1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
EC-EngineerWeb is a configuration and diagnosis tool for EtherCAT networks that are controlled by the EC-Master.
- The following screenshot shows the EC-Engineer in configuration mode:
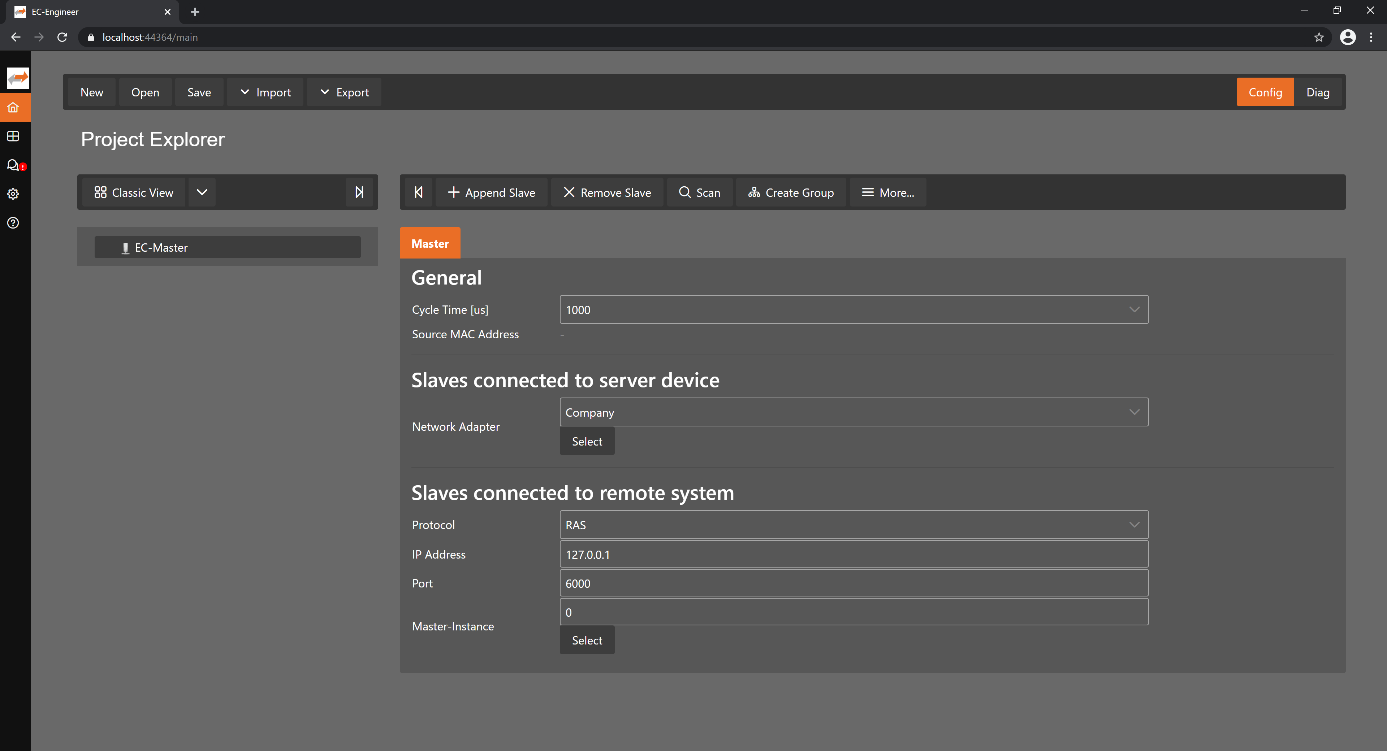
It runs on the Engineering System where the engineer can configure the EtherCAT network. All slaves default to settings that match the Slave’s typical use case.
Complex networks or installations with special requirements need adjustments to the default settings. Using the Configuration Mode, the user can configure his EtherCAT network according to the project’s needs.
