4. Graphical user interface
4.1. Overview
This section gives an overview about the graphical user interface:
- The graphical user interface is divided into five parts:
- Menu/Tool/Status bar:
Shows current status or mode of the EC-Engineer and allows the user to change it.
- Project Explorer:
Shows different views of the current network configuration
- Device Editor:
Show information about the selected device, like process variables.
- Short Info:
Show short information about selected device, like name, description or vendor.
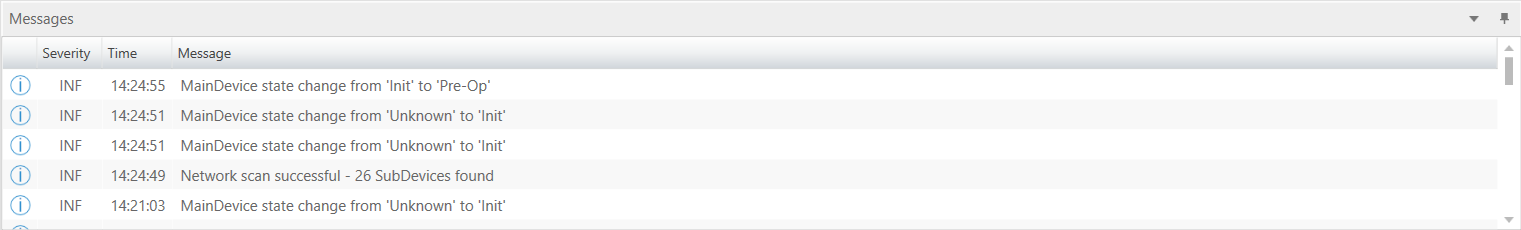
- Messages:
Shows notifications which occur e.g. when the EtherCAT Device has changed its operation state or a SubDevice has been removed from (or added to) the EtherCAT network.
4.3. Project Explorer
4.3.1. Drag and Drop
It is possible to drag and drop files here to import/open them
- Project file
Opens the configuration stored in the
ECC/ECI, only one project file can be imported at a time.- ESI files
Adds the files to the ESI-Manager, it only allows
ESI,SCIandZIPfiles, multiple files are allowed.
- The context menu of one or more selected SubDevices has the following entries:
- Append SubDevices:
Appends a new SubDevices
- Remove SubDevices:
Deletes the selected SubDevices
- Cut/Copy/Paste:
Extended clipboard operations, which should help the user to move or multiply existing SubDevice definitions.
- Enable SubDevices:
Appends disabled SubDevices to the process image at the previous position. If this is not possible, the SubDevice will be marked as “not connected” and the user can append the SubDevice by using “cut” & “paste”.
- Disable SubDevices:
Removes the SubDevices from process image and from the exported
ENIfile, but keeps the SubDevice as “disabled” in the project.- Reload ESI data:
Reloads
ESIdata which are stored in the project file from globalESIcache (after adding a SubDevice to the project theESIdata will be stored in the project file).- Export SCI:
Exports a
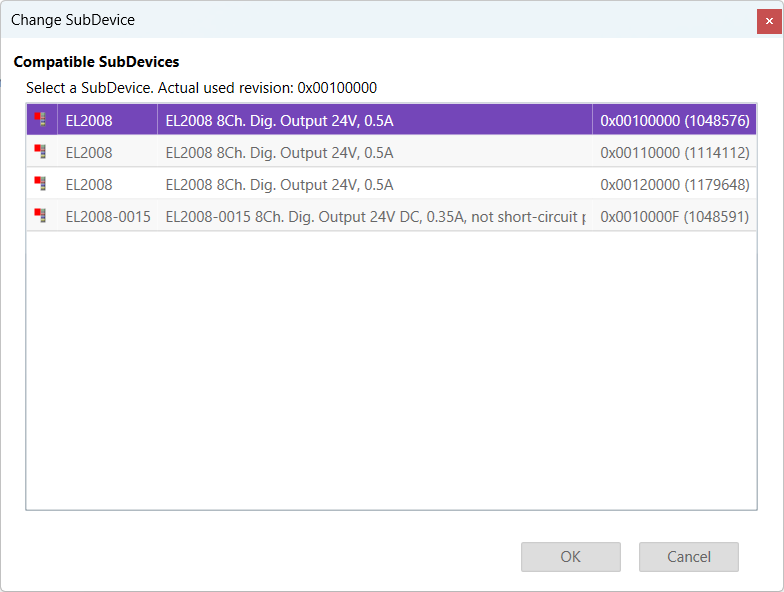
SCIfile. A SCI file is like an ESI file but preconfigured. So it is possible to create a fixed SubDevice which can be added to the configuration and is working out of the box.- Change SubDevice:
Opens the following dialog, where the user can select a compatible SubDevice (this is helpful, if the user wants to update the SubDevice to a new revision and keeps his configuration). This is also used to change from an ESI to a SCI file.
