1. Introduction
This guide describes how to set up a Ubuntu guest in the acontis Hypervisor. It is assumed, the steps listed in the Hypervisor Quick Start Guide have been successfully executed.
The last chapter describes how to set up an additional Ubuntu guest, if 2 (or more) Ubuntu guests are to be used.
2. Copy Ubuntu ISO installation media to Hypervisor Host
In a first step, we need to copy the Ubuntu installation media (ISO file) from a Windows (or Linux) system into the Hypervisor Host filesystem.
2.1. Using Filezilla (recommended)
Open a shell (right click on desktop and select ‘Open Terminal here’ or press CRTL + ALT + T) on the Hypervisor Host.
Determine the IP address of the system (with
ifconfigcommand and throughinetentry):rte@RTV-TP104:~$ ifconfig enp2s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 172.17.10.5 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.17.255.255 inet6 fe80::ccbb:85f1:38d3:fa2a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 90:1b:0e:18:c9:83 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 4618420 bytes 4033770375 (4.0 GB) RX errors 0 dropped 8865 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 1460482 bytes 96608727 (96.6 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback) RX packets 6864 bytes 427092 (427.0 KB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 6864 bytes 427092 (427.0 KB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 vnet0: flags=99<UP,BROADCAST,NOTRAILERS,RUNNING> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.157.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.157.255 ether 00:60:c8:00:00:00 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 765775 bytes 74216258 (74.2 MB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 767935 bytes 74780268 (74.7 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
In this example the IP address is 172.17.10.5.
Hint
The device name enp2s0 differs on different PC/IPC’s!
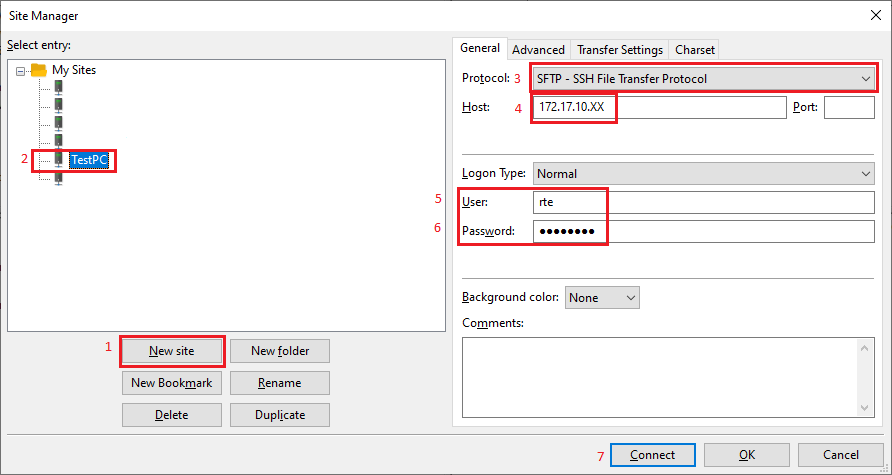
Open Filezilla (get current version from https://filezilla-project.org/) and create new connection entry:
Push New site button
Give a qualified name
Select SFTP - SSH File Transfer Protocol
Give Hypervisor Host IP/name. In screenshot above the last byte is
X-ed out. Replace it with the ‘detected’ IP address.Enter User name (same as at Hypervisor install)
Enter password (same as at Hypervisor install)
Push Connect button
Select the installation media file (the
.isoimage) in the Local tab on the left and upload it to/hv/guests/examples/ubuntuinto the Server tab on the right.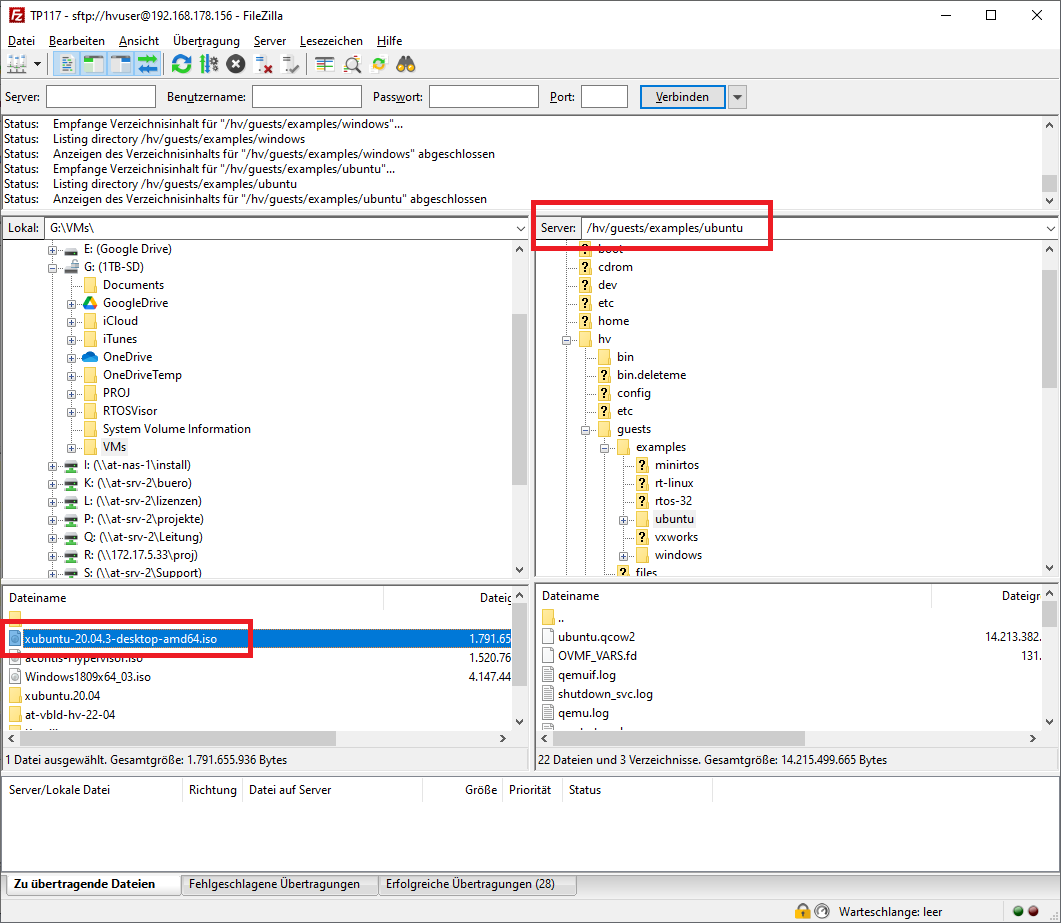
