8. Additional Tools
8.1. ESI-Manager
- This dialog helps the user to administrate his
ESIandSCIfiles. Here, he can add/delete/exportESIandSCIfiles. 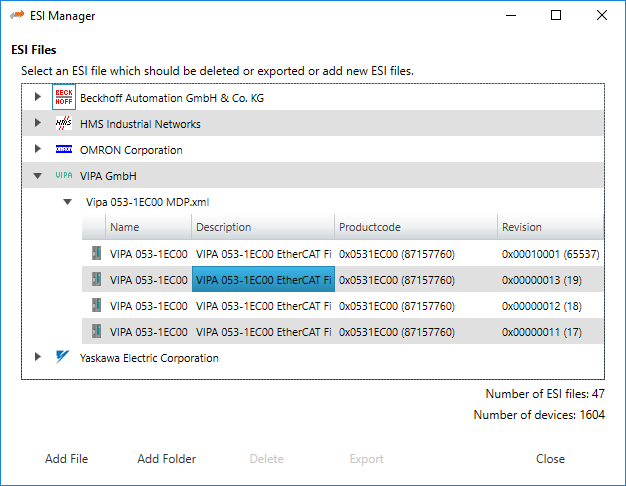
8.2. EMI-Manager
- This dialog helps the user to administrate his EtherCAT Master Information (
EMI) files. 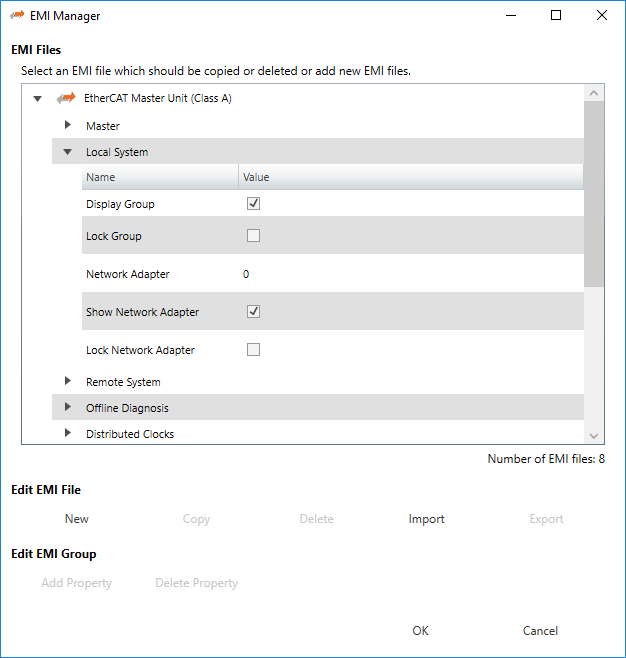
EMI files, are files which are specify the master features. Means that options and dialogs can be restricted to those features which are supported by the control system, e.g. available cycle times, support of scan for MDP modules or DC synchronization.
8.2.1. Administration
This dialog helps the user to administrate his EtherCAT Master Information (EMI) files.
- By default EC-Engineer has two files included (read-only):
EtherCATMaster_ClassA.emi:EMItemplate which is prepared for configuring a “Class A” masterEtherCATMaster_ClassB.emi:EMItemplate which is prepared for configuring a “Class B” master
If the user wants to customize EC-Engineer, he can create a new EMI file with defaults, copy an existing EMI template or import an EMI file.
If he wants to add new properties to a group, he can add this only to the group “Parameters”. This group is by default empty, but if user has added some properties, he will see the list of properties on tab “Advanced Options (Expert)” of the master, where the values can be modified.