- Import Beckhoff SubDevice Description, to import SubDevice settings from TwinCAT (or ET9000)
- Import SubDevice settings from “Beckhoff SubDevice Description” files
Open project in TwinCAT
Select SubDevice to export
Main menu “TwinCAT”
Selected Item
Export
XMLDescriptionImport the exported file (imported will be MDP configuration, PDOs, DC settings, …)
- Import init commands of SubDevice from “Beckhoff Init Command Description” files
Open project in TwinCAT
Select SubDevice to export
Open tab “Startup”
Context menu: “Export to
XML”Import the exported file (imported will be the exported init commands)
- If user tries to append SubDevice he will see the following dialog:
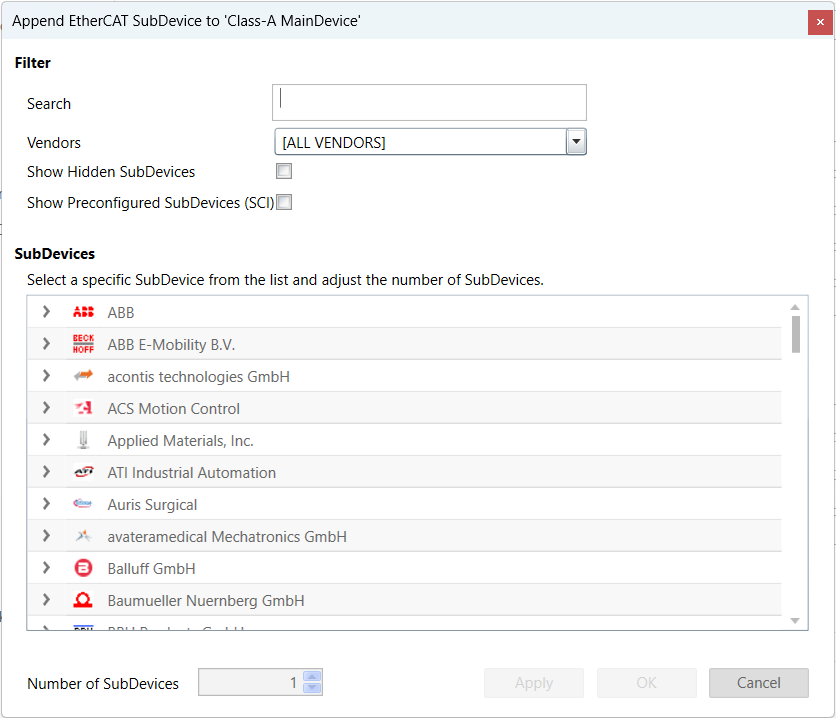
- Filter
Search: Keyword to filter the SubDevices by type name. Vendors: List of all available vendors. User can filter all SubDevices by selecting the desired vendor from the list. If it makes sense, the recommended vendor is already preselected, e.g. if you try to append a SubDevice to an E-Bus. Show Hidden SubDevices: Shows also hidden SubDevices (e.g. with older revisions, if newer SubDevices are available) Show Preconfiguren SubDevices: Shows also SubDevices from SCI files
- List of available SubDevices
User can select the SubDevice which should be added, be expanding the three levels: vendors, groups and the SubDevices themselves. The 3rd level consists of three parts: Type name, description and the revision number.
- Number of SubDevices
User can change this value to add more than one SubDevice of the same type.
- Apply
Add SubDevices of the same and different type, the dialog will automatically reopen after appending the previous SubDevice. The number of SubDevices must be set at “1” to use this function.
- Ok
Add SubDevices of the same type, based of the “Number of SubDevices” selected.