3. Guest Configuration
Prior to installing the guest, we need to configure the respective virtual machine (e.g. number of CPU cores, network settings etc.).
The configuration files guest_config.sh and usr_guest_config.sh are located in the guest folder.
The meaning of each configuration setting is explained in detail in those files.
You need to edit these files and adjust them according to your needs and environment.
Caution
If the guest is controlled by the System Manager tool, you must not change the guest_config.sh file (the content may be overwritten by the System Manager),
instead uncomment the respective settings in usr_guest_config.sh.
Example guests located in /hv/guests/examples are not controlled by the System Manager.
The number of CPU cores must not exceed the number of physical cores available in the system and not assigned to Real-time guests. For example, if on a quad core CPU, you need 2 cores for Real-time guests, the number of cores for the Windows guest must not exceed 2. The default parameters should fit for most cases.
gedit /hv/guests/examples/ubuntu/guest_config.sh (and/or usr_guest_config.sh)
# Adapt following lines to your system and needs:
vmname=...
vmid=...
windows_guest=...
cdrom_iso=...
num_cpus=...
ramsize=...
You have to set the cdrom_iso parameter to the appropriate folder where the installation media ISO file had been copied before.
By default, the network connection is set up automatically (using DHCP). Please check the Hypervisor Manual for other settings.
Caution
Automatic network setting will only work, if the Ethernet cable is connected!
Caution
Please do not configure more CPUs than physically available (CPUs used for the Real-time OS are not available for the Windows guest).
Example: The maximum number of of CPUs on a quad-core CPU where 1 CPU is used for the Real-time OS is 3.
Caution
Please do not configure more RAM than available. The VM may unexpectedly crash if too much RAM is configured. You can determine the available RAM as follows:
cat /proc/meminfo | grep MemAvailable
4. Guest installation
After VM configuration you need to start the guest for the first time. The guest console will be shown then (the guest output or desktop).
cd /hv/guests/examples/ubuntu
hv_guest_start -view
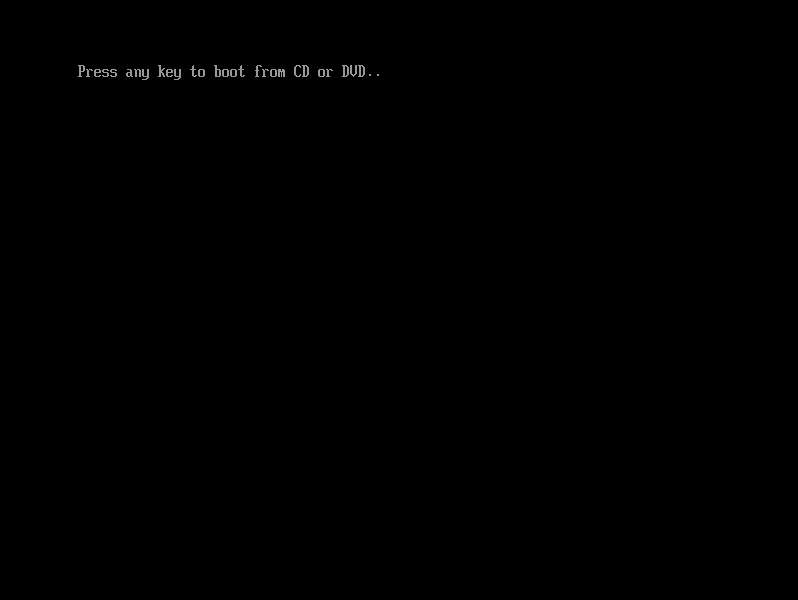
The installation media iso file will be detected by the virtual bios, you need to press a key to boot from it:
Hint
In case no key was pressed in time or the installation media was not found, the EFI shell will be started.