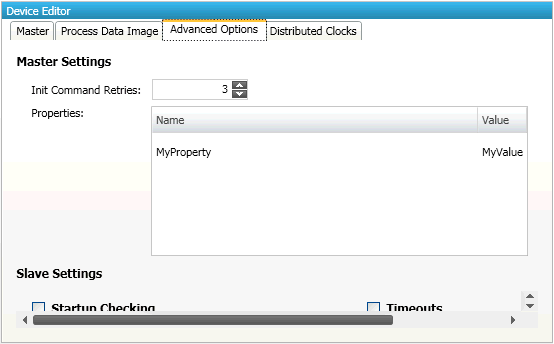
8.2.2. Supported Entries
The following EMI entries are supported:
- Master Group
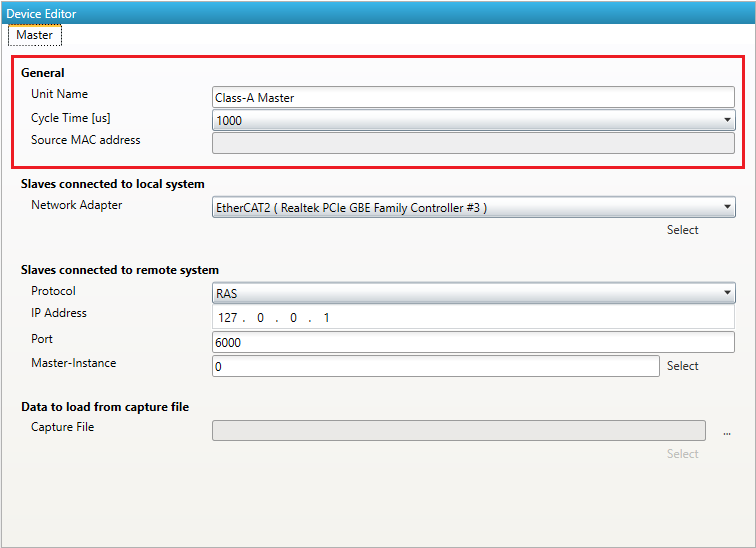
- Display Group:
Shows or hides group
- Lock Group:
Locks or unlocks group
- Name of Master-Unit:
Default Master-Unit name
- Show name of Master-Unit:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the name of the Master-Unit
- Lock name of Master-Unit:
Enable if user should not be able to change the name of the Master-Unit
- Cycle Time:
Default Cycle Time
- Show Cycle Time:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the Cycle Time
- Lock Cycle Time:
Enable if user should not be able to change the Cycle Time
- List values of Cycle Time:
Enter possible values of Cycle Time
- Frequency:
Default Frequency
- Show Frequency:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the Frequency
- Lock Frequency:
Enable if user should not be able to change the Frequency
- List values of Frequency:
Enter possible values of Frequency
- Cycle Time Mode:
Enter Cycle Time Mode (0 = Cycle Time, 1 = Frequency)
- Init Command Retries:
Init Command Retries
- Maximal Slave Count:
Enter maximal count of slaves which are allowed to configure (0 = use default limit of master)
- Slave Start Address:
Enter default start address for all slaves
- Scan for MDP slaves:
Enable for activating MDP-Scan if it is supported from slave
- PDO Upload:
Enable for activating PDO upload during scan if it is supported from slave
- Byte-Align Process Data Image:
Enable if process data image should be byte aligned and not as small as possible
- Edit Complete Variable Name:
Enable if user should be able to edit the complete variable name
- Process Image Layout:
Enter process image layout features (0 = default, 0x1 = with protocol data, 0x2 = with VLAN tag, 0x4 = without frame alignment, 0x8 = alphabetic port order, 0x10 = Compatibility to
ENIspec V1.0.0, 0x20 = Moves AL Status command to the end), 0x40 = Disable command splitting- Output Port Physics:
Enter output port physics of the master (Z = Ethernet, K = EBus)
- Output Port Vendor Id:
Enter output port vendor id of the master (0 = All Vendors, 1..n = Specific Vendor)