4.3.2. Configuration Mode
There are three topology visualisation views:
- Classic View
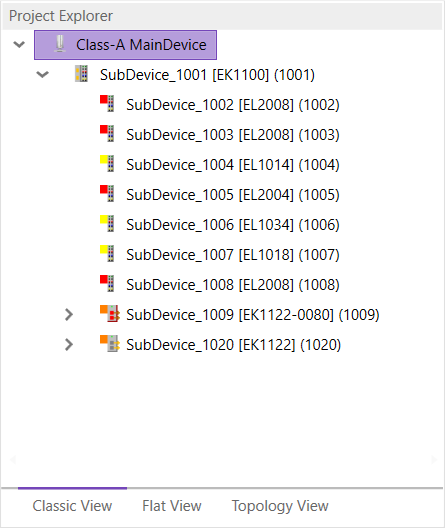
This is a tree view with multiple levels.
- Flat View
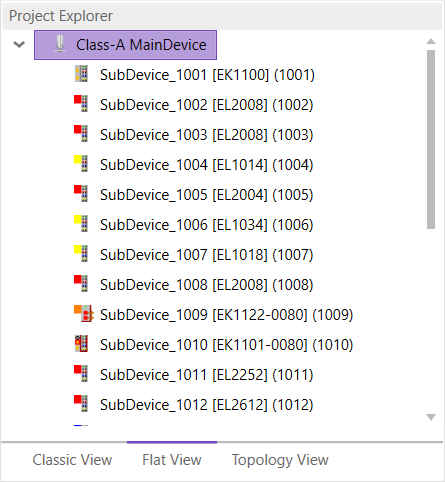
This view shows all SubDevices in a flat list, as they are connected in the EtherCAT network.
- Topology View
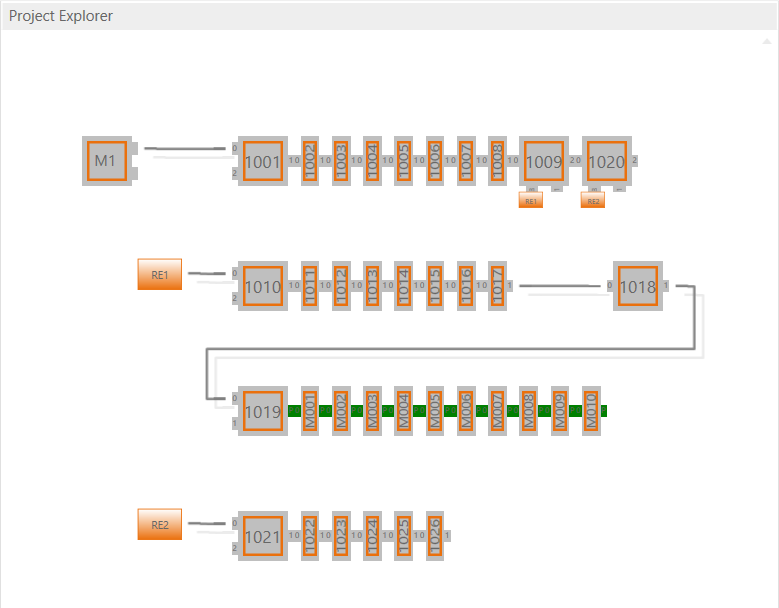
This view shows a graphical tree of all SubDevices, as they are connected in the EtherCAT network.
4.3.3. Diagnosis Mode
There are three topology visualisation views:
- Classic View
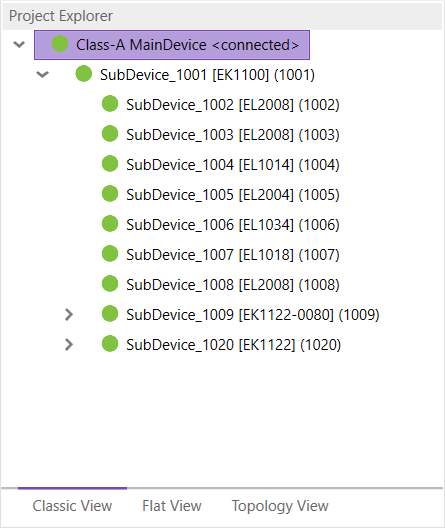
This is a tree view with multiple levels.
