2. Getting Started
2.1. EC-Simulator Architecture
The EC-Simulator library is implemented in C++ and can be easily ported to any embedded OS platforms using an appropriate C++ compiler. The API interfaces are C language interfaces, thus the stack can be used in ANSI-C as well as in C++ environments.
There are two different architecture editions as described below. The architectures contain the following:
EC-Simulator stack Core: In the core module cyclic (process data update) and acyclic (mailbox) EtherCAT commands are sent and received. Among others there exist some state machines to handle for example the mailbox protocols.
Configuration Layer: The EC-Simulator stack is configured using a XML file whose format is fixed in the EtherCAT specification ETG.2100 (ENI) with extended information (EXI). The EC-Simulator contains an OS independent XML parser.
Real-time Ethernet Driver Layer: This layer exchanges Ethernet frames between the master and the simulator. If hard real-time requirements exist, this layer has to be optimized for the network adapter card in use.
OS Layer: All OS dependent system calls are encapsulated in a small OS layer. Most functions are that easy that they can be implemented using simple C macros.
2.2. Extended EtherCAT Network Configuration (EXI)
The EC-Simulator stack has to know about the EtherCAT bus topology and the cyclic/acyclic frames to exchange with the slaves. This configuration is determined in a configuration file which has to be available in the EtherCAT Network Information Format (ENI). This format is completely independent from EtherCAT slave vendors, from master stack vendors and from EtherCAT configuration tools. Thus inter-operability between those vendors is guaranteed.
Because the ENI file does not include information about the slave hardware, the EXI (EtherCAT Extended Information) file includes EEPROM content and Slave Object Dictionary from ESI and ESC register values from real network is typically needed. The EXI file can be exported using EC-Engineer.
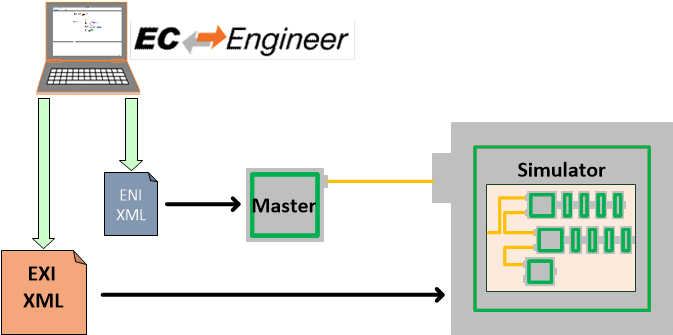
2.3. SiL Simulation Software architecture
The SiL Simulation Software architecture does not need a physical network interface for slave simulation. The EC-Simulator is loaded as Ethernet Driver instead to simulate the EtherCAT Network on a System controller running the EC-Master.
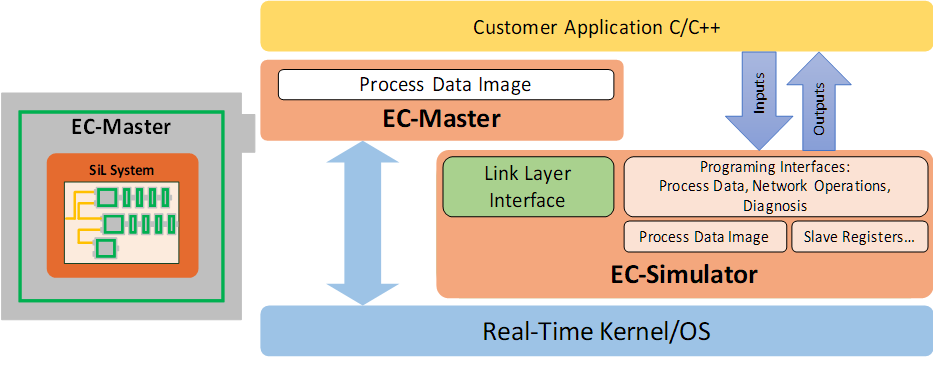
2.4. Mixed mode of real slaves and simulated slaves
In order to implement restbus simulation it is possible to mix real slaves and simulated slaves like this:
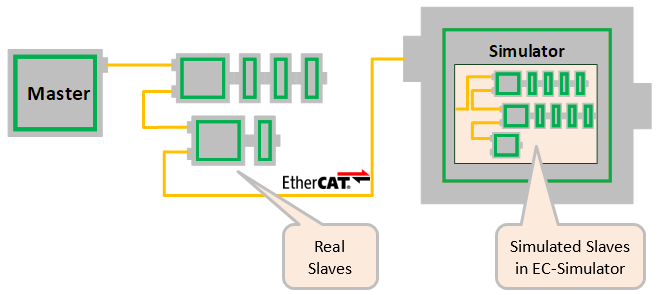
All real slaves must be configured accordingly:
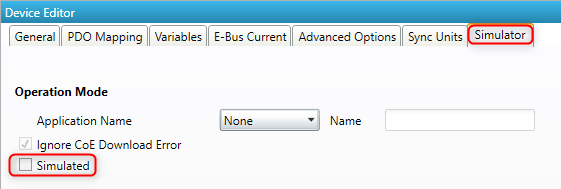
See also /EtherCATConfig/ExtendedConfig/Slaves/Slave/Simulated in the EXI file:

The EC-Simulator will automatically assign the network adapters to the corresponding ports in order of configuration.
See also
EC_T_SIMULATOR_INIT_PARMS::apLinkParms at esInitSimulator().
2.5. Operating system configuration
The main task is to setup the operating system to support the appropriate network adapter for EtherCAT usage and for some systems real-time configuration may be needed.
The operating system-specific settings and configurations are described in Platform and Operating Systems (OS).
2.6. Using emllSimulator (SiL)
The EcSimulatorSilDemo example program as well as all EC-Master example programs like EcMasterDemo, EcMasterDemoDc, etc. support the EC-Simulator (SiL) Ethernet Driver emllSimulator. In this case no physical Real-time Ethernet Driver is passed to the EC-Master. Instead the emllSimulator (SiL) simulates the physical network. The command line syntax is for example:
EcSimulatorSilDemo -simulator 1 1 <exi-file> -f <eni-file> -t 0 -sp
The EC-Simulator Instance ID when calling EC-Simulator APIs is the Real-time Ethernet Driver Instance ID given at command line:
EcSimulatorSilDemo -simulator <Instance-ID> 1 exi.xml -f exi.xml -t 0 -sp
Valid values for Instance ID of emllSimulator are 1 … 24 .
emllSimulator is dynamically loaded within ecatInitMaster() . In contrast to HiL, in case of SiL, ecatInitMaster() automatically calls esInitSimulator(), so the EC-Simulator SiL application may not call esInitSimulator() for the given Instance ID.
The EC-Simulator APIs can be used in the EcMasterDemo, too. The APIs are declared in SDK\INC\EcSimulator.h and EcSimulator.lib / libEcSimulator.so must be linked to the application to import the EC-Simulator APIs.
The EC-Simulator SiL Protected version with MAC based protection needs the corresponding Real-time Ethernet Driver settings provided.
See also
2.6.1. Simulator Ethernet Driver parameters
The parameters to the Simulator Ethernet Driver are setup-specific.
The function CreateLinkParmsSimulator() in EcSelectLinkLayer.cpp demonstrates how to initialize the Ethernet Driver instance.
-
struct EC_T_LINK_PARMS_SIMULATOR
Public Members
-
EC_T_LINK_PARMS linkParms
Common link parameters. Signature must be set to EC_LINK_PARMS_SIGNATURE_SIMULATOR
-
EC_T_OS_PARMS *pOsParms
OS layer parameters
-
EC_T_CNF_TYPE eCnfType
optional: create slaves from ENI/EXI, see esConfigureNetwork
-
EC_T_BOOL bConnectHcGroups
Connect hot connect groups in topology (floating group heads to free ports)
-
EC_T_BOOL bDisableProcessDataImage
Don’t allocate Process Data Image at simulator (legacy support, CiA402 simulation)
-
EC_T_BOOL bJobsExecutedByApp
EC_FALSE: esExecJob explicitly called by application, EC_TRUE: implicitly by emllSimulator
-
EC_T_LINK_PARMS *apLinkParms[EC_SIMULATOR_MAX_LINK_PARMS]
link parameters of network adapters passed to EC-Simulator Core, e.g. for validation of MAC address of license key
-
EC_T_PERF_MEAS_INTERNAL_PARMS PerfMeasInternalParms
Internal performance measurement parameters
-
EC_T_LINK_PARMS linkParms
emllSimulator accepts optional parameters, e.g.:
-simulator 1 1 <exi-file> [--mac <address>] [--lic <key>] [--link <link-parms>] [--sp] [--connect <type> <id> <address> <port>]
2.7. EC-Simulator Software Development Kit (SDK)
The EC-Simulator SDK is needed to write applications based on the EC-Simulator stack. The EC-Simulator stack is shipped as a library which is linked together with the application.
The following components are supplied together with an SDK:
….Bin: Executables containing the EC-Simulator stack
….Doc: Documentation
….Examples: Example application(s)
- Libraries and header files to build C/C++-applications.
….\SDK\INC: header files to be included with the application
….\SDK\LIB: libraries to be linked with the application
….\Sources\Common: Shared C++-files
For all operating systems the same principal rules to generate the example applications can be used.
Include search path
The header files are located in the following directories:
<InstallPath>\Examples\<ExampleName> (whith e.g. <ExampleName>=EcSimulatorHilDemo)
<InstallPath>\Examples\Common\<OS> (where <OS> is a placeholder for the operating system)
<InstallPath>\Examples\Common
<InstallPath>\SDK\INC\<OS> (where <OS> is a placeholder for the operating system)
<InstallPath>\SDK\INC
<InstallPath>\Sources\Common
Preprocessor macro
The demo applications are the same for all operating systems. The appropriate pre-processor macro has to be set for the operating system.
See also
Libraries
The libraries located in <InstallPath>\SDK\LIB\<OS>\<ARCH> have to be added (<OS> is a placeholder for the operating system used and <ARCH> for the architecture if different architectures are supported).
2.7.1. OS Compiler settings
2.7.1.1. Linux Compiler settings
The following settings are necessary to build the example application for Linux.
Possible ARCHs (see ATECAT_ARCHSTR in
SDK/INC/Linux/EcOsPlatform.h):
aarch64 (ARM 64Bit), armv4t-eabi (ARM 32Bit), armv6-vfp-eabihf (ARM 32Bit), armv7-vfp-eabihf (ARM 32Bit), PPC (PPC 32Bit with “-te500v2”), riscv64 (RISC-V 64Bit), x64 (x86 64Bit), x86 (x86 32Bit)
The ARM 32Bit architectures armv4t-eabi and armv6-vfp-eabihf/armv7-vfp-eabihf are incompatible with each other. An ARM VFP system returns success on “readelf -A /proc/self/exe | grep Tag_ABI_VFP_args”. If “readelf” isn’t available on the target, the matching ARM version can be figured out by trying to run EcSimulatorHilDemo.
- Extra include paths:
<InstallPath>/Examples/EcSimulatorHilDemo <InstallPath>/SDK/INC/Linux <InstallPath>/SDK/INC <InstallPath>/Sources/Common
- Extra source paths:
<InstallPath>/Examples/EcSimulatorHilDemo <InstallPath>/Sources/Common/EcTimer.cpp
- Extra library paths to the main EtherCAT components (replace “x86” according to ARCH):
<InstallPath>/SDK/LIB/Linux/x86
- Extra libraries (in this order)
EcSimulatorRasServer EcSimulator pthread dl rt
2.7.1.2. Microsoft Windows
The following settings are necessary to build the example application for Windows:
- Library path of the main EtherCAT components:
<InstallPath>/SDK/LIB/Windows/<Arch>
- Include path:
<InstallPath>/SDK/INC/Windows <InstallPath>/SDK/INC <InstallPath>/Sources/Common