- Word-Aligned EtherCAT Datagrams:
Enable if EtherCAT datagrams should be word aligned
- Cyclic Frame Layout:
Enter cyclic frame layout mode (0 = default, 1 = single logical command per frame)
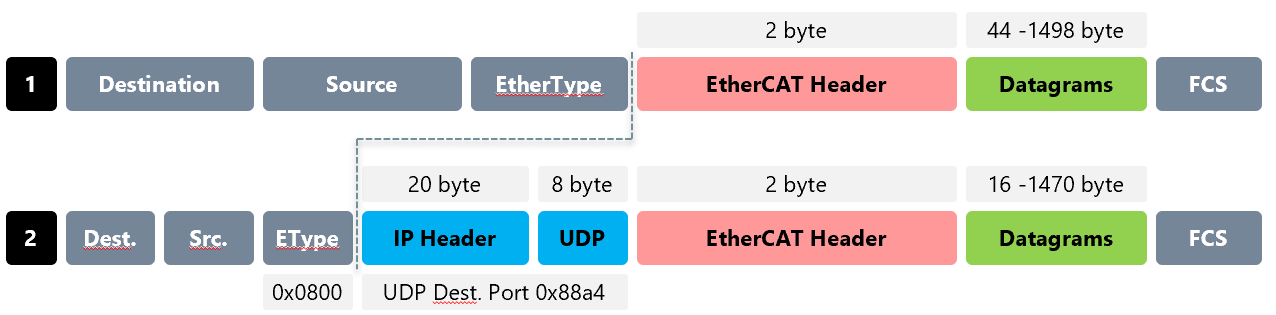
- Ethernet Type UDP:
- Support for Safety Slaves:
Enable if master supports safety slaves
- Remove DC NOP Command:
Does not include NOP Command in
ENI
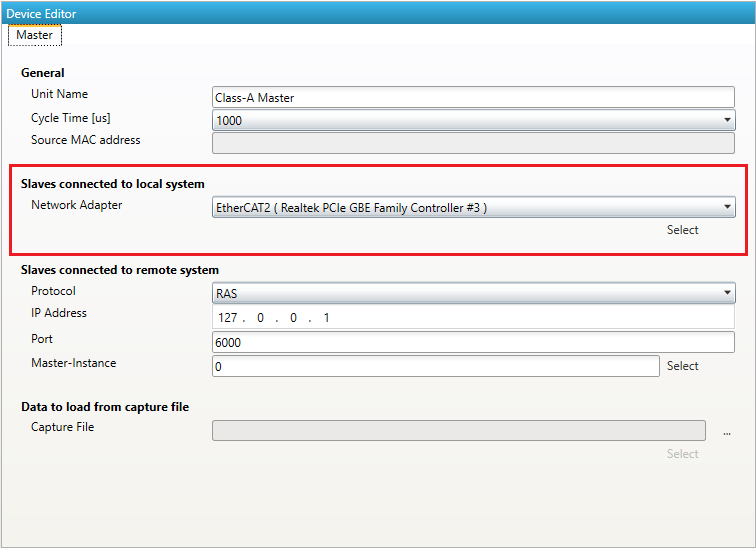
- Local System
Display Group: Shows or hides group
- Lock Group:
Locks or unlocks group
- Network Adapter:
Enter index of Network Adapter in the Network Adapter List
- Show Network Adapter:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the Network Adapter
- Lock Network Adapter:
Enable if user should not be able to change the Network Adapter
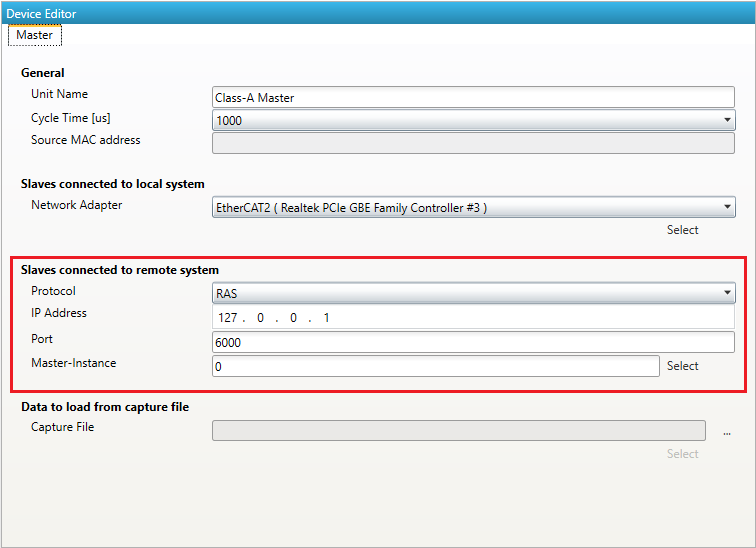
- Remote System
- Display Group:
Shows or hides group
- Lock Group:
Locks or unlocks group
- Protocol:
Select protocol for Remote System
- Show Protocol:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the protocol
- Lock Protocol:
Enable if user should be not able to change the protocol
- IP Address:
Enter IP Address for Remote System
- Show IP Address:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the IP Address
- Lock IP Address:
Enable if user should be not able to change the IP Address
- Port:
Enter Port for Remote System
- Show Port:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the Port”
- Lock Port:
Enable if user should be not able to change the Port
- Master-Instance:
Enter Master-Instance number
- Show Master-Instance:
Enable if user should be able to view and change the Master-Instance
- Lock Master-Instance:
Enable if user should be not able to change the Master-Instance
- Offline Diagnosis
- Display Group:
Shows or hides group
- Lock Group:
Locks or unlocks group
- Simulator Functions
- Display Group:
Shows or hides group
- Lock Group:
Locks or unlocks group
- Distributed Clocks
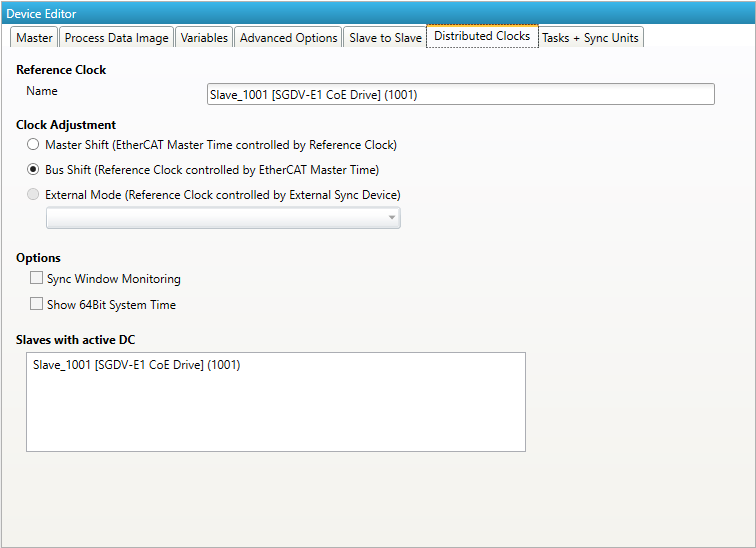
- Display Group:
Shows or hides group
- Clock Adjustment:
Enter clock adjustment value (0 = default, 1 = Master Shift, 2 = Bus Shift
- Lock Clock Adjustment:
Enable if user should not be able to change clock adjustment