Option a) You can leave into BIOS by entering
exit. If you also leave BIOS the boot begins again and you can press a key to boot from CD.- Option b) You can manually start the CD’s bootloader by entering
$ FS0:$ \EFI\BOOT\BOOTX64.EFI
5. Ubuntu Installation
Follow the steps as usual for Ubuntu. In this guide the default cases are used where applicable.
GRUB selection menu
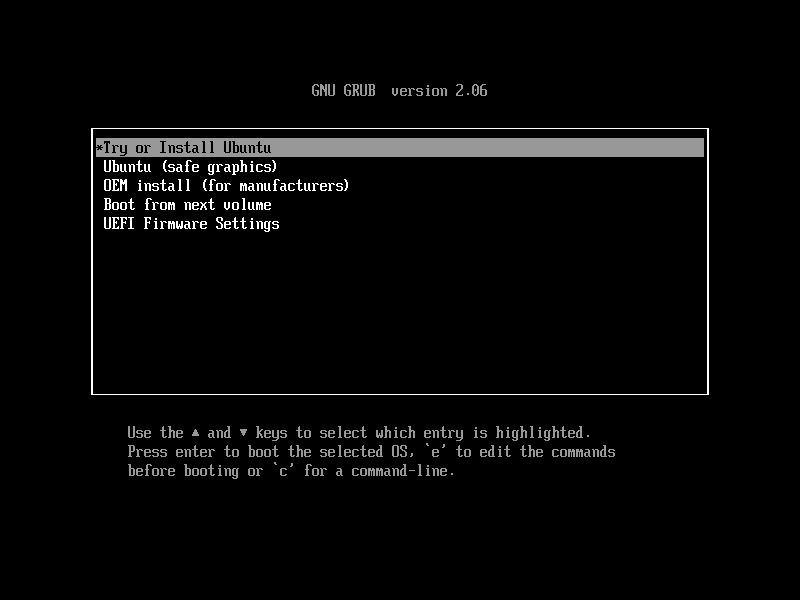
Fig. 5.1 Select
Try or Install Ubuntuat GRUB selection menu.Select Install Ubuntu
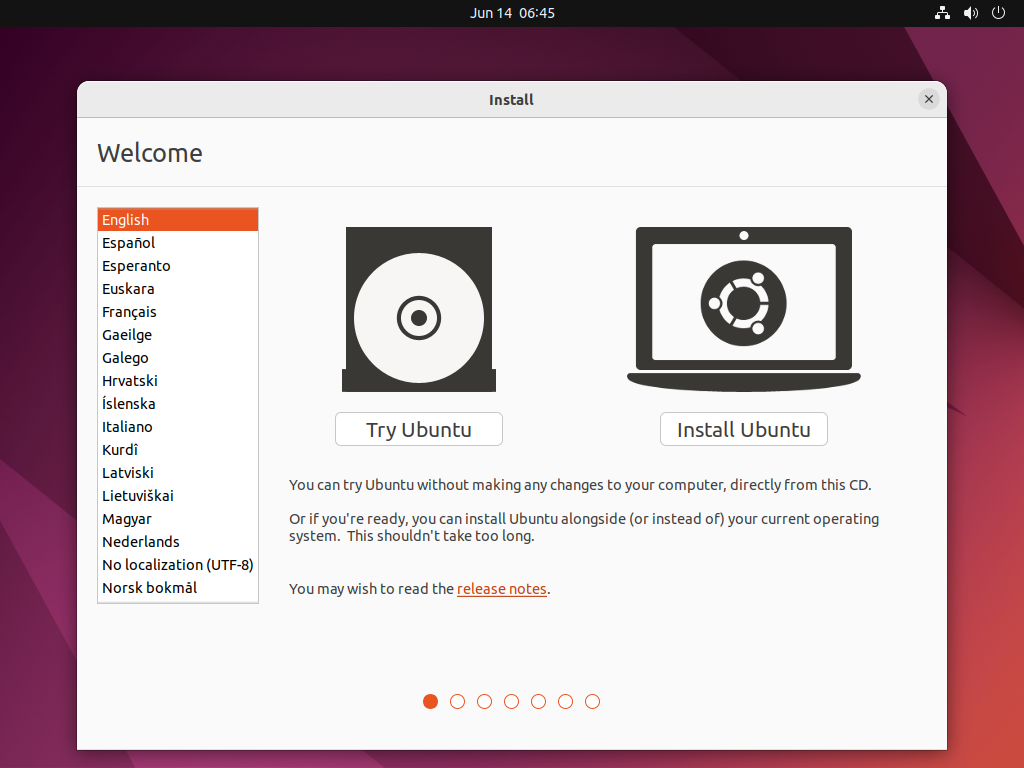
Select your Keyboard layout –> Continue