- Possible device states:
 Init Bootstrap
Init Bootstrap Pre-Op
Pre-Op Safe-Op
Safe-Op Op
Op
- Flat View
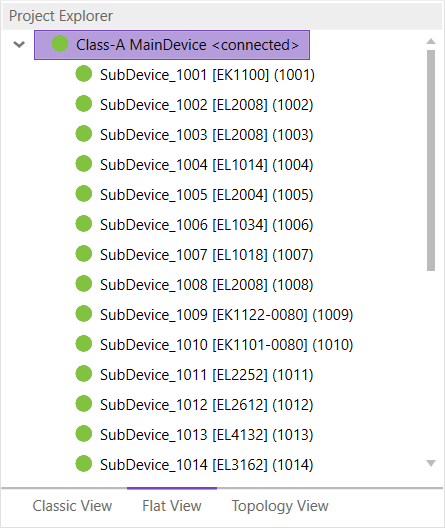
This view shows all SubDevices in a flat list, as they are connected in the EtherCAT network.
- Possible device states:
 Init Bootstrap
Init Bootstrap Pre-Op
Pre-Op Safe-Op
Safe-Op Op
Op
- Topology View
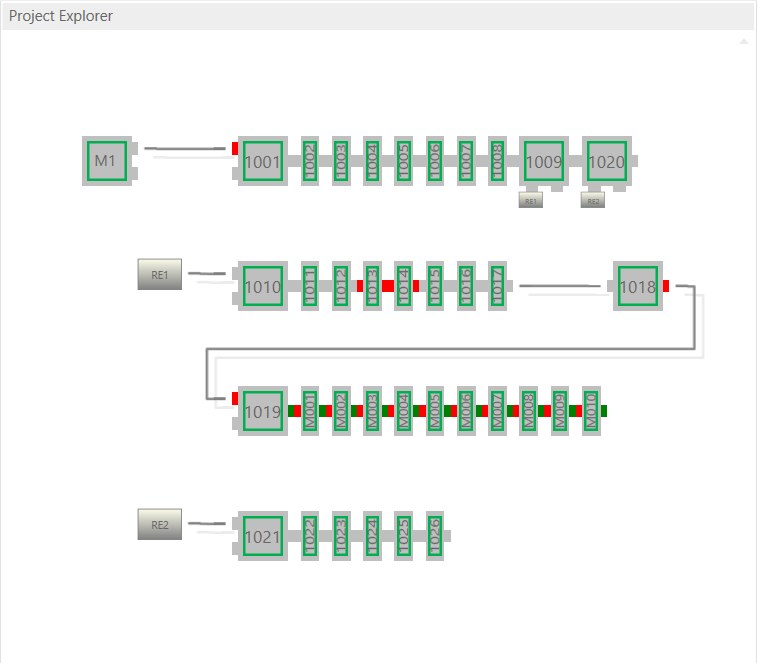
This view shows a graphical tree of all SubDevices, as they are connected in the EtherCAT network.
- Possible device states:
 Init Bootstrap
Init Bootstrap Pre-Op
Pre-Op Safe-Op
Safe-Op Op
Op- Possible port states:
 Bad Cable Quality
Bad Cable Quality Constricted Cable Quality
Constricted Cable Quality Good Cable Quality
Good Cable Quality
If cable quality is constricted or bad, please check the error counters of the SubDevice (for more information about the extended diagnosis, see Extended Diagnosis).
- The context menu of the MainDevice has the following entries:
- Network Mismatch Analyzer:
Compares the configured SubDevices with the connected SubDevices.
- Write all Station Aliases:
Write the current physical address of each SubDevice to the configured station alias in EEPROM.
- Acknowledge all warnings:
Clears the yellow warning icon of all SubDevices.
- Clear Error Counters:
Clears the error counters of all connected SubDevices.
- Hardware Diagnostics:
Enables or disables the additional hardware diagnosistics and warnings.
- Take Snapshot:
Takes a snapshot from the current diagnosis state and saves it into a capture file (for more information about the snapshots and capture files, see Capture File).
- Automatic Snapshot Mode:
Activates the automatic snapshot mode to take snapshots based on the configured rules.
- Enable Performance Monitoring:
Activates the Performance Monitoring.