- Continuous Propagation Compensation:
Enter default value of Continuous Propagation Compensation
- Show Continuous Propagation Compensation:
Enable if user should be able to change value of Continuous Propagation Compensation
- Sync Window Monitoring:
Enter default value of Sync Window Monitoring
- Show External Mode:
Enable if user should be able to use an external sync device as reference clock
- System Time 64 Bit:
Enter default value of System Time 64 Bit
- Features
- AoE:
Enable if master supports AoE
- EoE:
Enable if master supports EoE
- FoE:
Enable if master supports FoE
- SoE:
Enable if master supports SoE
- VoE:
Enable if master supports VoE
- Export Variables:
Enable if user should be able to export variables
- Show Enable Column:
Shows column for enable variables on
XMLexport- Export Slave Name with Type:
Enable if type of slave should be added to slave names on generating
ENIfile- Lock Variables:
Locks or unlocks variables for editing in diagnosis mode
- Show Variable Chart:
Enable if user should be able to view the chart of a variable
- Show Variable Comments:
Enable if user should be able to view and edit the comments of a variable
- Allow E-Bus as HC Head:
Enable if Ebus shall be allowed as HC Head
ENIDeployment:yes: something is done with
ENIafter export, no: nothing done ask: you will be ask to deploy- Deployment Mode:
0: copy to path, 1: execute batch at path
- Deployment Path:
Path to copy
ENIor to batch for execution
- Scripts
- Display Group:
Shows or hides the Scripts Tab
- P1:
- Scan Start Script 1:
First script executed before scanning
- Scan Start Script 2:
Second script executed before scanning
- Scan Stop Script 3:
First script executed after scanning
- Scan Stop Script 4:
Second script executed after scanning
- P2:
- Diag Start Script 1:
First script executed before switch to diag
- Diag Start Script 2:
Second script executed before switch to diag
- Diag Stop Script 3:
First script executed before switching to config
- Diag Stop Script 4:
Second script executed before switching to config
- Parameters
User defined properties, which will be written into
ENIfile and can be interpreted by the application inside EC-Master.