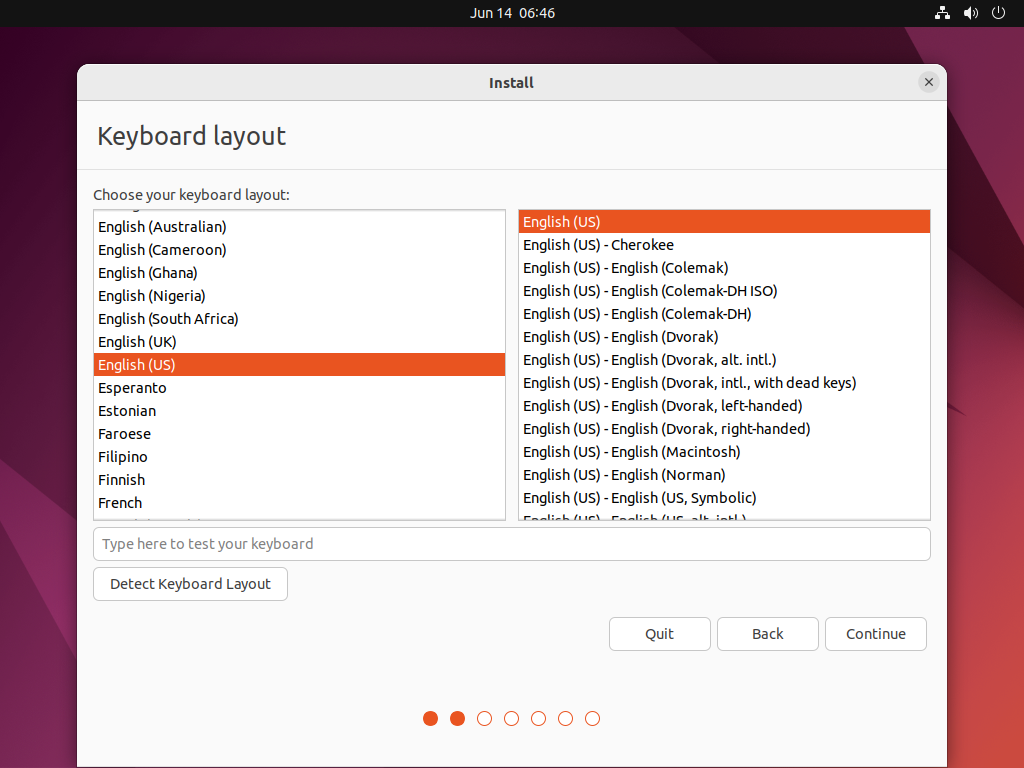
Updates and other software (default state) –> Continue
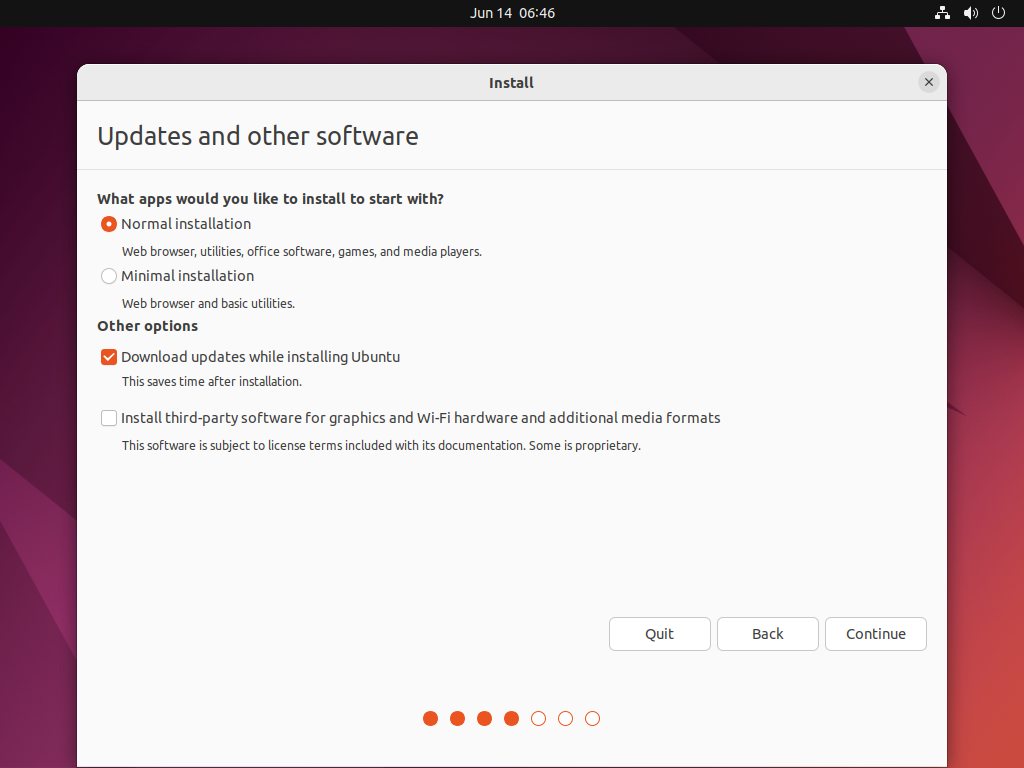
Installation type –>
Erase disk and install Ubuntu–> InstallNow
Fig. 5.5 Select
Erase disk and install Ubuntuat installation type page.Confirm
Write the changes to disks?dialog –> Continue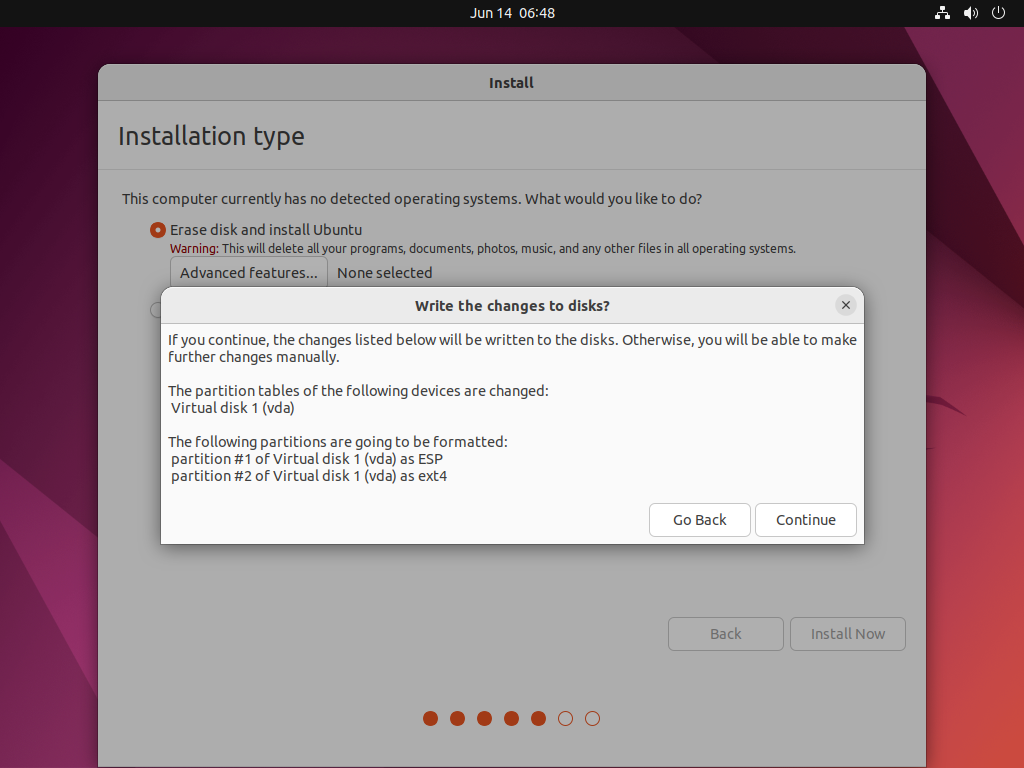
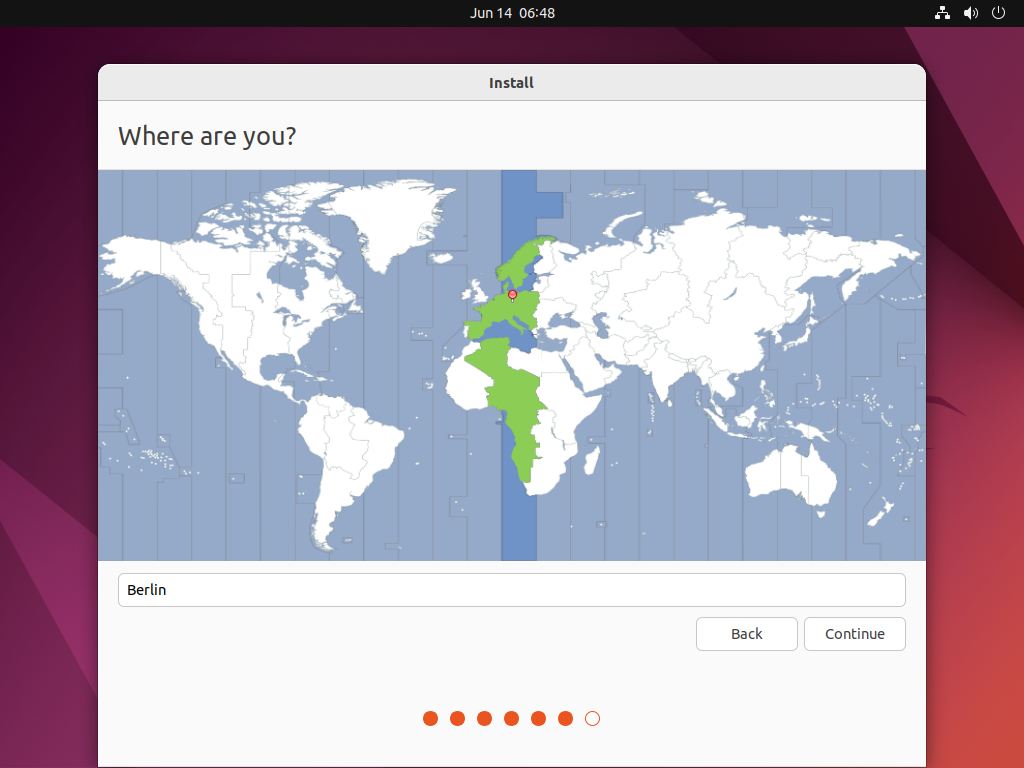
Where are you –> Continue
Create credentials –> Continue
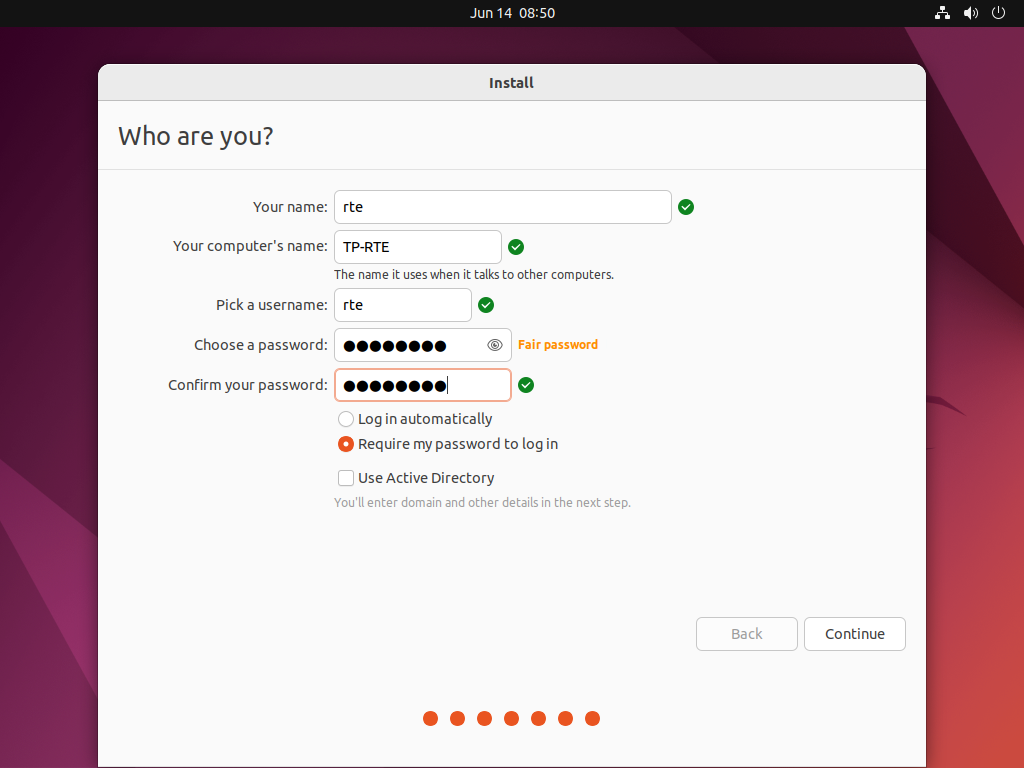
Hint
In this guide the default user used is rte. It’s recommended to supply a password.
Restart –> RestartNow
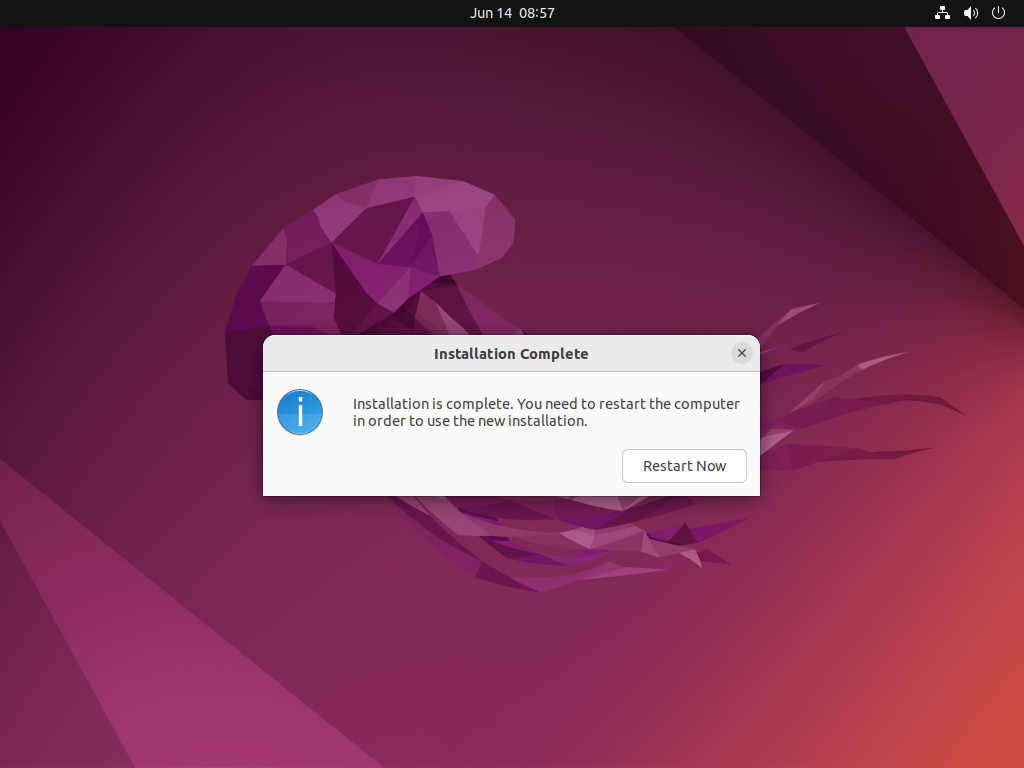
Press enter –> ENTER

Login (in this example with user rte and the supplied password)

OPTIONAL Update guest –> InstallNow

6. Running Ubuntu guest
After successfully installing Ubuntu, you need to shutdown Ubuntu.
Shutdown Ubuntu
Important
You need to shutdown the guest (do NOT reboot Ubuntu!).
If this not possible inside the guest, please run hv_guest_stop in the guest folder (/hv/guests/examples/ubuntu).
Adjust the file
usr_guest_config.sh(to avoid booting the installation media again)gedit /hv/guests/examples/ubuntu/usr_guest_config.shcomment "cdrom_iso" with #
Start the Ubuntu guest
hv_guest_start -view
Hint
Due to hardware changes, Ubuntu may automatically reboot once. Mouse and desktop may still not work properly. In this case, please install all of the latest Ubuntu updates.
7. RTOS Communication Support
7.1. Installation
To communicate with an RTOS via the Hypervisor we need to run install_attach.sh which will install the required drivers and packages.
The installation is provided in a mountable directory. To access this directory we need to install the network client software (cifs-utils) and mount the SMB drive from QEMU where the installation is located.
Open a console prompt in the Ubuntu guest and enter the following:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install cifs-utils sudo mkdir /mnt/qemu sudo mount -t cifs //10.0.2.4/qemu /mnt/qemu -o guest sudo /mnt/qemu/files/LinuxTools/install_attach.sh

With the installation process, the directory /hv is created. This is where all the essential binaries and files, required for the hypervisor in the Ubuntu guest environment, are stored.
Hint
If you encounter problems like hvconnectpackage depends on <package-name> when running the command install_attach.sh, you may have to install missing packages.
Read the messages to see which package is missing. Then install the missing package. Before you can call install_attach.sh skript again you must first remove the aborted installation.
Step 1: Run Ubuntu console
Step 2: Input the command in the window:
sudo dpkg -r hvconnectpackageand press Enter.Step 3: Input the command in the window:
sudo apt install <fill in missing packages here>and press Enter.Step 4: Input the command in the window:
sudo /mnt/qemu/files/LinuxTools/install_attach.shand press Enter.
7.2. Load the driver at startup
For enabling communication between the Hypervisor Host and other RTOS systems on the hypervisor the driver /hv/bin/rtosdrv.ko needs to be loaded. To accomplish this you can start the service manually with /hv/bin/load_rtosdrv.sh or link the service /hv/services/hv_loadrtosdrv.service to the autostart function and enable it.
Open console prompt in Ubuntu guest and enter the following:
sudo ln -s /hv/services/hv_loadrtosdrv.service /etc/systemd/system/hv_loadrtosdrv.service sudo systemctl start hv_loadrtosdrv.service sudo systemctl enable hv_loadrtosdrv.service
Upon system startup, this service triggers the execution of the script /hv/bin/load_rtosdrv.sh. The purpose of this script is to verify the compatibility of the driver, recompile it if necessary, and then initiate it. This process guarantees the ability to load the driver even in the event of an operating system update.
7.4. Verify installation
To verify whether the installation was successful, you can invoke the driver with the command hv_attach -osid <OSID>. The needed OSID was set with export rtosOsId=<OSID> in guest_config.sh when installing the Ubuntu guest. If hv_attach responds with ‘Finished successfully’, it indicates that the driver was correctly loaded and a connection was successfully established.
In this case, you can also check if a virtual network has been set up using ip address. Here you should see a vnet address.

8. Ubuntu and Real-time guest in parallel
Caution
The hv.config configuration file is a link to the RT-Linux example guest configuration file. See also chapter Example guest folders in the Hypervisor Manual for more information.
In this step, we will run Ubuntu and Real-Time Linux in parallel.
Shutdown Ubuntu, do NOT reboot!
Run the
Real-Time Linuxguestcd /hv/guests/examples/rt-linux hv_guest_start -view
Open a second shell (right click on desktop and select ‘Open Terminal here’ or press CRTL + ALT + T)
Start the Ubuntu guest
cd /hv/guests/examples/ubuntu hv_guest_start -view
- After logging in into Ubuntu, execute “Hypervisor Attach” (Desktop icon)
or open a shell and call
hv_attach -osid OSIDThe needed OSID was set with
export rtosOsId=<OSID>inguest_config.shwhen installing the Ubuntu guest.
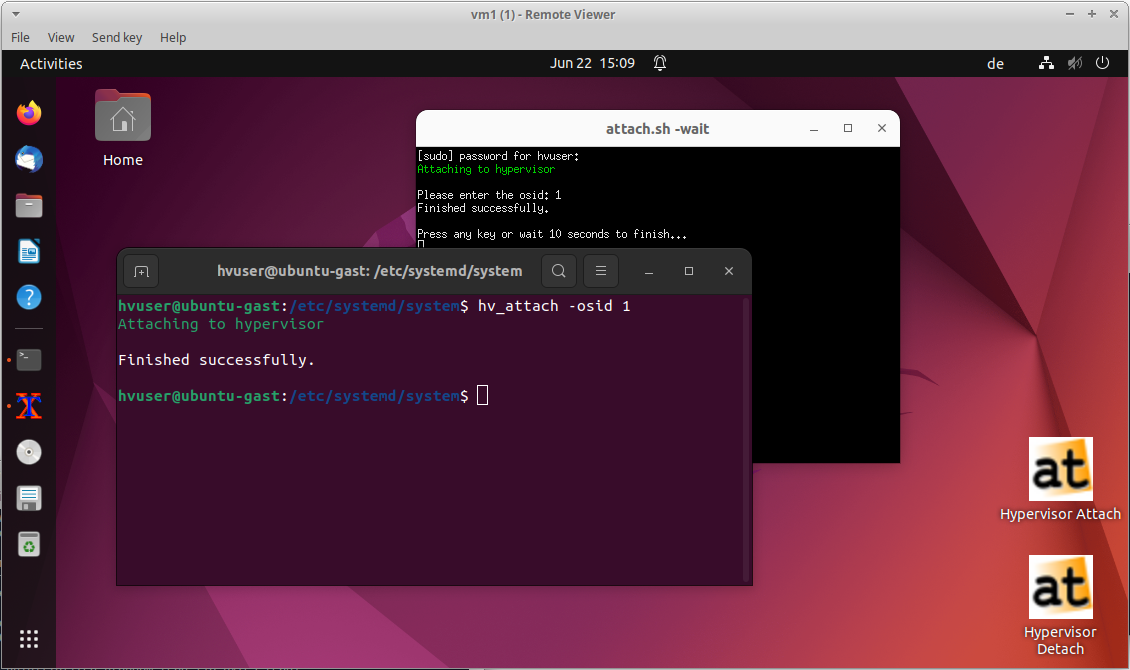
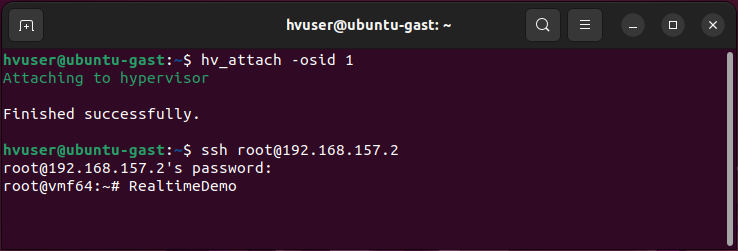
To open the RT-Linux shell in Ubuntu guest: execute
ssh root@192.168.157.2in Ubuntu shell
Hint
With hv_attach, the driver establishes a virtual TCP/IP connection to the Hypervisor Host and the initiated RTOS systems on the hypervisor using the built-in rtosvnet driver.
The IP Address is configured in guest.config:
[Rtos2\\Vnet\\0]
"IpAddress"="192.168.157.3"
"MacAddress"="AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:03"
Log into
Real-Time Linuxand run the Real-time demo:vmf64 login: root password: root RealtimeDemo