- As the result of his work the user can export the EtherCAT Network Information
ENIfile, which is necessary to run the EC-Master on the Control System: 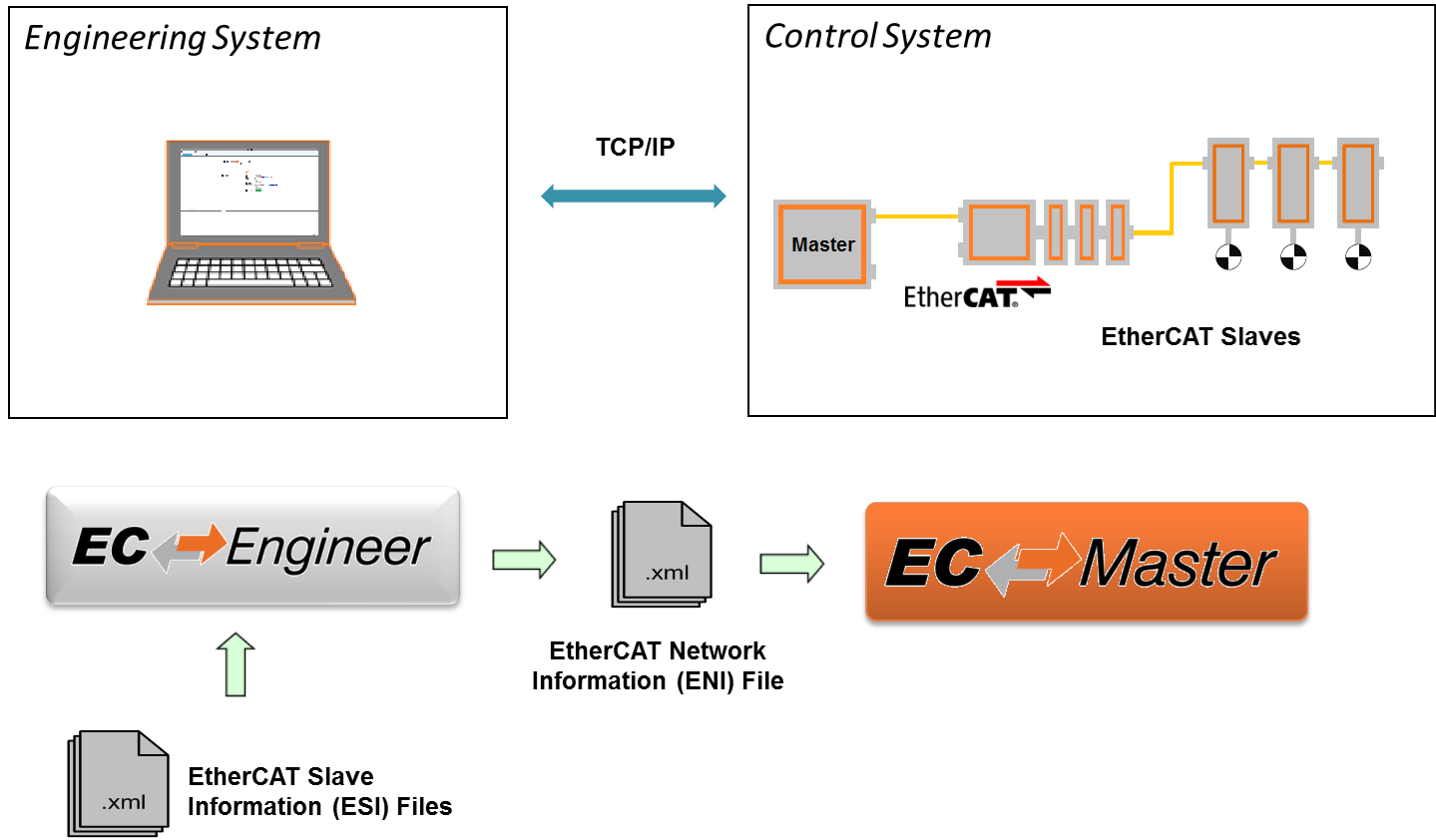
If he has the possibility to connect his Engineering System to the Control System, he can also scan his existing EtherCAT network. The EC-Engineer will then read the network configuration and add all slaves to the project explorer. Now the user can fine tune the network or directly export the ENI file.
If the control system is now running, he can connect to it by using the remote diagnosis functionality and verify that everything is fine by accessing the states, variables, object dictionaries and so on.
1.2. Requirements
- Client
Screen resolution at least 1024x768 pixel
- Supported browsers
Chrome
Firefox
Opera
Edge
Safari
- Server
Memory as recommended for operating system
- Disk space approximately 80 MB (depend on number of
ESIfiles) - Windows (x86/x64)
Microsoft Windows 10 and above
- Linux (x64/ARM)
Ubuntu 16.04 x64 and above
- MacOS (x64)
MacOS High Sierra 10.13 and above
- Disk space approximately 80 MB (depend on number of
1.3. EtherCAT Slave descriptions (ESI files)
The EC-Engineer needs information about each Slave Type to correctly initialize it, give reasonable default settings and present the configurable properties to the user. The knowledge about the different Slave types is gathered from ESI files. The ESI files can be managed by the ESI-Manager.
1.4. Offline Configuration
To configure the network, you can add slaves to the existing EC-Master by using the toolbar.