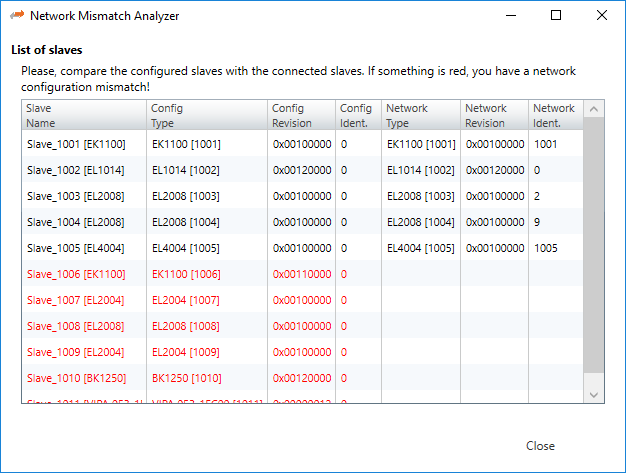
8.3. Network Mismatch Analyzer
- If you have a network mismatch in your EtherCAT network it is not so easy to find the problem. For this you have the Network Mismatch Analyzer. You find it in the network main menu. If you see here some “red” entries, means that this is the start point of your network mismatch:
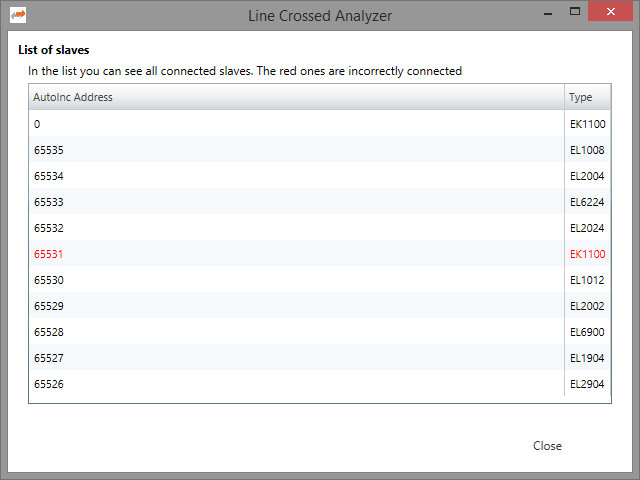
8.4. Line Crossed Analyzer
- If you have connected a line to a wrong port, you can see in the Line Crossed Analyzer which slave is incorrectly connected. The wron entries will be red:
8.5. EoE Endpoint Configuration
If you want to use EoE slaves with your local master, you can activate the EoE Endpoint.
Note
This feature is only available if the package “Tap-Windows” from OpenVPN is installed: http://openvpn.net/index.php/download/community-downloads.html
- If this package is installed, you will see the following dialog:
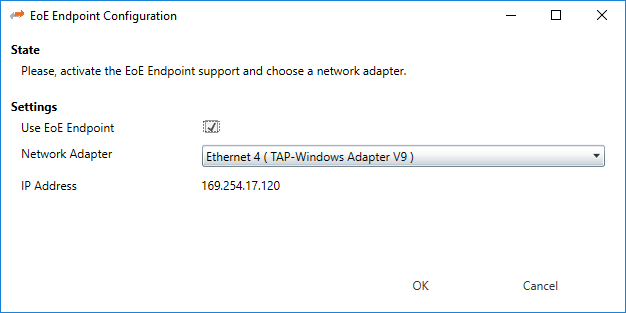
- Settings
- Use EoE Endpoint:
Activate EoE Endpoint support for the selected device
- Network Adapter:
List of installed network adapters (TAP)
- IP Address:
IP Address of the selected network adapter
8.6. Edit Topology
- Disconnect:
Disconnets the selected port
- Connect:
Connects the selected slave in the not connect slaves list, with the selected port in the configuration
- Up:
Moves the slave up in the configuration
- Down:
Moves the slave down in the configuration
- Scan:
Scans the network. The network is shown by the scanned configuration. It is possible to add slave to the configuration with “Add Slave”.
- Apply:
The configuration will be applied to the EC-Engineer (only possible if all slaves are connected)
8.7. Capture File
A capture file could be helpful, if you have a very large system or system is not always available. In that case you can connect to your system, save one or more snapshots into a capture file and analyse the created capture file later.
Another use case is, that your system from time to time some problems. In that case you can activate the automatic mode and create the snapshots every specific interval or based on specific master notifications.
- At the moment there are the following options:
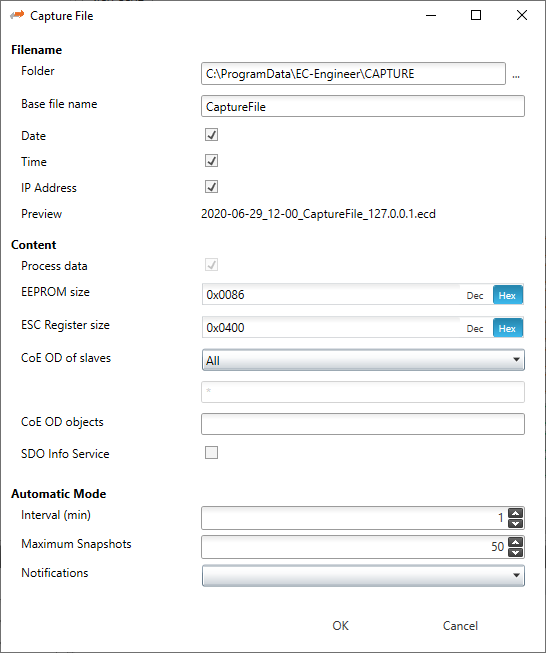
- Filename
- Folder:
Path, where the capture files should be saved
- Base file name:
Base file name of the generated capture file name
- Date:
Activate, to add the date to the generated capture file name
- Time:
Activate, to add the time to the generated capture file name
- IP Address:
Activate, to add the IP address to the generated capture file name
- Preview:
Shows a preview of the generated capture file name
- Content
- Process data:
Activate to add process data to the capture file (read-only)
- EEPROM size:
Enter size of the EEPROM (0x86 = default, 0 = no EEPROM)
- ESC Register size:
Enter size of the ESC Registers (0x400 = default, 0 = no ESC register)
- CoE OD of slaves:
- Select the slaves of which the CoE OD information will be captured
- None:
CoE OD will be not captured
- All:
CoE OD will be captured of all slaves
- User defined:
CoE OD will be captured of the defined slaves by physical address (e.g. 1001-1003; 1005)
- CoE OD objects:
Enter index of specific objects or all objects will be collected (e.g. 0x1018; 0x7000-0x7FFF)
- SDO Info Service:
Activate to use the SDO Info Service for loading the CoE Object Dictionary instead of readying the information from the
ESIfile.
- Automatic Mode
- Interval (min):
Time to wait until next snapshot will be taken
- Maximum Snapshots:
Enter count of maximum snapshots
- Notifications:
- Select the notifications, which will trigger a snapshot. The following notifications are availabe (for more information about notifications please refer the manual of EC-Master):
STATECHANGED
ETH_LINK_CONNECTED
ETH_LINK_NOT_CONNECTED
SLAVE_STATECHANGED
SLAVE_PRESENCE
SLAVE_INITCMD_RESPONSE_ERROR
STATUS_SLAVE_ERROR
SLAVE_UNEXPECTED_STATE
DC_SLV_SYNC
DCM_SYNC
8.8. Project Templates
If you have a lot of slaves with the same configuration (e.g. PDOs, InitCmds) you can use a project template. In that case new slaves will be first copied from this template (if available) and then taken from the ESI cache. This behaviour is also used for the bus scan.
- At the moment there are the following options:
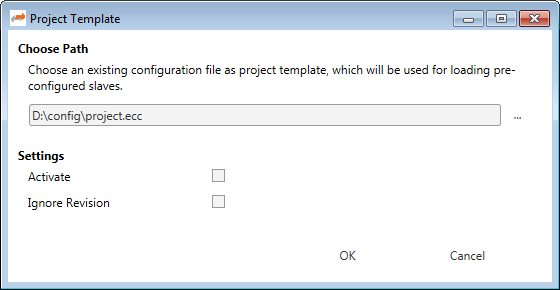
Path: Path to the selected project template
- Settings
- Activate:
True, for activating this project template (necessary if you want to turn it temporary off)
- Ignore Revision:
The revision will be not used as search criteriom
- If the project template mode is active, it will be displayed in the status bar:
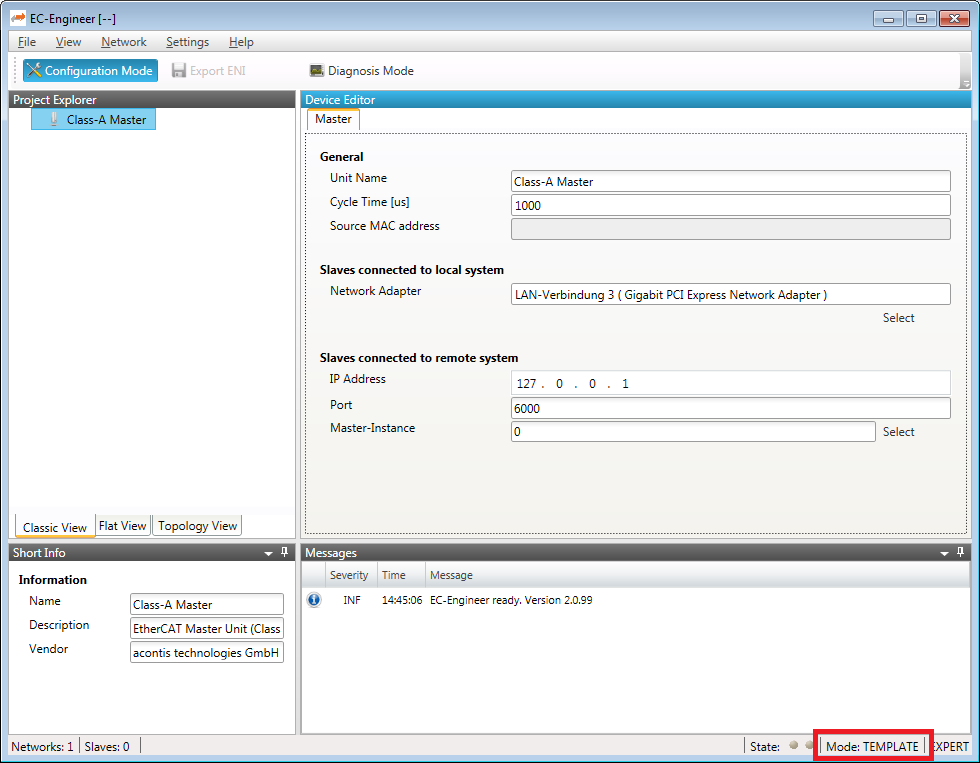
- Normally the first match will be taken from project template. If this is wrong, you can open the context menu and select another one:
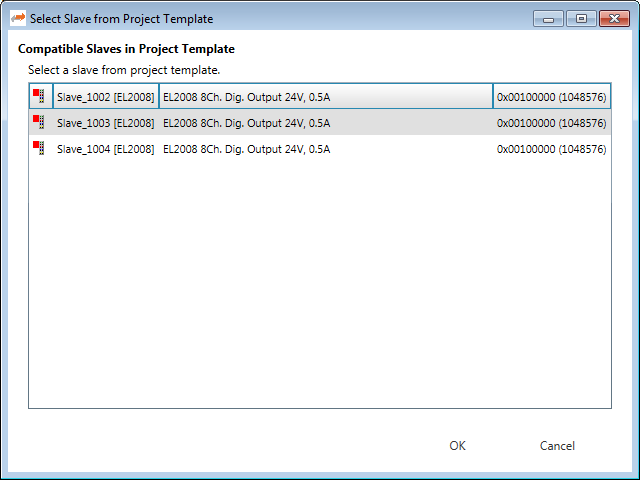
8.9. Real-time Support
Normally on Windows you do not have real-time support, but to get DCM in sync you can install the “ECAT driver” in the following modes:
- Auxillary Clock
This auxillary clock is accurate enough to get DCM in sync (ECAT driver does not guarantee response to the cycle’s deadline)
- Network driver
The network driver can be used from the optimized link layers
The real-time support is normally hidden in EC-Engineer. It can be activate by copying the specific link layer libraries into the installation directory of EC-Engineer.
8.9.1. Real-time Clock
- After activating the real-time support the real-time clock support can be activated by selecting the option “Real-Time Clock”:
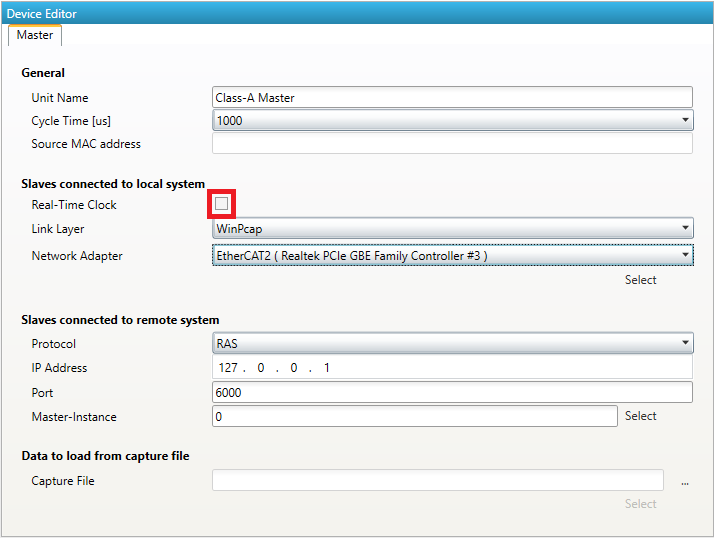
For the local system, EC-Engineer will turn on ECM and use the real-time clock for generating the job task cylces. For more information about how to install the “ECAT driver” please refer the manual of EC-Master Class A DCM on Windows
8.9.2. Optimized Link Layers
- After activating the real-time support the optimized link layer can be selected in the option “Link Layer”:
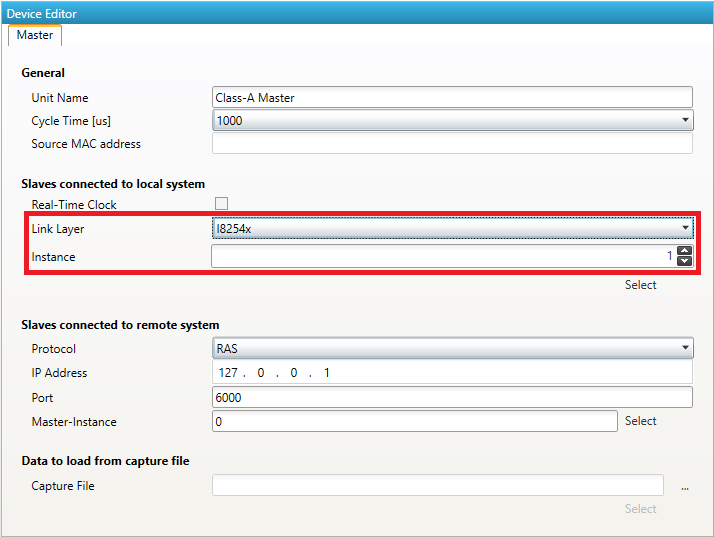
Depending on the link layer type the user can chose the network adapter or the instance.
The following optimized link layers are currenty supported:
emllI8254x.dll (Intel PRO/1000 Network Adapters)
emllI8255x.dll (Intel PRO/100 Network Adapters)
emllIRTL8139.dll (Realtek 8139 Fast Ethernet Adapters)
emllIRTL8169.dll (Realtek Gigabit Ethernet Adapters)
emllICCAT.dll (BECKHOFF CCAT)
For more information about optimized link layers and how to install the ECAT driver please refer the manual of EC-Master Class B EcatDrv for Optimized Link Layers