4.4. Device Editor
- This Editor gives the user the possibility to read and write information of the selected device or SubDevice:
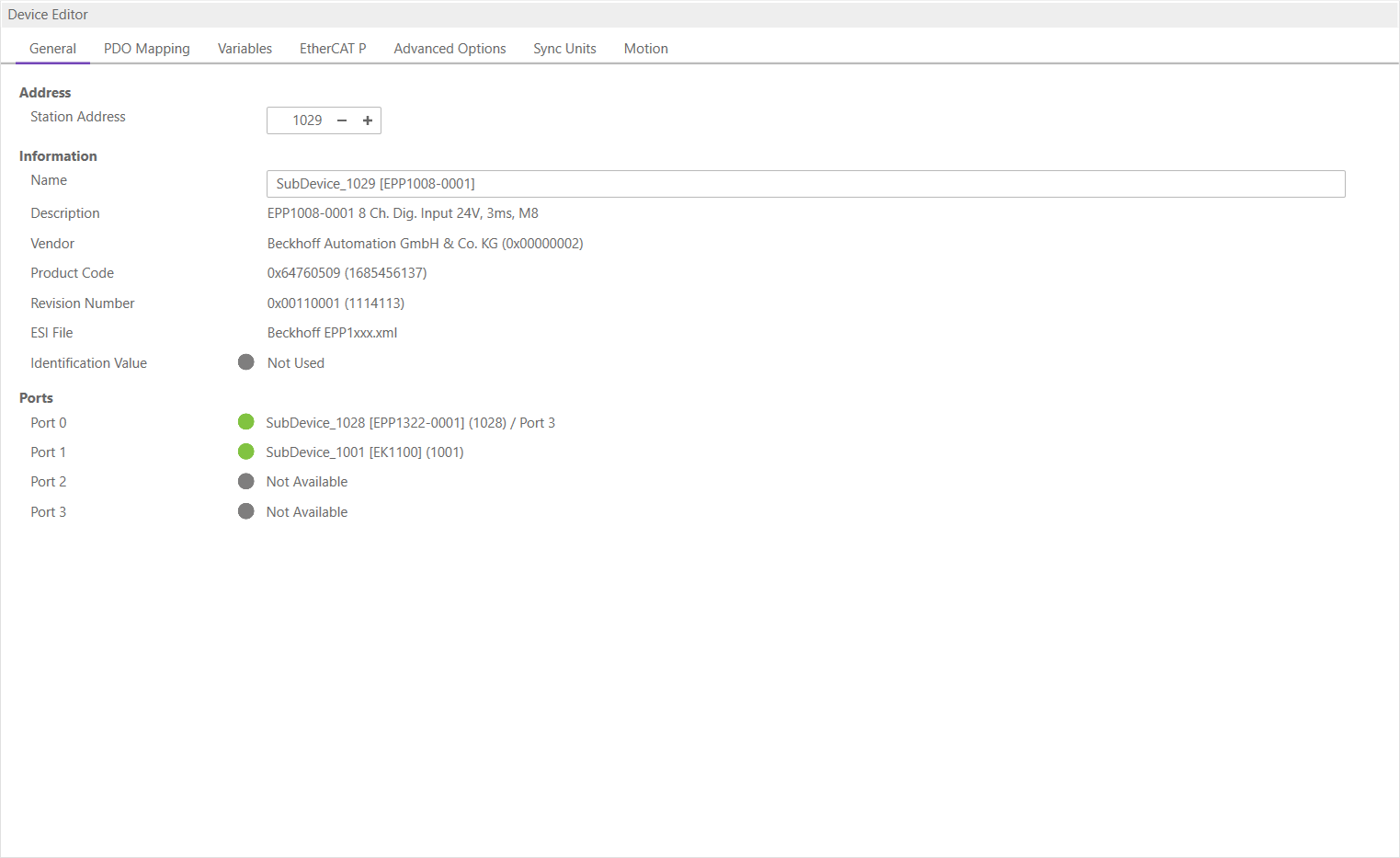
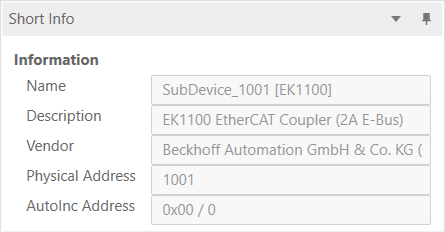
4.5. Short Info
- This window shows short information about selected device, like name, description or vendor:
4.6. Message Window
- Shows notifications which occur e.g. when the EtherCAT MainDevice has changed its operation state or a SubDevice has been removed from (or added to) the EtherCAT network: