SubDevice Filename:
Name of the file on the SubDevice
- Password:
Password on the SubDevice as a hex-number
- Timeout:
Timeout for downloading or uploading the file in milliseconds
- Max File Size:
Maximal file size which should be uploaded from the SubDevice in kilo bytes
6.3.10. History (SubDevice)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the diagnosis history of the SubDevice. It is also possible to export the data:
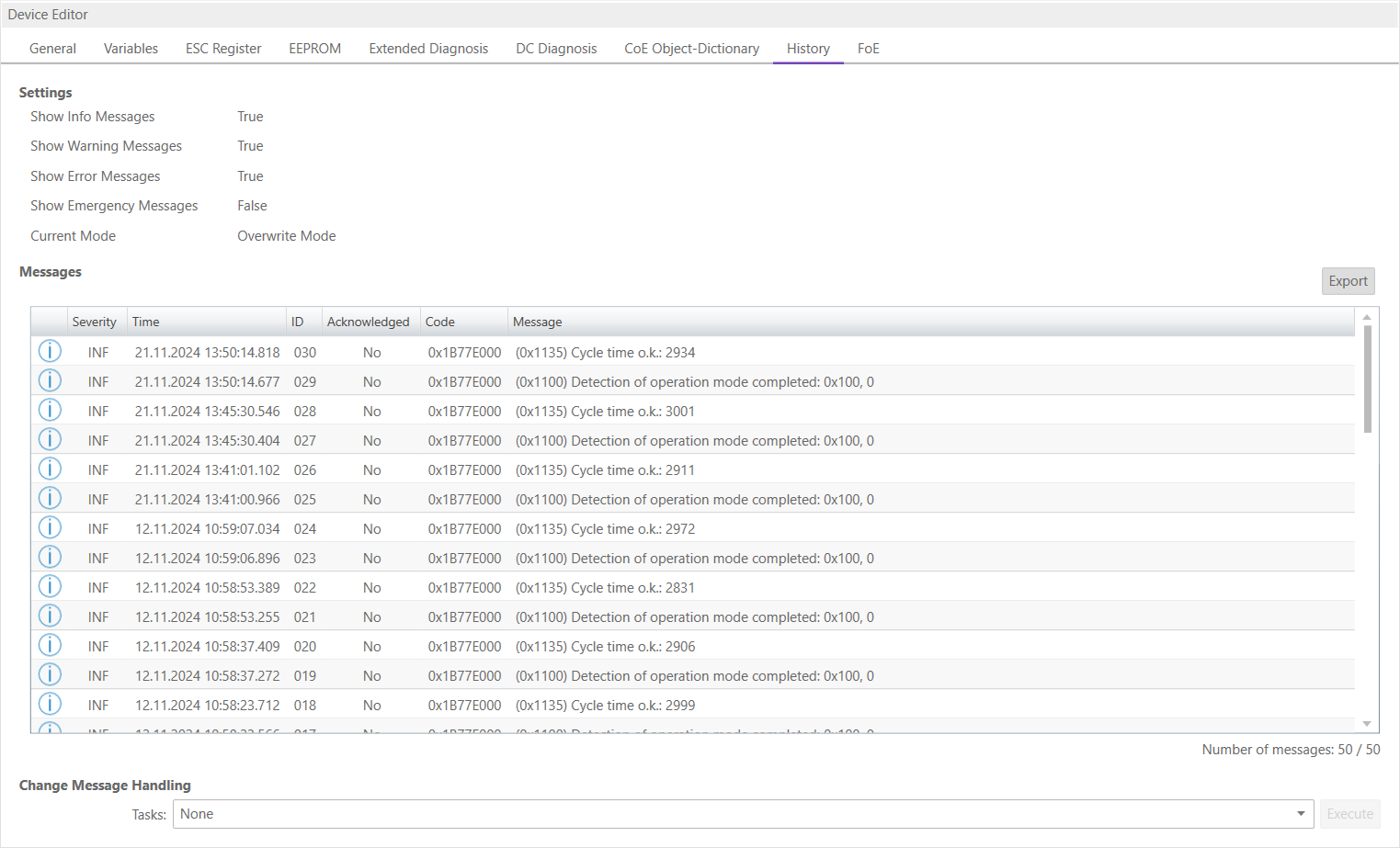
- Settings
- Show Info Messages:
Info messages will be collected from SubDevice
- Show Warning Messages:
Warning messages will be collected from SubDevice
- Show Error Messages:
Error messages will be collected from SubDevice
- Show Emergency Messages:
Emergency messages will be collected from SubDevice
- Current Mode:
Overwrite Mode: Messages will be overwritten if buffer is full Acknowledge Mode: Messages will be discarded if buffer is full
- Messages
List of history messages
- Change Message Handling
- Enable/Disable Info Messages:
Enable or disable info messages
- Enable/Disable Warning Messages:
Enable or disable warning messages
- Enable/Disable Info Messages:
Enable or disable info messages
- Enable/Disable Error Messages:
Enable or disable error messages
- Enable/Disable Emergency Messages:
Enable or disable emergency messages
- Enable Acknowledge Mode:
Enable acknowledge mode
- Enable Overwrite Mode:
Enable overwrite mode
- Clear All Messages:
Clear all messages (only available if “Overwrite Mode” is active)
- Clear All Acknowledged Messages:
Clear all acknowledged messages (only available if “Acknowledge Mode” is active)
- Acknowledge All Messages:
Acknowledge all messages, that they can be overwritten from new messages (only available if “Acknowledge Mode” is active)
6.3.11. Motion (Motion Tabs only)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the motion settings of the SubDevice. He can read important variables and change velocity and direction of the axis. Also gearing and camming are possible to use:
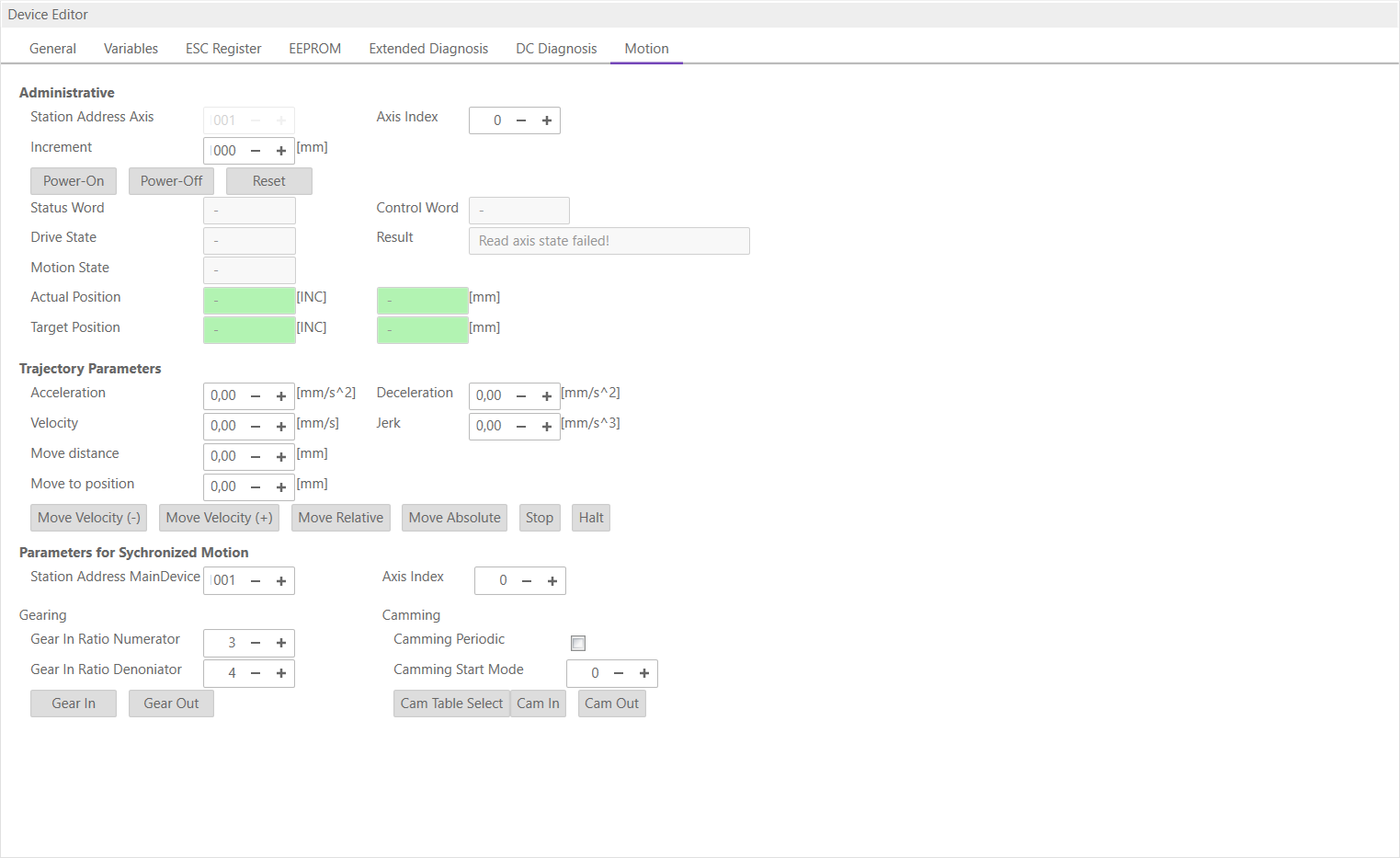
6.3.12. Simulator (Simulator Tabs only)
- In this tab, the user can see and change the simulator settings of the SubDevice. He can manipulate the SubDevice e.g. power, disconnect and produce errors:
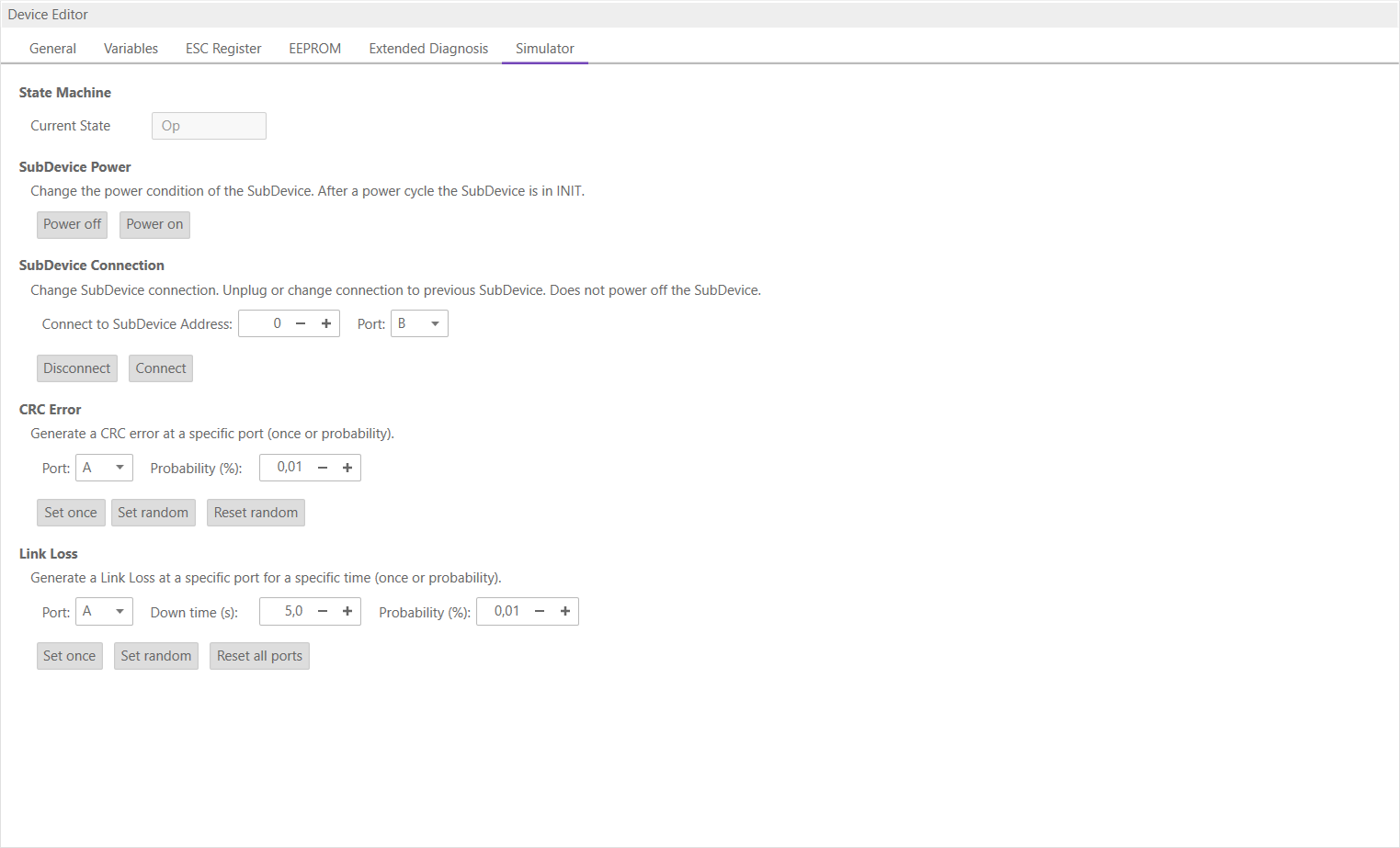
- State Machine
Shows the current state of the SubDevice
- SubDevice Power
- Power off:
Turn the SubDevice power off
- Power on:
Turn the SubDevice on to Init state
- SubDevice Connection
- Disconnect:
Disconnect the SubDevice. SubDevice will not be turned off
- Connect:
Connect SubDevice to selected address and port. Default is the port where the SubDevice was connected before
- CRC Error
- Set once:
Create one CRC error at the selected port
- Set random:
Generate CRC errors at the selected port with the selected probability until reset is executed
- Reset random:
Reset the CRC generation
- Link Loss
- Set once:
Create one Link Loss at the selected port for the selected time
- Set random:
Generate Link Losses at the selected port with the selected probability for the selected time until reset is executed
- Reset random:
Reset the Link Loss on all ports