- The following dialog appears to select your slave:
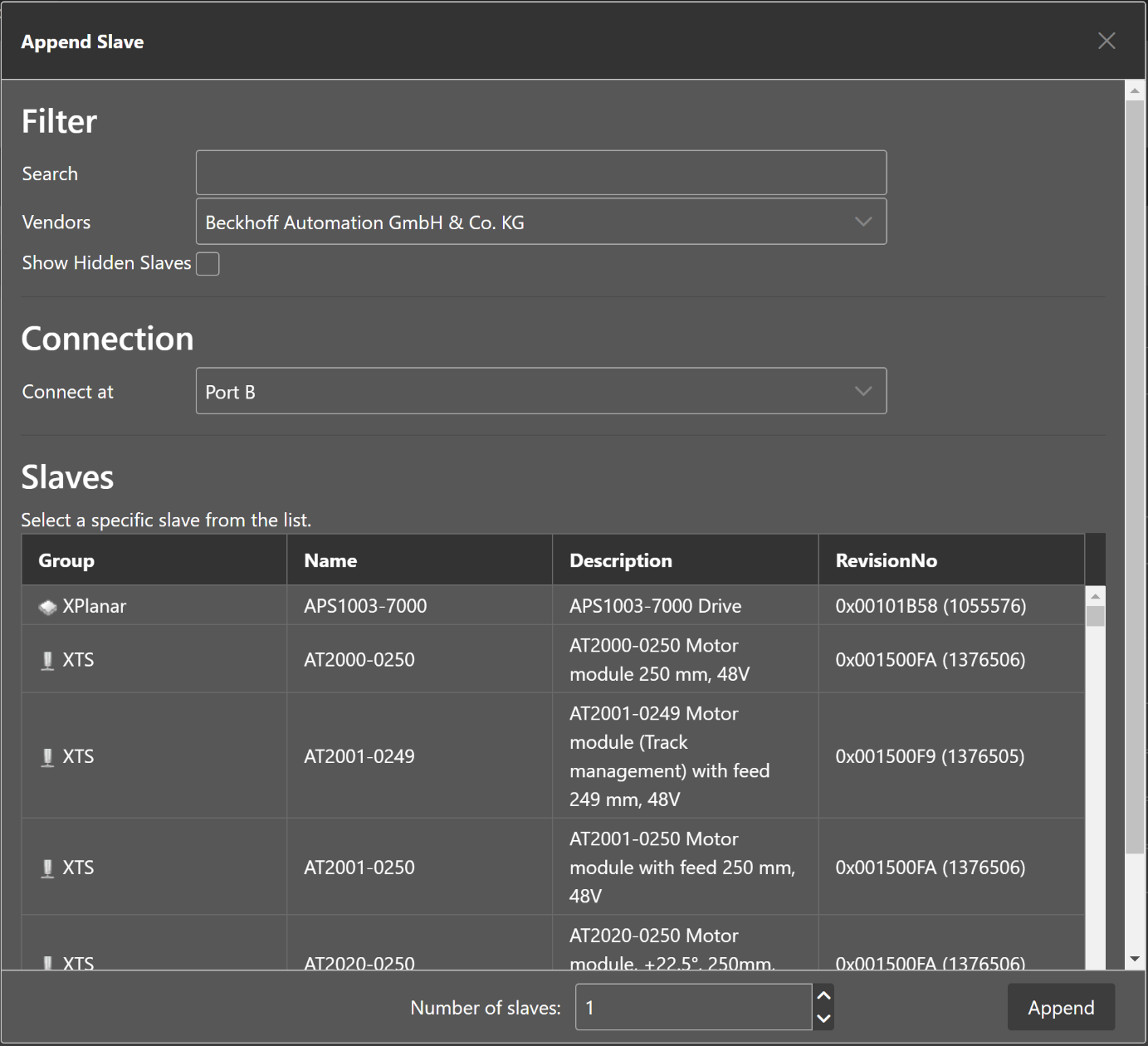
After that you are able to configure the slaves and export an ENI file. If you can not find your slave or if you want to use your own ESI file, you can edit this list by using the ESI-Manager from the side bar main menu. After configuring the network you can select the export the ENI through the top menu.
1.5. Slaves connected to local system
This mode can be used if slaves are connected to the Engineering System by scanning the EtherCAT network configuration.
User can select the local system network adapter to scan the slaves. The slaves are added to tree and can be configured. At the end an ENI file can be exported or you switch to diagnosis mode with the intern master of the EC-Engineer.
1.6. Slaves connected to remote system
This can be used if slaves are connected to the control system. Means user can connect via TCP/IP to the control system if EC-Master RAS (remote access service) server is running and scan the EtherCAT network configuration.
The user have to enter the IP, port and master instance and click select. The network can be scanned now and it is possible to switch to diag mode, too.